一级缓存和二级缓存

mybatis一二级缓存测试实例:

package com.atguigu.mybatis.test; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder; import org.junit.Test; import com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Department; import com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee; import com.atguigu.mybatis.dao.DepartmentMapper; import com.atguigu.mybatis.dao.EmployeeMapper; import com.atguigu.mybatis.dao.EmployeeMapperAnnotation; import com.atguigu.mybatis.dao.EmployeeMapperDynamicSQL; import com.atguigu.mybatis.dao.EmployeeMapperPlus; public class MyBatisTest { public SqlSessionFactory getSqlSessionFactory() throws IOException { String resource = "mybatis-config.xml"; InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); return new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); } /** * 两级缓存: * 一级缓存:(本地缓存):sqlSession级别的缓存。一级缓存是一直开启的;SqlSession级别的一个Mapper * 与数据库同一次会话期间查询到的数据会放在本地缓存中。 * 以后如果需要获取相同的数据,直接从缓存中拿,没必要再去查询数据库; * * 一级缓存失效情况(没有使用到当前一级缓存的情况,效果就是,还需要再向数据库发出查询): * 1、sqlSession不同。 * 2、sqlSession相同,查询条件不同.(当前一级缓存中还没有这个数据) * 3、sqlSession相同,两次查询之间执行了增删改操作(这次增删改可能对当前数据有影响) * 4、sqlSession相同,手动清除了一级缓存(缓存清空) * * 二级缓存:(全局缓存):基于namespace级别的缓存:一个namespace对应一个二级缓存: * 工作机制: * 1、一个会话,查询一条数据,这个数据就会被放在当前会话的一级缓存中; * 2、如果会话关闭;一级缓存中的数据会被保存到二级缓存中;新的会话查询信息,就可以参照二级缓存中的内容; * 3、sqlSession===EmployeeMapper==>Employee * DepartmentMapper===>Department * 不同namespace查出的数据会放在自己对应的缓存中(map) * 效果:数据会从二级缓存中获取 * 查出的数据都会被默认先放在一级缓存中。 * 只有会话提交或者关闭以后,一级缓存中的数据才会转移到二级缓存中 * 使用: * 1)、开启全局二级缓存配置:<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/> * 2)、去mapper.xml中配置使用二级缓存: * <cache></cache> * 3)、我们的POJO需要实现序列化接口 * * 和缓存有关的设置/属性: * 1)、cacheEnabled=true:false:关闭缓存(二级缓存关闭)(一级缓存一直可用的) * 2)、每个select标签都有useCache="true": * false:不使用缓存(一级缓存依然使用,二级缓存不使用) * 3)、【每个增删改查标签的:flushCache标签的:flushCache="true":(一级二级都会清除),这就是为啥执行增删改后一级缓存被清空了,查询标签默认是false】 * 增删改执行完成后就会清楚缓存; * 测试:flushCache="true":一级缓存就清空了;二级也会被清除; * 查询标签:flushCache="false": * 如果flushCache=true;每次查询之后都会清空缓存;缓存是没有被使用的; * 4)、sqlSession.clearCache();只是清楚当前session的一级缓存; * 5)、localCacheScope:本地缓存作用域:(一级缓存SESSION);当前会话的所有数据保存在会话缓存中; * STATEMENT:可以禁用一级缓存; * *第三方缓存整合: * 1)、导入第三方缓存包即可; * 2)、导入与第三方缓存整合的适配包;官方有; * 3)、mapper.xml中使用自定义缓存 * <cache type="org.mybatis.caches.ehcache.EhcacheCache"></cache> * * @throws IOException * */ @Test public void testSecondLevelCache02() throws IOException{ SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = getSqlSessionFactory(); SqlSession openSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); SqlSession openSession2 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); try{ //1、 DepartmentMapper mapper = openSession.getMapper(DepartmentMapper.class); DepartmentMapper mapper2 = openSession2.getMapper(DepartmentMapper.class); Department deptById = mapper.getDeptById(1); System.out.println(deptById); openSession.close(); Department deptById2 = mapper2.getDeptById(1); System.out.println(deptById2); openSession2.close(); //第二次查询是从二级缓存中拿到的数据,并没有发送新的sql }finally{ } } @Test public void testSecondLevelCache() throws IOException{ SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = getSqlSessionFactory(); SqlSession openSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); SqlSession openSession2 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); try{ //1、 EmployeeMapper mapper = openSession.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class); EmployeeMapper mapper2 = openSession2.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class); Employee emp01 = mapper.getEmpById(1); System.out.println(emp01); openSession.close(); //第二次查询是从二级缓存中拿到的数据,并没有发送新的sql //mapper2.addEmp(new Employee(null, "aaa", "nnn", "0")); Employee emp02 = mapper2.getEmpById(1); System.out.println(emp02); openSession2.close(); }finally{ } } @Test public void testFirstLevelCache() throws IOException{ SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = getSqlSessionFactory(); SqlSession openSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); try{ EmployeeMapper mapper = openSession.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class); Employee emp01 = mapper.getEmpById(1); System.out.println(emp01); //xxxxx //1、sqlSession不同。 //SqlSession openSession2 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); //EmployeeMapper mapper2 = openSession2.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class); //2、sqlSession相同,查询条件不同 //3、sqlSession相同,两次查询之间执行了增删改操作(这次增删改可能对当前数据有影响) //mapper.addEmp(new Employee(null, "testCache", "cache", "1")); //System.out.println("数据添加成功"); //4、sqlSession相同,手动清除了一级缓存(缓存清空) //openSession.clearCache(); Employee emp02 = mapper.getEmpById(1); //Employee emp03 = mapper.getEmpById(3); System.out.println(emp02); //System.out.println(emp03); System.out.println(emp01==emp02); //openSession2.close(); }finally{ openSession.close(); } } }
mybatis-config.xml

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> <configuration> <!-- 1、mybatis可以使用properties来引入外部properties配置文件的内容; resource:引入类路径下的资源 url:引入网络路径或者磁盘路径下的资源 --> <properties resource="dbconfig.properties"></properties> <!-- 2、settings包含很多重要的设置项 setting:用来设置每一个设置项 name:设置项名 value:设置项取值 --> <settings> <setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/> <setting name="jdbcTypeForNull" value="NULL"/> <!--显式的指定每个我们需要更改的配置的值,即使他是默认的。防止版本更新带来的问题 --> <setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/> <setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/> <setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false"/> </settings> <!-- 3、typeAliases:别名处理器:可以为我们的java类型起别名 别名不区分大小写 --> <typeAliases> <!-- 1、typeAlias:为某个java类型起别名 type:指定要起别名的类型全类名;默认别名就是类名小写;employee alias:指定新的别名 --> <!-- <typeAlias type="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee" alias="emp"/> --> <!-- 2、package:为某个包下的所有类批量起别名 name:指定包名(为当前包以及下面所有的后代包的每一个类都起一个默认别名(类名小写),) --> <package name="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean"/> <!-- 3、批量起别名的情况下,使用@Alias注解为某个类型指定新的别名 --> </typeAliases> <!-- 4、environments:环境们,mybatis可以配置多种环境 ,default指定使用某种环境。可以达到快速切换环境。 environment:配置一个具体的环境信息;必须有两个标签;id代表当前环境的唯一标识 transactionManager:事务管理器; type:事务管理器的类型;JDBC(JdbcTransactionFactory)|MANAGED(ManagedTransactionFactory) 自定义事务管理器:实现TransactionFactory接口.type指定为全类名 dataSource:数据源; type:数据源类型;UNPOOLED(UnpooledDataSourceFactory) |POOLED(PooledDataSourceFactory) |JNDI(JndiDataSourceFactory) 自定义数据源:实现DataSourceFactory接口,type是全类名 --> <environments default="dev_mysql"> <environment id="dev_mysql"> <transactionManager type="JDBC"></transactionManager> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}" /> <property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" /> <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" /> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" /> </dataSource> </environment> <environment id="dev_oracle"> <transactionManager type="JDBC" /> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="${orcl.driver}" /> <property name="url" value="${orcl.url}" /> <property name="username" value="${orcl.username}" /> <property name="password" value="${orcl.password}" /> </dataSource> </environment> </environments> <!-- 5、databaseIdProvider:支持多数据库厂商的; type="DB_VENDOR":VendorDatabaseIdProvider 作用就是得到数据库厂商的标识(驱动getDatabaseProductName()),mybatis就能根据数据库厂商标识来执行不同的sql; MySQL,Oracle,SQL Server,xxxx --> <databaseIdProvider type="DB_VENDOR"> <!-- 为不同的数据库厂商起别名 --> <property name="MySQL" value="mysql"/> <property name="Oracle" value="oracle"/> <property name="SQL Server" value="sqlserver"/> </databaseIdProvider> <!-- 将我们写好的sql映射文件(EmployeeMapper.xml)一定要注册到全局配置文件(mybatis-config.xml)中 --> <!-- 6、mappers:将sql映射注册到全局配置中 --> <mappers> <!-- mapper:注册一个sql映射 注册配置文件 resource:引用类路径下的sql映射文件 mybatis/mapper/EmployeeMapper.xml url:引用网路路径或者磁盘路径下的sql映射文件 file:///var/mappers/AuthorMapper.xml 注册接口 class:引用(注册)接口, 1、有sql映射文件,映射文件名必须和接口同名,并且放在与接口同一目录下; 2、没有sql映射文件,所有的sql都是利用注解写在接口上; 推荐: 比较重要的,复杂的Dao接口我们来写sql映射文件 不重要,简单的Dao接口为了开发快速可以使用注解; --> <!-- <mapper resource="mybatis/mapper/EmployeeMapper.xml"/> --> <!-- <mapper class="com.atguigu.mybatis.dao.EmployeeMapperAnnotation"/> --> <!-- 批量注册: --> <package name="com.atguigu.mybatis.dao"/> </mappers> </configuration>
第三方缓存ehchace
由于mybatis的一二级缓存只是一个map,所以比较简陋,mybatis自定义了cache接口,第三方提供实现.比如ehcache-cache等.地址:
https://github.com/mybatis?utf8=%E2%9C%93&q=ehc&type=&language= -------->mybatis/mybatis-3的第一级mybatis目录下,会有很多第三方包.
通过点击see the doc就可以看到如何下载及安装:

使用一二级缓存和ehcache的mapper。xml文件如下:

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="com.atguigu.mybatis.dao.EmployeeMapper"> <cache type="org.mybatis.caches.ehcache.EhcacheCache"></cache> <!-- <cache eviction="FIFO" flushInterval="60000" readOnly="false" size="1024"></cache> --> <!-- eviction:缓存的回收策略: • LRU – 最近最少使用的:移除最长时间不被使用的对象。 • FIFO – 先进先出:按对象进入缓存的顺序来移除它们。 • SOFT – 软引用:移除基于垃圾回收器状态和软引用规则的对象。 • WEAK – 弱引用:更积极地移除基于垃圾收集器状态和弱引用规则的对象。 • 默认的是 LRU。 flushInterval:缓存刷新间隔 缓存多长时间清空一次,默认不清空,设置一个毫秒值 readOnly:是否只读: true:只读;mybatis认为所有从缓存中获取数据的操作都是只读操作,不会修改数据。 mybatis为了加快获取速度,直接就会将数据在缓存中的引用交给用户。不安全,速度快 false:非只读:mybatis觉得获取的数据可能会被修改。 mybatis会利用序列化&反序列的技术克隆一份新的数据给你。安全,速度慢 size:缓存存放多少元素; type="":指定自定义缓存的全类名; 实现Cache接口即可; --> <!-- namespace:名称空间;指定为接口的全类名 id:唯一标识 resultType:返回值类型 #{id}:从传递过来的参数中取出id值 public Employee getEmpById(Integer id); --> <!--public Map<Integer, Employee> getEmpByLastNameLikeReturnMap(String lastName); --> <select id="getEmpByLastNameLikeReturnMap" resultType="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee"> select * from tbl_employee where last_name like #{lastName} </select> <!--public Map<String, Object> getEmpByIdReturnMap(Integer id); --> <select id="getEmpByIdReturnMap" resultType="map"> select * from tbl_employee where id=#{id} </select> <!-- public List<Employee> getEmpsByLastNameLike(String lastName); --> <!--resultType:如果返回的是一个集合,要写集合中元素的类型 --> <select id="getEmpsByLastNameLike" resultType="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee"> select * from tbl_employee where last_name like #{lastName} </select> <!-- public Employee getEmpByMap(Map<String, Object> map); --> <select id="getEmpByMap" resultType="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee"> select * from ${tableName} where id=${id} and last_name=#{lastName} </select> <!-- public Employee getEmpByIdAndLastName(Integer id,String lastName);--> <select id="getEmpByIdAndLastName" resultType="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee"> select * from tbl_employee where id = #{id} and last_name=#{lastName} </select> <select id="getEmpById" resultType="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee"> select * from tbl_employee where id = #{id} </select> <select id="getEmpById" resultType="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee" databaseId="mysql" useCache="true"> select * from tbl_employee where id = #{id} </select> <select id="getEmpById" resultType="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee" databaseId="oracle"> select EMPLOYEE_ID id,LAST_NAME lastName,EMAIL email from employees where EMPLOYEE_ID=#{id} </select> <!-- public void addEmp(Employee employee); --> <!-- parameterType:参数类型,可以省略, 获取自增主键的值: mysql支持自增主键,自增主键值的获取,mybatis也是利用statement.getGenreatedKeys(); useGeneratedKeys="true";使用自增主键获取主键值策略 keyProperty;指定对应的主键属性,也就是mybatis获取到主键值以后,将这个值封装给javaBean的哪个属性 --> <insert id="addEmp" parameterType="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id" databaseId="mysql" flushCache="true"> insert into tbl_employee(last_name,email,gender) values(#{lastName},#{email},#{gender}) </insert> <!-- 获取非自增主键的值: Oracle不支持自增;Oracle使用序列来模拟自增; 每次插入的数据的主键是从序列中拿到的值;如何获取到这个值; --> <insert id="addEmp" databaseId="oracle"> <!-- keyProperty:查出的主键值封装给javaBean的哪个属性 order="BEFORE":当前sql在插入sql之前运行 AFTER:当前sql在插入sql之后运行 resultType:查出的数据的返回值类型 BEFORE运行顺序: 先运行selectKey查询id的sql;查出id值封装给javaBean的id属性 在运行插入的sql;就可以取出id属性对应的值 AFTER运行顺序: 先运行插入的sql(从序列中取出新值作为id); 再运行selectKey查询id的sql; --> <selectKey keyProperty="id" order="BEFORE" resultType="Integer"> <!-- 编写查询主键的sql语句 --> <!-- BEFORE--> select EMPLOYEES_SEQ.nextval from dual <!-- AFTER: select EMPLOYEES_SEQ.currval from dual --> </selectKey> <!-- 插入时的主键是从序列中拿到的 --> <!-- BEFORE:--> insert into employees(EMPLOYEE_ID,LAST_NAME,EMAIL) values(#{id},#{lastName},#{email<!-- ,jdbcType=NULL -->}) <!-- AFTER: insert into employees(EMPLOYEE_ID,LAST_NAME,EMAIL) values(employees_seq.nextval,#{lastName},#{email}) --> </insert> <!-- public void updateEmp(Employee employee); --> <update id="updateEmp"> update tbl_employee set last_name=#{lastName},email=#{email},gender=#{gender} where id=#{id} </update> <!-- public void deleteEmpById(Integer id); --> <delete id="deleteEmpById"> delete from tbl_employee where id=#{id} </delete> </mapper>
ehcache。xml文件内容

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <ehcache xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="../config/ehcache.xsd"> <!-- 磁盘保存路径 --> <diskStore path="D:44ehcache" /> <defaultCache maxElementsInMemory="10000" maxElementsOnDisk="10000000" eternal="false" overflowToDisk="true" timeToIdleSeconds="120" timeToLiveSeconds="120" diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="120" memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU"> </defaultCache> </ehcache> <!-- 属性说明: l diskStore:指定数据在磁盘中的存储位置。 l defaultCache:当借助CacheManager.add("demoCache")创建Cache时,EhCache便会采用<defalutCache/>指定的的管理策略 以下属性是必须的: l maxElementsInMemory - 在内存中缓存的element的最大数目 l maxElementsOnDisk - 在磁盘上缓存的element的最大数目,若是0表示无穷大 l eternal - 设定缓存的elements是否永远不过期。如果为true,则缓存的数据始终有效,如果为false那么还要根据timeToIdleSeconds,timeToLiveSeconds判断 l overflowToDisk - 设定当内存缓存溢出的时候是否将过期的element缓存到磁盘上 以下属性是可选的: l timeToIdleSeconds - 当缓存在EhCache中的数据前后两次访问的时间超过timeToIdleSeconds的属性取值时,这些数据便会删除,默认值是0,也就是可闲置时间无穷大 l timeToLiveSeconds - 缓存element的有效生命期,默认是0.,也就是element存活时间无穷大 diskSpoolBufferSizeMB 这个参数设置DiskStore(磁盘缓存)的缓存区大小.默认是30MB.每个Cache都应该有自己的一个缓冲区. l diskPersistent - 在VM重启的时候是否启用磁盘保存EhCache中的数据,默认是false。 l diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds - 磁盘缓存的清理线程运行间隔,默认是120秒。每个120s,相应的线程会进行一次EhCache中数据的清理工作 l memoryStoreEvictionPolicy - 当内存缓存达到最大,有新的element加入的时候, 移除缓存中element的策略。默认是LRU(最近最少使用),可选的有LFU(最不常使用)和FIFO(先进先出) -->
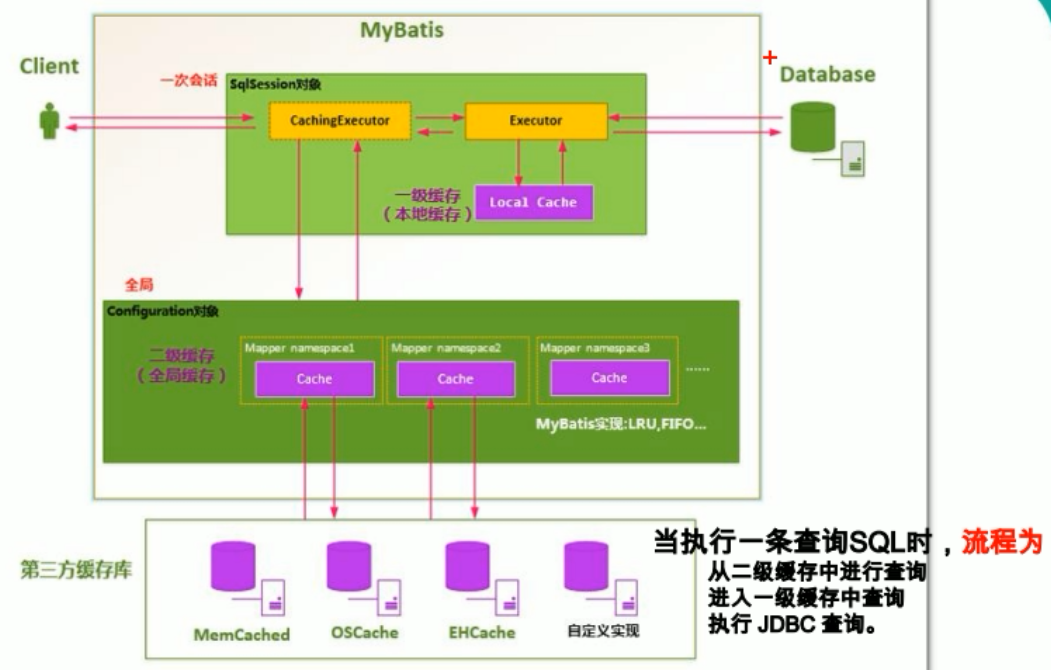
mybatis缓存原理图总结:
mybatis逆向工程

网站: https://github.com/mybatis

mybatis运行原理
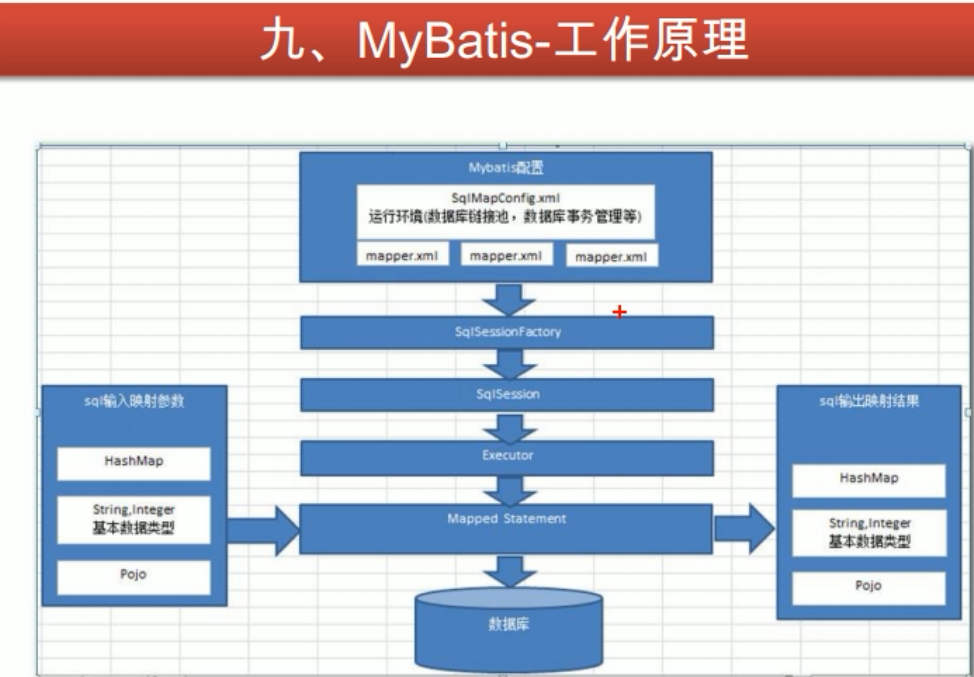
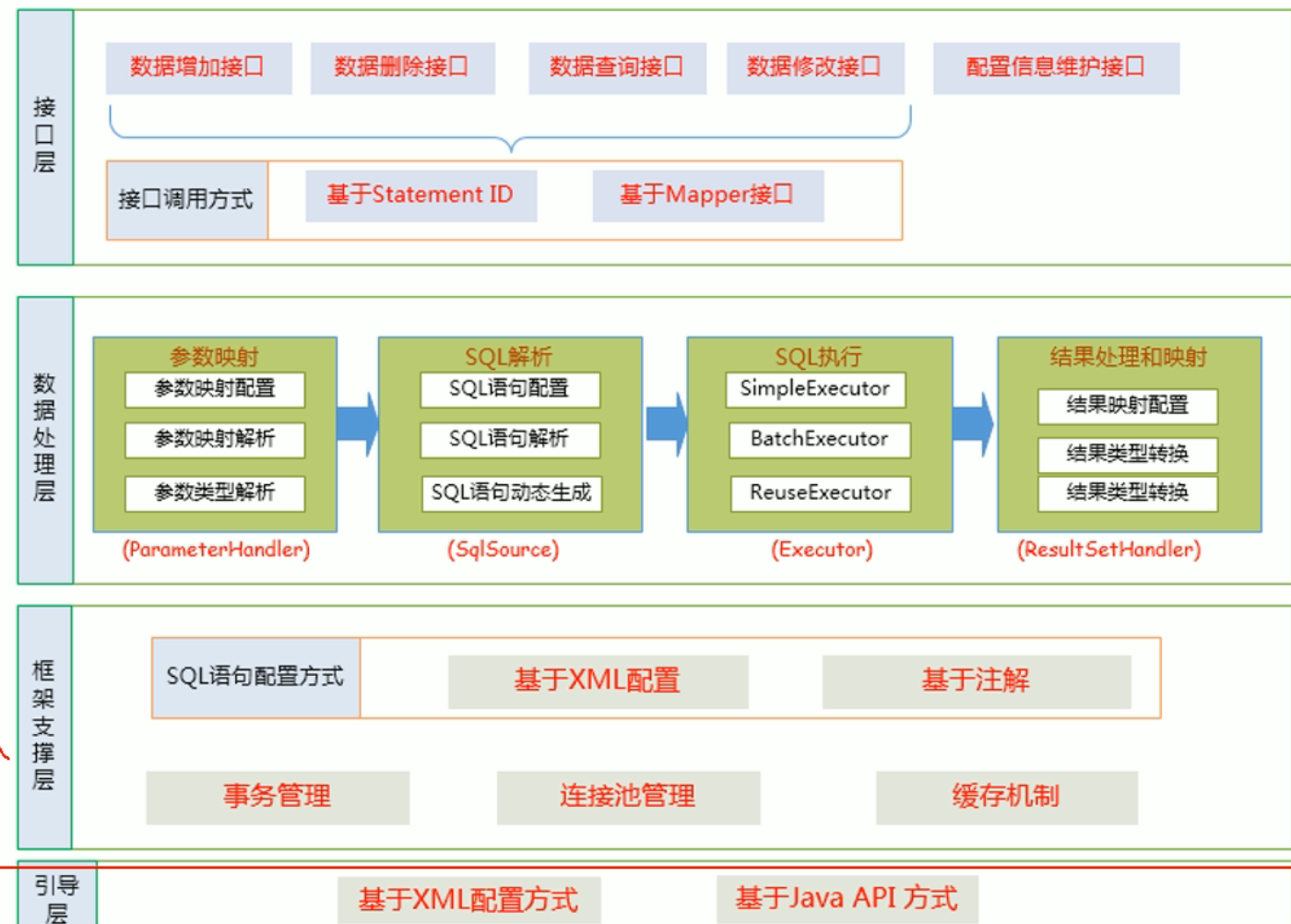
mybat运行流程总结

代码总结:

package com.atguigu.mybatis.test; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder; import org.junit.Test; import com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee; import com.atguigu.mybatis.dao.EmployeeMapper; public class MyBatisTest { public SqlSessionFactory getSqlSessionFactory() throws IOException { String resource = "mybatis-config.xml"; InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); return new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); } /** * 1、获取sqlSessionFactory对象: * 解析文件的每一个信息保存在Configuration中,返回包含Configuration的DefaultSqlSession; * 注意:【MappedStatement】:代表一个增删改查的详细信息 * * 2、获取sqlSession对象 * 返回一个DefaultSQlSession对象,包含Executor和Configuration; * 这一步会创建Executor对象; * * 3、获取接口的代理对象(MapperProxy) * getMapper,使用MapperProxyFactory创建一个MapperProxy的代理对象 * 代理对象里面包含了,DefaultSqlSession(Executor) * 4、执行增删改查方法 * * 总结: * 1、根据配置文件(全局,sql映射)初始化出Configuration对象 * 2、创建一个DefaultSqlSession对象, * 他里面包含Configuration以及 * Executor(根据全局配置文件中的defaultExecutorType创建出对应的Executor) * 3、DefaultSqlSession.getMapper():拿到Mapper接口对应的MapperProxy; * 4、MapperProxy里面有(DefaultSqlSession); * 5、执行增删改查方法: * 1)、调用DefaultSqlSession的增删改查(Executor); * 2)、会创建一个StatementHandler对象。 * (同时也会创建出ParameterHandler和ResultSetHandler) * 3)、调用StatementHandler预编译参数以及设置参数值; * 使用ParameterHandler来给sql设置参数 * 4)、调用StatementHandler的增删改查方法; * 5)、ResultSetHandler封装结果 * 注意: * 四大对象每个创建的时候都有一个interceptorChain.pluginAll(parameterHandler); * * @throws IOException */ @Test public void test01() throws IOException { // 1、获取sqlSessionFactory对象 SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = getSqlSessionFactory(); // 2、获取sqlSession对象 SqlSession openSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); try { // 3、获取接口的实现类对象 //会为接口自动的创建一个代理对象,代理对象去执行增删改查方法 EmployeeMapper mapper = openSession.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class); Employee employee = mapper.getEmpById(1); System.out.println(mapper); System.out.println(employee); } finally { openSession.close(); } } }
自定义类型处理器
当javabean中有字段是枚举类型时,我们可以自定义类型处理器,处理枚举类型存储到数据库中的值.

package com.atguigu.mybatis.typehandler; import java.sql.CallableStatement; import java.sql.PreparedStatement; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.sql.SQLException; import org.apache.ibatis.type.JdbcType; import org.apache.ibatis.type.TypeHandler; import com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.EmpStatus; /** * 1、实现TypeHandler接口。或者继承BaseTypeHandler * @author lfy * */ public class MyEnumEmpStatusTypeHandler implements TypeHandler<EmpStatus> { /** * 定义当前数据如何保存到数据库中 */ @Override public void setParameter(PreparedStatement ps, int i, EmpStatus parameter, JdbcType jdbcType) throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("要保存的状态码:"+parameter.getCode()); ps.setString(i, parameter.getCode().toString()); } @Override public EmpStatus getResult(ResultSet rs, String columnName) throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub //需要根据从数据库中拿到的枚举的状态码返回一个枚举对象 int code = rs.getInt(columnName); System.out.println("从数据库中获取的状态码:"+code); EmpStatus status = EmpStatus.getEmpStatusByCode(code); return status; } @Override public EmpStatus getResult(ResultSet rs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub int code = rs.getInt(columnIndex); System.out.println("从数据库中获取的状态码:"+code); EmpStatus status = EmpStatus.getEmpStatusByCode(code); return status; } @Override public EmpStatus getResult(CallableStatement cs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub int code = cs.getInt(columnIndex); System.out.println("从数据库中获取的状态码:"+code); EmpStatus status = EmpStatus.getEmpStatusByCode(code); return status; } }
2.配置typeHandler
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> <configuration> <properties resource="dbconfig.properties"></properties> <typeHandlers> <!--1、配置我们自定义的TypeHandler --> <typeHandler handler="com.atguigu.mybatis.typehandler.MyEnumEmpStatusTypeHandler" javaType="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.EmpStatus"/> <!--2、也可以在处理某个字段的时候告诉MyBatis用什么类型处理器 保存:#{empStatus,typeHandler=xxxx} 查询: <resultMap type="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee" id="MyEmp"> <id column="id" property="id"/> <result column="empStatus" property="empStatus" typeHandler=""/> </resultMap> 注意:如果在参数位置修改TypeHandler,应该保证保存数据和查询数据用的TypeHandler是一样的。 --> </typeHandlers> <plugins> <plugin interceptor="com.github.pagehelper.PageInterceptor"></plugin> </plugins> <environments default="dev_mysql"> <environment id="dev_mysql"> <transactionManager type="JDBC" /> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" /> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis" /> <property name="username" value="root" /> <property name="password" value="123456" /> </dataSource> </environment> <environment id="dev_oracle"> <transactionManager type="JDBC" /> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="${orcl.driver}" /> <property name="url" value="${orcl.url}" /> <property name="username" value="${orcl.username}" /> <property name="password" value="${orcl.password}" /> </dataSource> </environment> </environments> <databaseIdProvider type="DB_VENDOR"> <property name="MySQL" value="mysql"/> <property name="Oracle" value="oracle"/> <property name="SQL Server" value="sqlserver"/> </databaseIdProvider> <!-- 将我们写好的sql映射文件(EmployeeMapper.xml)一定要注册到全局配置文件(mybatis-config.xml)中 --> <mappers> <mapper resource="EmployeeMapper.xml" /> </mappers> </configuration>
