反向代理服务器面对用户请求和后端服务器响应,需要将两者联系起来,于是就涉及到socket关联查询了。
代理服务器处理用户的请求和后端服务器的响应,并且这两方的请求和响应是相互对应的,因此对于代理接收到服务器的响应该如何找到这个响应对应的用户请求;甚至代理在处理一个socket描述符时,如何确定是发送给用户的响应,还是发给后端服务器的请求。
我提出来的方案是
socket关联查询整体模型如下图所示:
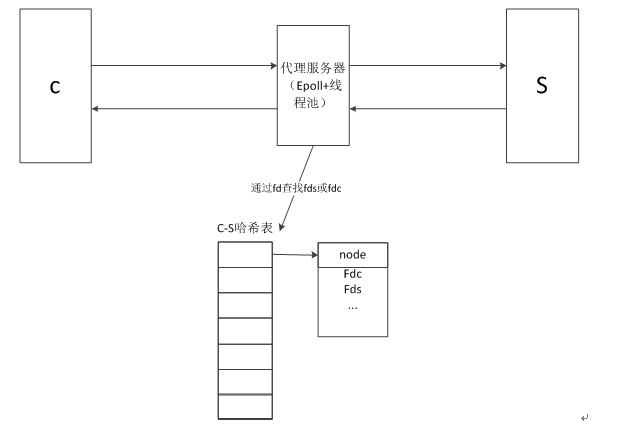
socket关联查询整体模型
为了建立代理对客户端的请求与后端服务器的响应,建立一个映射哈希表。socket关联查询详细模型如图所示:
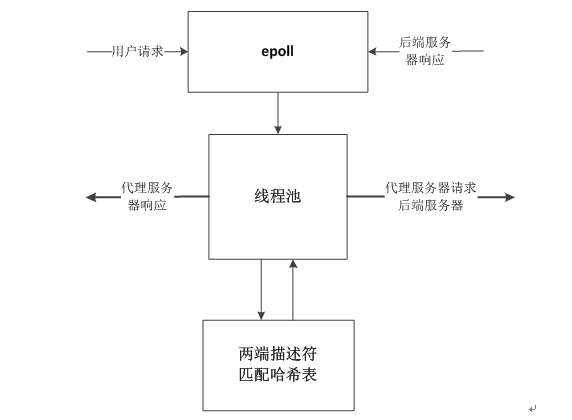
socket关联查询详细模型
1、用户请求连接时,先加入到epoll中,建立连接后,并且有请求任务到来时,将该任务加入到线程池,即对fdc进行操作;
2、当用户实际上是与后端服务器交互时,代理需要与后端服务器建立连接,这时需要创建一个fds,这时将以fdc和fds为关键字加入到哈希表中;
3、当后端服务器有响应时,加入到epoll中;当有响应任务时,加入到线程池处理响应任务;
4、当代理需要将后端服务器的响应再次响应给用户时,查询匹配哈希表,即可找到fds与fdc的映射,这样就能正确的对该请求的用户进行响应。
对于哈希表的设计,下面又给出实验代码:当然具体实现还待将代理的功能实现在将这个整合。代码如下:
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define HASHSIZE 997 #define C_S 2 #define S_C 1 typedef struct _Node Node; typedef struct _Hash Hash; struct _Node{ int value; int fds; int fdc; /* conn_staut=1表示ref_fd=fds,代理把数据发送给fdc * conn_staut=2表示ref_fd=fdc,代理把数据发送给fds */ int conn_staut; Node *next; }; struct _Hash{ int key; Node *next; }; static Hash hash[HASHSIZE]; /* 哈希函数 */ int hash_fun(int ref_fd) { return ref_fd % HASHSIZE; } /* 初始化哈希表 */ void hash_init() { int i = 0; for(i = 0; i < HASHSIZE; i++) { hash[i].key = 0; hash[i].next = NULL; } } /* 哈希节点的匹配 */ Node* hash_fdmate(int ref_fd) { int hash_val; hash_val = hash_fun(ref_fd); if(hash[hash_val].next == NULL) return NULL; Node *p = hash[hash_val].next; for(; p->next == NULL; p = p->next) { if(ref_fd == p->fds || ref_fd == p->fdc) { return p; } } return NULL; } /* 哈希节点的插入 */ Node* hash_insert(int fdc, int fds) { Node *node_c = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node)); Node *node_s = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node)); if(node_c == NULL || node_s == NULL) return NULL; bzero(node_c, sizeof(Node)); bzero(node_s, sizeof(Node)); node_c->fds = fds; node_c->fdc = fdc; node_c->conn_staut = C_S; node_s->fds = fds; node_s->fdc = fdc; node_s->conn_staut = S_C; /* 先以fdc加入到哈希表中 */ int hash_val; hash_val = hash_fun(fdc); if(hash[hash_val].next == NULL) { hash[hash_val].next = node_c; }else { node_c->next = hash[hash_val].next; hash[hash_val].next = node_c; } /* 先以fds加入到哈希表中 */ hash_val = hash_fun(fds); if(hash[hash_val].next == NULL) { hash[hash_val].next = node_s; }else { node_s->next = hash[hash_val].next; hash[hash_val].next = node_s; } return node_c; } /* 销毁整哈希表*/ void hash_destroy() { } /* 删除哈希中的某个节点 */ Node* hash_delete(int ref_fd) { } #if 1 int main(void) { int fdc = 12; int fds = 13; hash_init(); hash_insert(fdc, fds); Node *np = hash_fdmate(13); if(np == NULL) { printf("no find! "); return 0; } printf("%d ", np->conn_staut); return 0; } #endif