调用自身;
明确的结束条件,递归出口;
简洁但低效;
调用过程中系统开销大,每层递归需开辟栈储存局部变量和返回点,递归次数过多栈易溢出。
辗转相除:
循环实现:
Function1:
public static int gcd(int m, int n){ while (true){ if ((m = m % n) == 0) return n; if ((n = n % m) == 0) return m; } }
Function2:
long gcd_norecur(int a,int b){
int temp;
while(b != 0) {
temp=a % b;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
return a;
}

递归实现:
long gcd(int a,int b) {
if(a%b==0) return b;
return gcd(b,a%b);
}

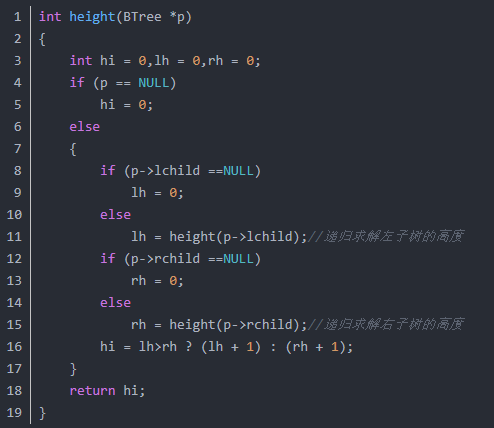
求二叉树高度(递归实现):
int height(BTree *p){
int hi = 0,lh = 0,rh = 0;
if (p == NULL)
hi = 0;
else{
if (p->lchild ==NULL)
lh = 0;
else
lh = height(p->lchild);//递归求解左子树的高度
if (p->rchild ==NULL)
rh = 0;
else
rh = height(p->rchild);//递归求解右子树的高度
hi = lh>rh ? (lh + 1) : (rh + 1);
}
return hi;
}