二叉树
二叉树是一种非常重要的数据结构,非常多其他数据结构都是基于二叉树的基础演变而来的。对于二叉树,有深度遍历和广度遍历,深度遍历有前序、中序以及后序三种遍历方法,广度遍历即我们寻常所说的层次遍历。由于树的定义本身就是递归定义,因此採用递归的方法去实现树的三种遍历不仅easy理解并且代码非常简洁,而对于广度遍历来说,须要其他数据结构的支撑。比方堆了。所以。对于一段代码来说,可读性有时候要比代码本身的效率要重要的多。
遍历路径
前序遍历:根->左->右
中序遍历:左->根->右(最重要)
后续遍历:左->右->根
层次遍历:根->左->右
树遍历框架
所有树的遍历均可以套用树遍历框架
void traverse(TreeNode root) {
// 前序遍历
traverse(root.left)
// 中序遍历
traverse(root.right)
// 后序遍历
}
例子1(二叉搜索树转换为单向链表)
二叉树数据结构TreeNode可用来表示单向链表(其中left置空,right为下一个链表节点)。实现一个方法,把二叉搜索树转换为单向链表,要求值的顺序保持不变,转换操作应是原址的,也就是在原始的二叉搜索树上直接修改。
返回转换后的单向链表的头节点。
示例:
输入: [4,2,5,1,3,null,6,0]
输出: [0,null,1,null,2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6]
//上级节点
TreeNode preNode;
//头节点
TreeNode headNode;
public TreeNode convertBiNode(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
search(root);
return headNode;
}
/**
* 中序遍历框架
* search(node.left)
* do current value
* search(node.right)
* @param node
*/
public void search(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
//1.遍历左节点
search(node.left);
//2.处理当前节点
if (preNode != null) {
//当前节点设置为上个节点的右节点
preNode.right = node;
} else {
headNode = node;
}
//当前节点的左节点设置为null
node.left = null;
preNode = node;
//3.遍历右节点
search(node.right);
}
例子2(删除二叉搜索树中的 key 对应的节点)
给定一个二叉搜索树的根节点 root 和一个值 key,删除二叉搜索树中的 key 对应的节点,并保证二叉搜索树的性质不变。返回二叉搜索树(有可能被更新)的根节点的引用。
一般来说,删除节点可分为两个步骤:
首先找到需要删除的节点;
如果找到了,删除它。
说明: 要求算法时间复杂度为 O(h),h 为树的高度。
分析:
-
当前节点没有左子节点
返回root.right
-
当前节点没有右子节点
返回root.left
-
当前节点既有左子节点和右子节点时
-
找到右子节点下面最后一个左子结点
-
将root的左子节点放到右子节点下面最后一个左子结点的左子节点上
-
直接返回右子节点
-
BTS数遍历框架
二叉搜索树(Binary Search Tree,简称 BST)是一种很常用的的二叉树。它的定义是:
一个二叉树中,任意节点的值要大于等于左子树所有节点的值,且要小于等于右边子树的所有节点的值
void BST(TreeNode root, int target) {
if (root.val == target)
// 找到目标,做点什么
if (root.val < target)
//目标比节点值大,目标肯定在右节点
BST(root.right, target);
if (root.val > target)
//目标比节点值小,目标肯定在左节点
BST(root.left, target);
}
public TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key) {
if(root == null) {
return null;
}
if(root.val == key){
if(root.right == null){
return root.left;
}
if(root.left == null) {
return root.right;
}
//当目标节点左右子节点都存在时
TreeNode node = root.right;
//找到右子节点下面最后一个左子结点
while(node.left != null){
node = node.left;
}
//将root的左子节点放到右子节点下面最后一个左子结点的左子节点上
node.left = root.left;
//直接返回右子节点
return root.right;
}else if(key < root.val){
root.left = deleteNode(root.left,key);
}else{
root.right = deleteNode(root.right,key);
}
return root;
}
例子3(根据前序中序遍历结果重建二叉树)
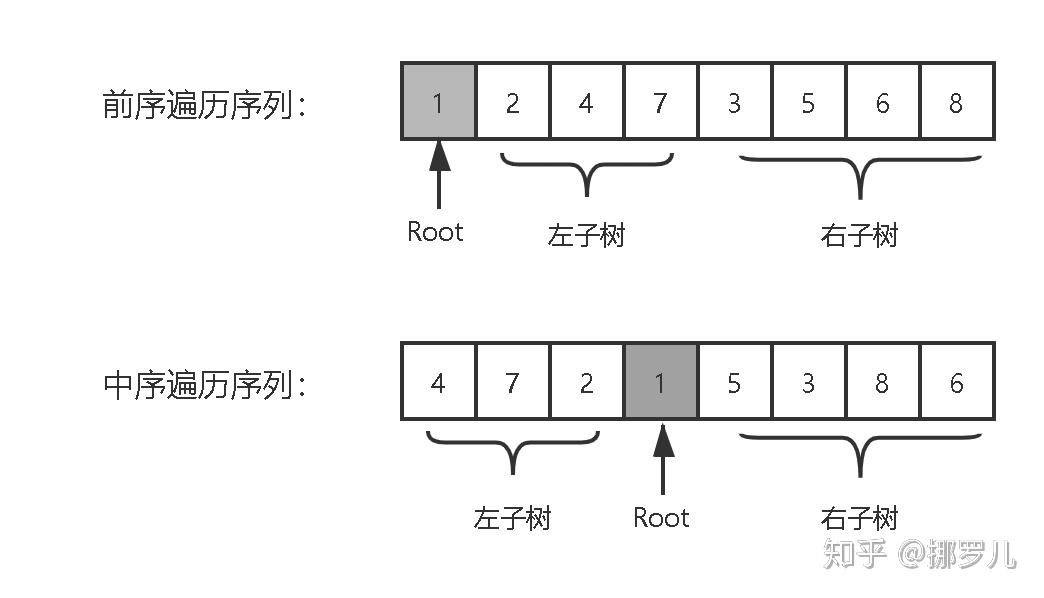
//根据前序中序遍历结果重建二叉树框架
//pre 前序
//mid 中序
TreeNode buildNode(List<Integer> pre,List<Integer> mid){
if(pre.size() == 0){
return null;
}
//前序第一个值肯定是根节点
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(pre.get(0));
//中序对应值的索引作为左右子树分割点
int i = mid.indexOf(pre.get(0));
//重建左树
root.left = buildNode(pre.subList(1,i+1),mid.subList(0,i));
//重建右树
root.right = buildNode(pre.subList(i+1,pre.size()),mid.subList(i+1,mid.size()));
return root;
}
java代码
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
List<Integer> mid=new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> pre=new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0;i<preorder.length;i++){
pre.add(preorder[i]);
mid.add(inorder[i]);
}
return buildNode(pre,mid);
}
/**
*pre 前序
*mid 中序
*/
TreeNode buildNode(List<Integer> pre,List<Integer> mid){
if(pre.size() == 0){
//1.递归停止条件
return null;
}
//2.前序第一个是root节点
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(pre.get(0));
//3.找到中序中root节点的索引
//中序遍历的顺序是左->根->右,所以root节点的索引左边一定是左子节点,右边一定是右子节点,
//这样就就分成左右两部分了
int i = mid.indexOf(pre.get(0));
//这样就处理完毕了,接下来就递归重复上面步骤了
//递归处理左节点数据,前序1->i+1,中序:0->i
root.left = buildNode(pre.subList(1,i+1),mid.subList(0,i));
//递归处理右节点数据,前序i+1->end,中序:i+1->end
root.right = buildNode(pre.subList(i+1,pre.size()),mid.subList(i+1,mid.size()));
return root;
}