栈
定义:栈是限定仅在表尾进行插入或删除操作的线性表。
由于栈只有一边开口存取数据,称开口的那一端为“栈顶”,封死的那一端为“栈底”(类似于盛水的木桶,从哪进去的最后还得从哪出来)。
栈操作数据元素的方法
栈操作数据元素只有两种动作:
入栈:在栈顶插入一个元素的操作;
出栈:从栈顶删除一个元素的操作;
栈的“先进后出”原则(Last In First Out)
使用栈存储数据元素,对数据元素的“存”和“取”有严格的规定:数据按一定的顺序存储到栈中,当需要调取栈中某数据元素时,需要将在该数据元素之后进栈的先出栈,该数据元素才能从栈中提取出来。
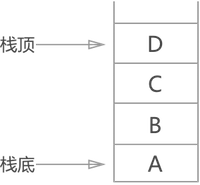
如图 1 ,栈中存放了 4 个数据元素,进栈的顺序是 A 先进栈,然后 B 进,然后 C 进,最后 D 进栈;当需要调取 A 时,首先 D 出栈,然后 C 出栈,然后 B 出栈,最后 A 才能出栈被调用。
就好比只有一个门的车库(每次仅允许一辆车通过),每辆车好比一个数据元素,只有离门最近的车先开出来,里边的车才能出来;最里边的车是最先开进去的,注定要最后出来。
栈的表示和实现
既然栈也是线性表,那么它就同样有线性表的两种表示形式:顺序栈 和 链式栈(简称“链栈”)。
栈的顺序存储结构(顺序栈)
顺序栈:是利用一组地址连续的存储单元依次存放自栈底到栈顶的数据元素。
#define MAXSIZE 100 /* 栈的最大容量 */
typedef int ElemType; /*元素类型*/
/* 顺序栈 */
typedef struct{
SElemType data[MAXSIZE];
int top; //栈顶指针 ,约定指向栈顶元素的下一个位置
} SqStack;
顺序栈的算法实现
初始化空栈
约定:非空栈的栈顶指针top始终指向栈顶元素的下一个位置.
void initSqStack(SqStack *s)
{
s->top= 0;
}
bool isEmptyStack(SqStack s)
{
if (s.top==0) //栈顶指针应该指向栈顶元素的下一个位置,否则栈空。
return true;
else
return false;
}
入栈
bool push(SqStack s,SElemType e) / s指向栈的指针变量,指针作为参数,可以将变化后的栈的值传递出来 /
{
if (s->top >=MAXSIZE)
return false;
else
{
s->data[s->top]=e; //先插入,
s->top ++; //栈顶指针后加1
//相当于 s->data[s->top++]
return true;
}
}
出栈
bool pop(SqStack *s,SElemType *e) /* 指针作为参数,可将修改后的值传递出来 */
{
if (s->top ==0)
return false ;
else
{
--s->top; //栈顶指针先减1
*e=s->data[s->top]; //再读取删除元素
//*e=s->data[--s->top ]; //等价
return true;
}
}
读栈顶
SElemType getTop(SqStack s)
{
SElemType e;
if (s.top ==0)
return false ;
else
{
e=s.data[s.top-1];
return e;
}
}
注意:上面的顺序栈是静态栈,空间一旦定下就难改而且一旦没有一段连续的内存,就会申请失败
那么,就出现了动态顺序存储栈,代码附下:
点击查看代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define TURE 1
#define FALSE 0
#define STACK_INIT_SIZE 100
#define STACKINCREMENT 10
typedef int SelemType;
/*---动态分配栈--*/
typedef struct
{
SelemType *base;
SelemType *top;
int StackSize;
} SeqStack;
/*---初始化---*/
int InitStack(SeqStack *s)
{
s->base = (SeqStack *)malloc(STACK_INIT_SIZE*sizeof(SeqStack));
if(!s->base)
printf("创建失败");
else
{
s->top = s->base;
s->StackSize = STACK_INIT_SIZE;
}
}
/*---判断栈是否为空---*/
int IsEmpty(SeqStack *s)
{
if(s->top==s->base)
{
return TURE;
}
else
{
return FALSE;
}
}
/*---入栈操作---*/
int push(SeqStack *s,SelemType x)
{
if((s->base)-(s->base)==s->StackSize)
{
s->base = (SeqStack *)realloc(s->base,(s->StackSize+STACKINCREMENT)*sizeof(SeqStack));
if(s->base==NULL)
{
return FALSE;
}
s->top =s->base+s->StackSize;
s->StackSize +=STACKINCREMENT;
}
else
{
*s->top = x;
s->top++;
return(TURE);
}
}
/*---出栈操作---*/
int Pop(SeqStack *s,SelemType *x)
{
if(s->top==s->base)
{
return FALSE;
}
else
{
s->top--;
*x = *s->top;
return (TURE);
}
}
链式存储结构(链式栈)
链栈,用线性表的链式存储结构实现。
用链表表示栈时,用链表头结点的一端作为栈的栈顶端,这样做的好处是当数据元素压栈或者弹栈时,直接使用头指针就可以完成,不需要增设额外的指针。
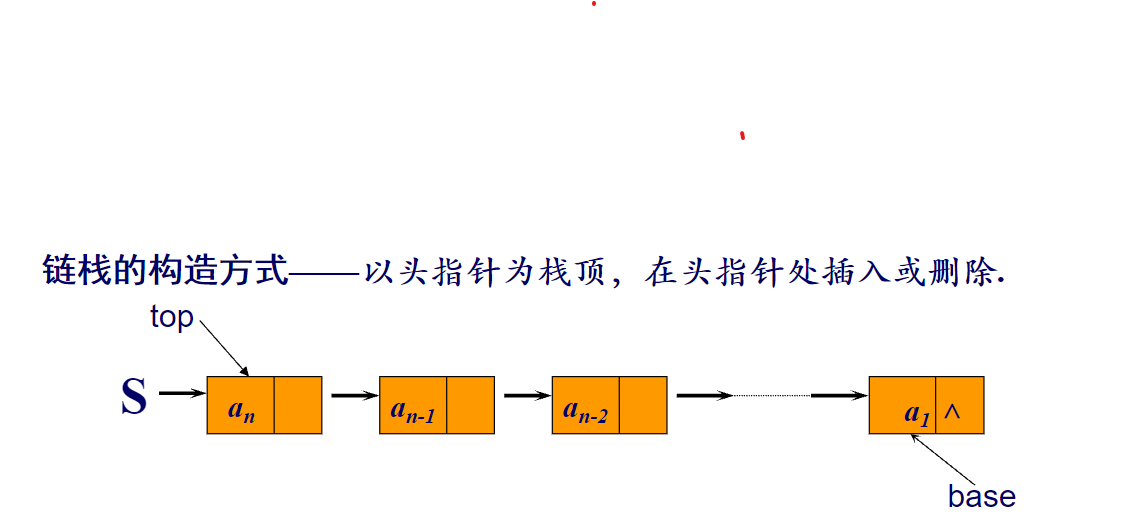
typedef Struct SNode{
ElemType data;
Struct SNode * next;
} SNode;
栈的应用举例
数制的转换(以8进制为例)
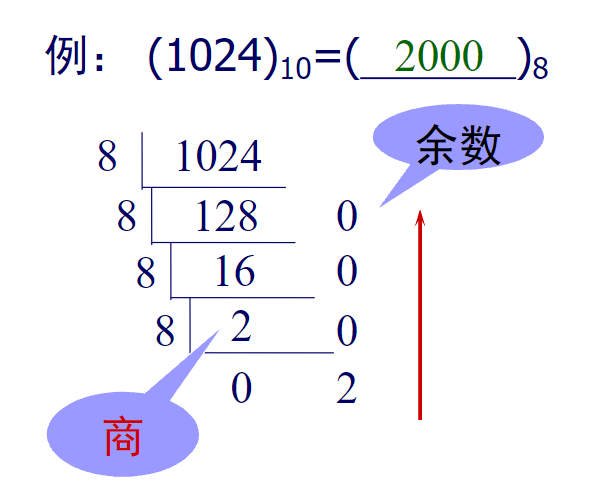
void conversion(int n)
{
SqStack s;
ElemType e;
bool tmp;
initSqStack(&s);
while(n)
{
tmp=push(&s,n%8); /* 求余数压栈 */
n=n/8;
}
while(!isEmptyStack (s))
{
tmp=pop(&s,&e);
printf("%3d",e);
}
printf("
");
}
编写算法,输入一个十进制数,转换为m进制数输出
点击查看代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "SStact.h" //栈的自定义头文件 内部有栈的基本操作
/*---进制转换---*/
int main(){
int x;
int system;
scanf("%d %d",&x,&system);
SeqStack *s;
s = (SeqStack *)malloc(sizeof(SeqStack));
InitStack(s);
while(x)
{
push(s,x%system);
x = x/system;
}
printf("在%d进制下为:",system);
while(!IsEmpty(s))
{
Pop(s,&x);
printf("%d",x);
}
}
算术表达式求值
一个表达式由操作数、运算符和界限符组成。
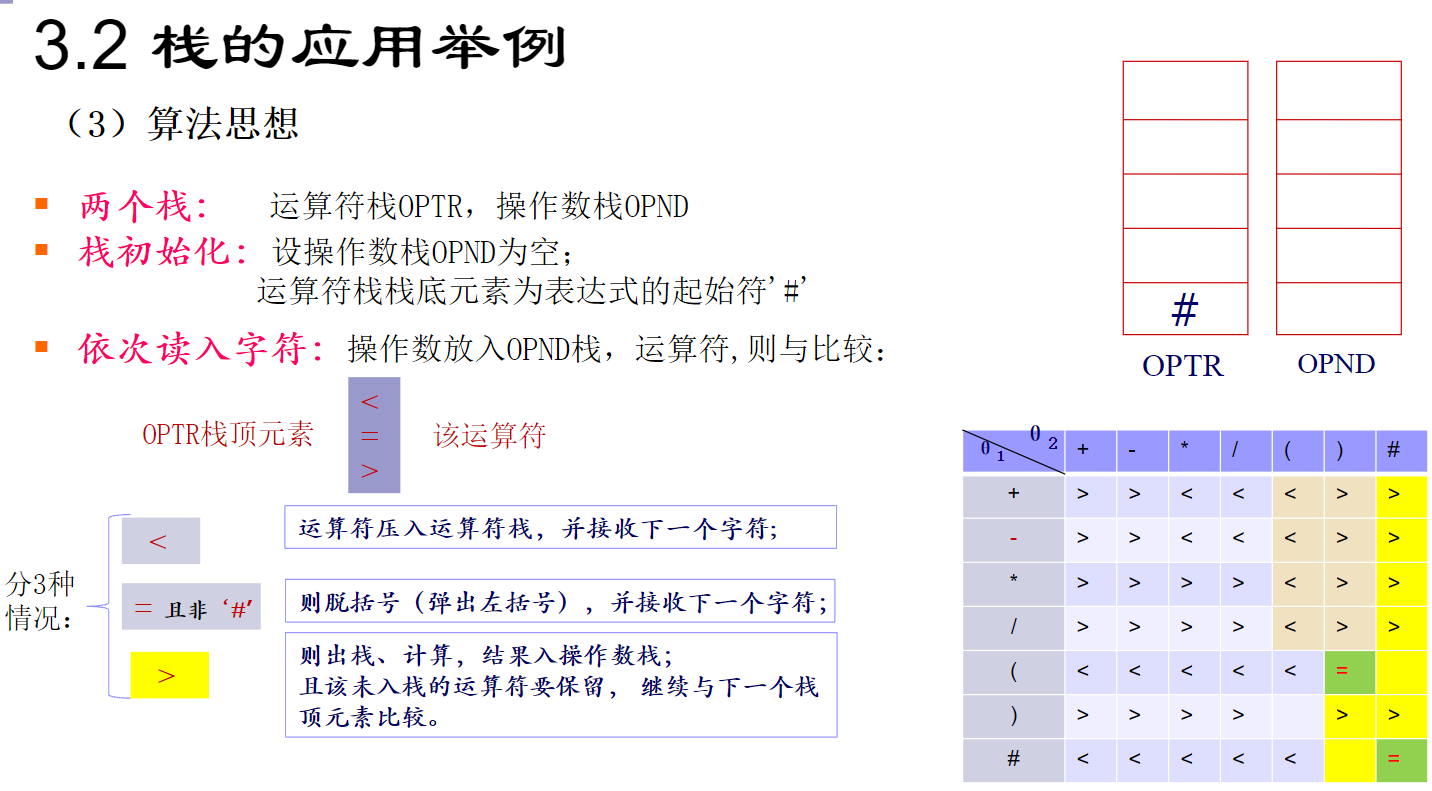
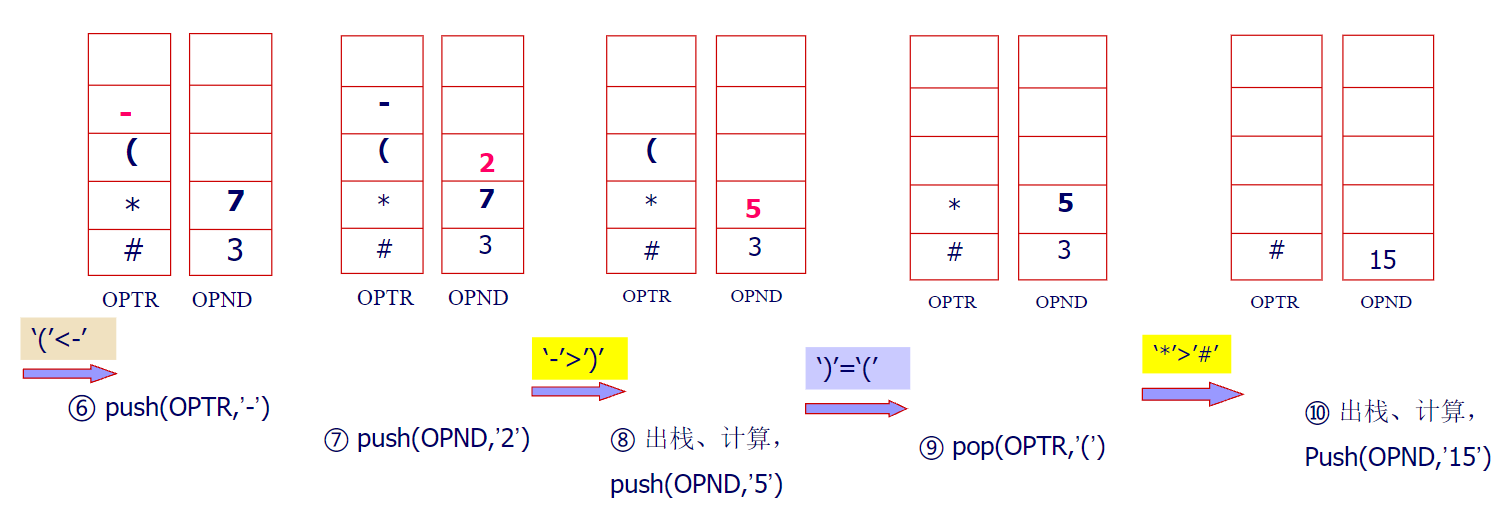

伪代码:
OprandType EvaluateExpression( ){
InitStack(OPTR); PUSH(OPTR,’#’);
InitStack(OPND); c=getchar();
While(c!=‘#’||GetTop(OPTR)!=‘#’){
If(!In(c,op)) {PUSH(OPND,c);c=getchar();} //In(c,op) C是运算符吗?
Else
switch(Precede(GetTop(OPTR) , c )){
case ‘<’ PUSH(OPTR,c);c=getchar();break;
case ‘=’ POP(OPTR,x);c=getchar();break;
case ‘>’ POP(OPTR,theta);
POP(OPND,b); POP(OPND,a);
PUSH(OPND,operate(a,theta,b));
break;
}//switch
}//while
}//EvaluateExpression