1.委托的BeginEnvoke/EndInvoke
BeginEnvokeEndInvoke是委托的异步版本。
public class AsyncFroDelegate
{
public delegate int AddHandler(int a, int b);
public static int Add(int a, int b)
{
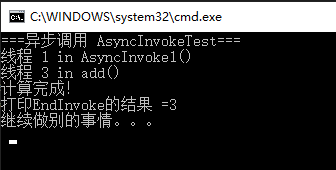
Console.WriteLine($"线程 {Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId} in add()");
Thread.Sleep(3000);
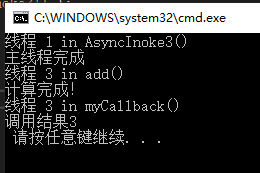
Console.WriteLine("计算完成!");
return a + b;
}
public static void AsyncInvoke1()
{
Console.WriteLine("===异步调用 AsyncInvokeTest===");
AddHandler handler = new AddHandler(Add);
IAsyncResult result = handler.BeginInvoke(1, 2, null, null);
//EndInvoke,使得主线程处于阻塞状态
Console.WriteLine($"线程 {Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId} in AsyncInvoke1()");
Console.WriteLine("打印EndInvoke的结果 =" + handler.EndInvoke(result));
Console.WriteLine("继续做别的事情。。。");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
BeginInvoke使得CLR创建了一个新的线程去执行Add方法。此时主线程不受影响可以继续做其他事情。直到遇到EndInvoke,需要等待异步调用结果才被阻塞。如果主线程不依赖这个调用结果。可是使用回调,让主线不被阻塞。
/// <summary>
/// 异步回调
/// </summary>
public static void AsyncInoke3()
{
Console.WriteLine($"线程 {Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId} in AsyncInoke3()");
AddHandler handler = new AddHandler(Add);
IAsyncResult arr = handler.BeginInvoke(1, 2, myCallback, handler);
Console.WriteLine("主线程完成");
}
private static void myCallback(IAsyncResult ar)
{
Console.WriteLine($"线程 {Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId} in myCallback()");
//AddHandler handler = (AddHandler)((AsyncResult)ar).AsyncDelegate;
//AsyncState就是通过BeginInvoke函数的最后一个参数传递过来的的
AddHandler handler1 = (AddHandler)ar.AsyncState;
//Console.WriteLine("调用结果" + handler.EndInvoke(ar));
Console.WriteLine("调用结果" + handler1.EndInvoke(ar));
}
2.Thread
public Thread(ThreadStart start); public Thread(ParameterizedThreadStart start); public Thread(ThreadStart start, int maxStackSize); public Thread(ParameterizedThreadStart start, int maxStackSize);
ThreadStart 无参数,无返回值的委托
ParameterizedThreadStart 带一个参数,无返回值的委托
maxStackSize 线程要使用的堆栈的大小,默认1M。
public class AsyncForThread
{
public static void Client()
{
Thread thread1 = new Thread(Print);
thread1.Start();
Thread thread2 = new Thread(PrintEx);
thread2.Start("test");
}
private static void PrintEx(object content)
{
int threadID = Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId;
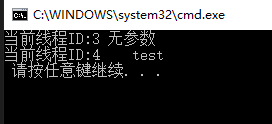
Console.WriteLine($"当前线程ID:{threadID} {content}");
}
private static void Print()
{
int threadID = Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId;
Console.WriteLine($"当前线程ID:{threadID} 无参数");
}
}
3.ThreadPool
在面向对象的编程中,创建和销毁对象是很费事的,因为创建一个对象要获取内存资源或者其他更多的资源。.Net Framework已经为我们提供了一个“线程池””供使用。
需要注意的是,线程池中的线程均为后台线程,即他们的IsBAckground属性为true,这意味着在所有的前台线程都已退出后,ThreadPool中的线程不会让应用程序继续保持运行。
使用线程池的一些限制:
- 当需要创建一个前台线程时不应该使用线程池
- 无法设置线程优先级
- 执行任务是无法选择具体线程
- 执行时间过长
public class AsyncForThreadPool
{
public static void Client()
{
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(Counter);
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(Counter, "test");
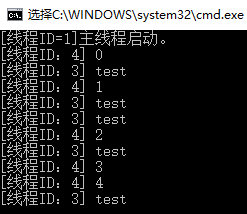
Console.WriteLine($"[线程ID={Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId}]主线程启动。");
}
private static void Counter(object state)
{
//throw new NotImplementedException();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Thread.Sleep(50);
if (state != null)
{
Console.WriteLine($"[线程ID:{Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId}] {state}");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine($"[线程ID:{Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId}] {i.ToString()}");
}
}
}
}
4.Task
由于使用ThreadPool无法获取到并发完成时的返回值。引入了Task。
public static void Client()
{
var parent = new Task(() => {
CancellationTokenSource cts = new CancellationTokenSource();
//TaskCreationOptions.AttachedToParent 该创建的任务为子任务
//TaskContinuationOptions.ExecuteSynchronously 创建的延续任务为同步执行
var tf = new TaskFactory(cts.Token, TaskCreationOptions.AttachedToParent, TaskContinuationOptions.ExecuteSynchronously, TaskScheduler.Default);
//创建三个子任务
var childTasks = new[] {
tf.StartNew(()=>Sum(cts.Token,50)),
tf.StartNew(()=>Sum(cts.Token,100)),
tf.StartNew(()=>Sum(cts.Token,int.MaxValue))
};
//任何子任务异常则取消所有其他子任务
for(int i=0;i<childTasks.Length;i++)
{
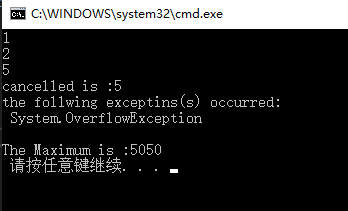
Console.WriteLine(childTasks[i].Id);
childTasks[i].ContinueWith(t => { Console.WriteLine("cancelled is :"+t.Id);cts.Cancel(); },TaskContinuationOptions.OnlyOnFaulted);
};
//所有子任务抛出异常,从未出错、未取消的任务获取返回的最大值,
//然后将最大值由另一个任务来显示
tf.ContinueWhenAll(childTasks, tasks => tasks.Where(t => !t.IsFaulted && !t.IsCanceled).Max(t => t.Result), CancellationToken.None)
.ContinueWith(t => Console.WriteLine("The Maximum is :" + t.Result),TaskContinuationOptions.ExecuteSynchronously);
});
parent.ContinueWith(p =>
{
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("the follwing exceptins(s) occurred:" + Environment.NewLine);
foreach (var e in p.Exception.Flatten().InnerExceptions)
{
sb.AppendLine(" " + e.GetType().ToString());
Console.WriteLine(sb.ToString());
}
}, TaskContinuationOptions.OnlyOnFaulted);
parent.Start();
}
private static int Sum(CancellationToken ct,int n)
{
int result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= n;i++)
{
ct.ThrowIfCancellationRequested();
checked
{
result += i;
}
}
return result;
}
5.async/await
这两个词比较有迷惑性。目前从实验得出来的结论是:
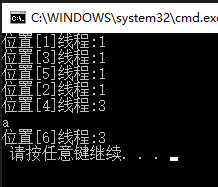
主线程执行路径:1-->3-->5 后面遇到await 关键字会立即返回主调函数紧接着到2的位置。
任务t1 开始执行位置4,然后去执行一堆“等着”他的代码,那就是await关键字之后的代码,像极了“回调”。
public static void TaskRun5()
{
ShowThread(1);
Test();
ShowThread(2);
}
private async static Task Test()
{
ShowThread(3);
Task<string> t1 = Task.Run(()=> {
Thread.Sleep(1000);
ShowThread(4);
return "a";
});
ShowThread(5);
Console.WriteLine(await t1);
ShowThread(6);
}
static void ShowThread(int pos)
{
Console.WriteLine($"位置[{pos}]线程:"+Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
}