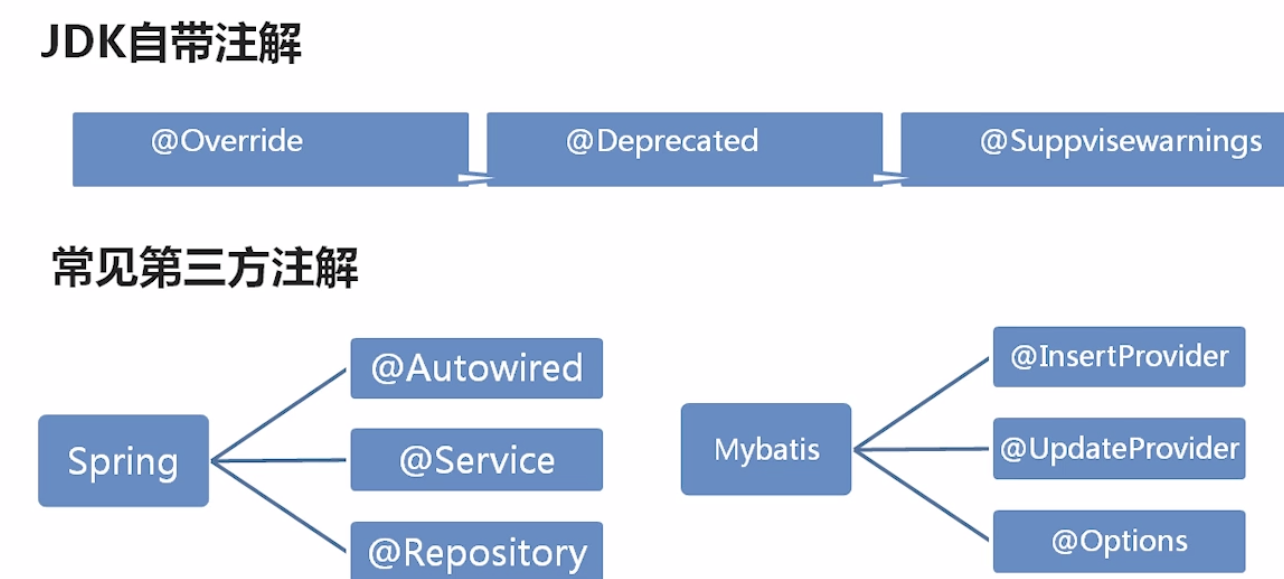
分类:
源码注解:只在编译器存在 变成class文件时不存在
编译时注解:注解再源码和。class文件中都存在 Override
运行时注解:运行阶段还起作用,甚至会影响运行逻辑 AutoWired
自定义注解:
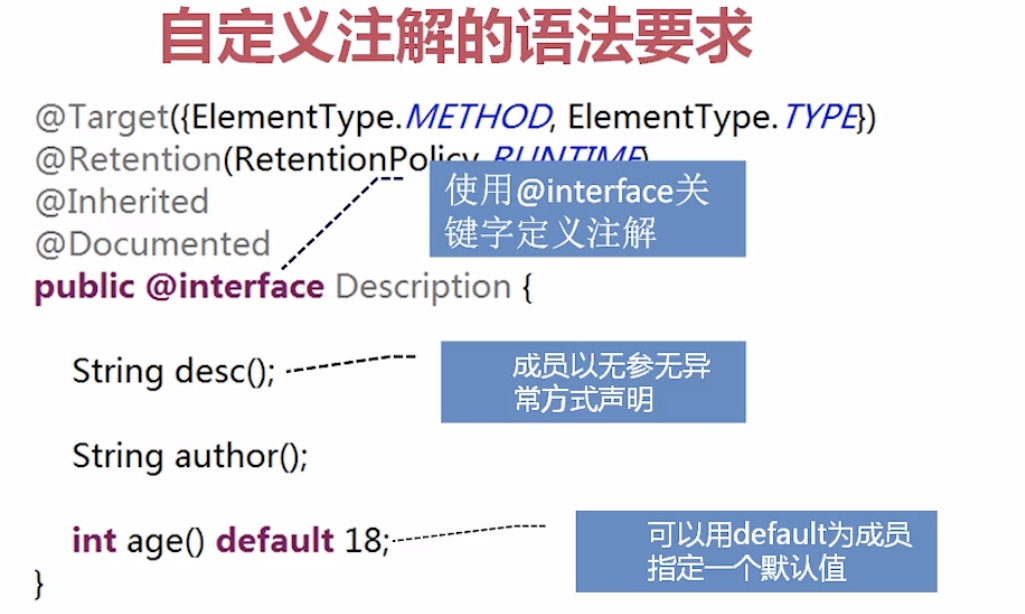

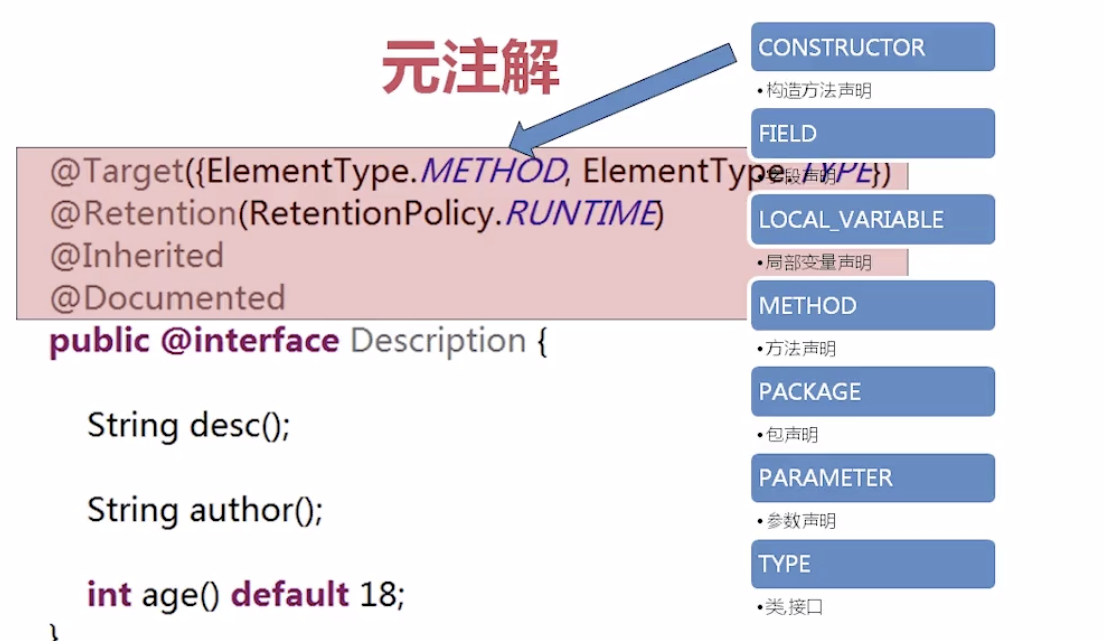
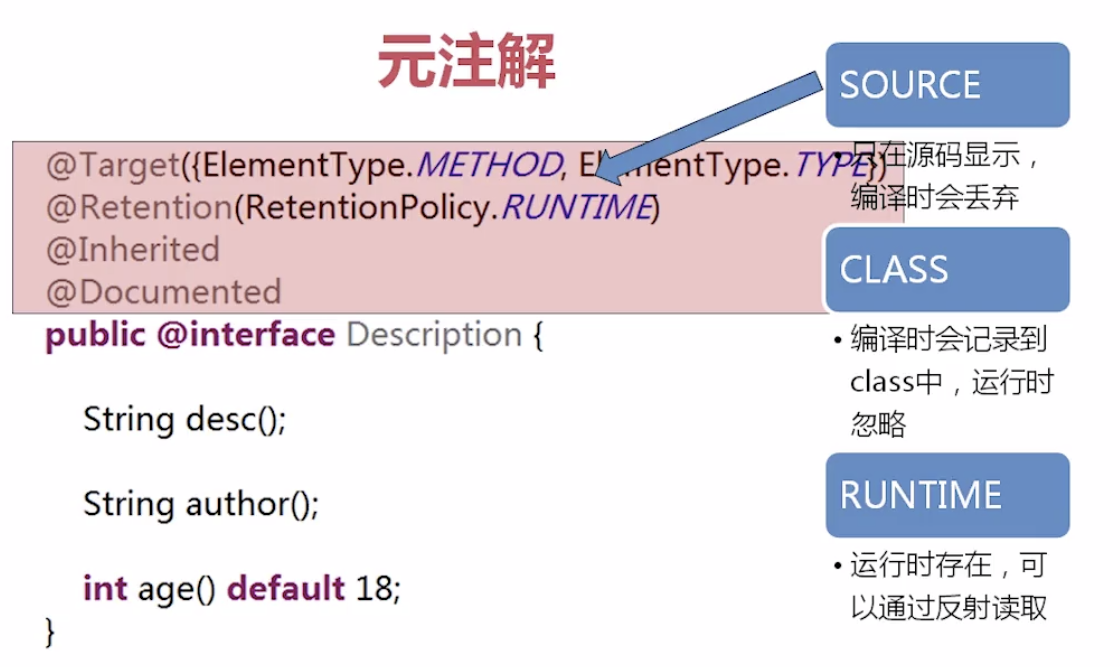

Inherited父类有这个注解 子类默认就有

自定义java注解 TestAnnotation:并且为两个属性设置默认值
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface TestAnnotation {
public int id() default -1;
public String msg() default "hello";
}
Check注解 自定义 当注解只有一个属性的时候默认属性名为value
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Check {
String value();
}
没有任何属性的注解 Perform
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
public @interface Perform {
}
Java内置的注解:
@Deprecated:表示一个元素已经过时 例如过时的方法、类、成员变量。
public class Hero {
@Deprecated
public void say(){
System.out.println("hero say method");
}
public void speak(){
System.out.println("hero speak method");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Hero hero = new Hero();
hero.speak();
hero.say();;
}
@Override:表示对父类中方法的重写
public class Child extends Father{
@Override
public void method() {
System.out.println("child method");
}
}
class Father{
public void method(){
System.out.println("fathre method");
}
}
@SuppressWarnings:阻止警告 被Deprecated注解的方法,编译器会警告提示,使用这个注解可以屏蔽掉警告
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
public class Hero {
@Deprecated
public void say(){
System.out.println("hero say method");
}
public void speak(){
System.out.println("hero speak method");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Hero hero = new Hero();
hero.speak();
hero.say();
}
}
@SafeVarargs:参数安全类型注解。提醒开发者不要用啊参数做一些不安全的操作,使用该注解会阻止编译器产生Unchecked这样的警告
@SafeVarargs // Not actually safe!
static void m(List<String>... stringLists) {
Object[] array = stringLists;
List<Integer> tmpList = Arrays.asList(42);
array[0] = tmpList; // Semantically invalid, but compiles without warnings
String s = stringLists[0].get(0); // Oh no, ClassCastException at runtime!
}
@FunctionalInterface:java1.8的新特性 函数式接口 lambda表达式 例如 Runnable接口 是一个函数式接口 很容易转换为lambda
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Runnable {
/**
* When an object implementing interface <code>Runnable</code> is used
* to create a thread, starting the thread causes the object's
* <code>run</code> method to be called in that separately executing
* thread.
* <p>
* The general contract of the method <code>run</code> is that it may
* take any action whatsoever.
*
* @see java.lang.Thread#run()
*/
public abstract void run();
}
注解的提取:
注解和反射:
注解通过反射获取。使用isAnnotationPresent方法判断它是否应用了某个注解
public boolean isAnnotationPresent(Class<? extends Annotation> annotationClass){}
通过getAnnotation方法获取Annotation对象 返回制定类型的注解
public <A extends Annotation> A getAnnotation(Class<A> annotationClass) {}
或者是getAnnotations()方法 返回注解到这个元素上的所有注解
public Annotation[] getAnnotations() {}
代码示例:
@TestAnnotation
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean hasAnn = Test.class.isAnnotationPresent(TestAnnotation.class);
if (hasAnn) {
TestAnnotation testAnnotation = Test.class.getAnnotation(TestAnnotation.class);
System.out.println("id:" + testAnnotation.id());
System.out.println("msg:" + testAnnotation.msg());
}
}
}
属性和方法上的注解同样可以获取到:通过java反射
@TestAnnotation(msg = "qwert") public class Test { @Check("hi") int a; @Perform public void test(){} @SuppressWarnings("deprecation") public void test1(){ Hero hero = new Hero(); hero.speak(); hero.say(); } public static void main(String[] args) { boolean hasAnn = Test.class.isAnnotationPresent(TestAnnotation.class); if (hasAnn) { TestAnnotation testAnnotation = Test.class.getAnnotation(TestAnnotation.class); System.out.println("id:" + testAnnotation.id()); System.out.println("msg:" + testAnnotation.msg()); } try{ Field a = Test.class.getDeclaredField("a"); a.setAccessible(true); //获取一个成员变量上注解 Check check = a.getAnnotation(Check.class); if(check!=null){ System.out.println("check value :"+check.value()); } Method testMethod = Test.class.getDeclaredMethod("test"); if(testMethod!=null){ Annotation[] anns= testMethod.getAnnotations(); for(Annotation ann : anns){ System.out.println(ann.annotationType().getSimpleName()); } } } catch (NoSuchFieldException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (NoSuchMethodException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
java官方文档对注解的解释:
注解是一系列元数据,它提供数据用来解释程序代码,但是注解并非是所解释的代码本身的一部分。注解对于代码的运行效果没有直接影响。 注解有许多用处,主要如下: - 提供信息给编译器: 编译器可以利用注解来探测错误和警告信息 - 编译阶段时的处理: 软件工具可以用来利用注解信息来生成代码、Html文档或者做其它相应处理。 - 运行时的处理: 某些注解可以在程序运行的时候接受代码的提取
注解不是代码本身的一部分
当开发者使用了Annotation修饰了类、方法、Field等成员之后,这些Annotation不会自己生效,必须有开发者提供相应的代码来提取并处理Annotation信息。这些提取和处理Annotation的代码统称为APT(Annotation Processing Tool)。
示例:
定义注解Jiecha
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface Jiecha { }
NoBug.java
public class NoBug { @Jiecha public void suanshu(){ System.out.println("123456"); } @Jiecha public void jiafa(){ System.out.println("1+1="+1+1); } @Jiecha public void jianfa(){ System.out.println("1-1="+(1-1)); } @Jiecha public void chengfa(){ System.out.println("3*5="+(3*5)); } @Jiecha public void chufa(){ System.out.println("6/0="+6/0); } public void desc(){ System.out.println("this is a noBug class desc"); } }
TestTool.java测试NoBug的方法
public class TestTool { public static void main(String[] args) { NoBug noBug = new NoBug(); Class clazz = noBug.getClass(); //反射获取方法 Method[] methods=clazz.getDeclaredMethods(); //用来记录测试产生的log信息 StringBuilder log = new StringBuilder(); //记录异常的次数 int errorNum =0; for(Method method : methods){ if(method.isAnnotationPresent(Jiecha.class)){ try { method.setAccessible(true); method.invoke(noBug,null); } catch (IllegalAccessException | InvocationTargetException e) { errorNum++; log.append(method.getName()); log.append(" "); log.append("has error:"); log.append(e.getCause().getClass().getSimpleName()); log.append(" "); log.append(e.getCause().getMessage()); log.append(" "); } } } log.append(clazz.getSimpleName()); log.append(" has "); log.append(errorNum); log.append(" error."); // 生成测试报告 System.out.println(log.toString()); } }
结果:
3*5=15 1+1=11 123456 1-1=0 chufa has error:ArithmeticException / by zero NoBug has 1 error.