1. 打开文件
(1) open(name[, mode[, buffering]])
功能:打开文件或者新建一个文件
参数说明:
mode:
"r" : 读模式(默认)
"w" :写模式
"a" :追加模式
"b" :二进制模式(添加到其它模式中使用)
"+" : 读写模式(添加到其他模式使用)
buffering:
0:无缓冲(默认)
1:有缓冲
大于1:缓冲区的大写(单位:字节)
小于0:使用默认缓冲器大小
备注:
1) 模式以“w”或者"a"开头
a) 路径存在,文件不存在时,系统会新建文件
b) 路径不存在,文件不存在时,系统会IOError:No such file or directory
c) 路径存在,文件存在(文件中存在内容),以“w”开头的模式会清空文件中的内容,以“a”开头的模式,不会清空文件中的内容
2) 模式以“r”开头
a) 路径存在,文件不存在时,系统会报IOError:No such file or directory
b) 路径不存在,文件不存在时,系统会报IOError:No such file or directory
c) 路径存在,文件存在(文件中存在内容),不会清空文件中的内容
2. 读取文件
(1) read([charCount])
功能:读取文件内容
参数说明:
charCount:字节数,不填写,则读取所有内容
(2) readline()
功能:读取一行
(3) readlines()
功能:读取文件所有内容,并返回行列表
3. 写入内容
(1) write(data)
功能: 将内容写入文件
(2) writelines(sequence_of_strings)
功能:将行列表写入文件
4. 关闭文件
(1) close()
功能:关闭文件
5. 其他文件操作
(1) seek(offset[, whence])
功能: 将当前位置,移动到offset定义的位置
参数说明:
offset:必须为非负
whence:
0: 相对于文件开头的移动(默认)
1:相对于当前位置的移动
2:相对于文件末尾的移动
(2) tell()
功能: 返回当前文件位置
6. 示例:
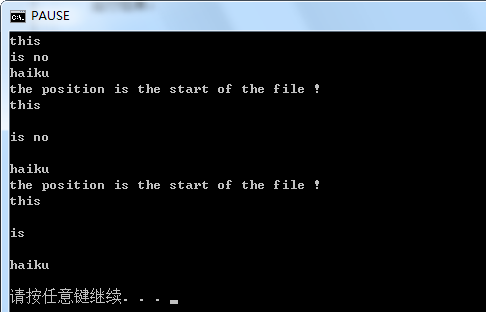
# encoding: UTF-8 #路径存在,文件不存在,则直接创建文件 f = open("e:/test.txt", "w") f.write("this is no haiku") f.close() f = open("e:/test.txt") #一次性读取所有内容 print f.read() print "the position is the start of the file !" f.seek(0) #逐行读取所有内容 while True: line = f.readline() if not line: break print line print "the position is the start of the file !" f.seek(0) lines = f.readlines() f.close() lines[1] = "is " f = open("e:/test_01.txt", "w") #将行列表写入内容 f.writelines(lines) f.close() f = open("e:/test_01.txt") #读取所有内容转换为行列表 for line in f.readlines(): if not line: break print line f.close()
运行结果: