ORM之聚合、分组、F与Q查询,orm中常见字段,自定义char字段,查询优化,django orm中的事务操作。
聚合查询
聚合(利用聚合函数)
关键字: aggregate()是QuerySet 的一个终止子句,意思是说,它返回一个包含一些键值对的字典。
from django.db.models import Max,Min,Count,Sum,Avg
# 统计所有书平均价格
res = models.Book.objects.all().aggregate(Avg('ptice'))
res1 = models.Book.objects.all().aggregate(Max('ptice'))
res2 = models.Book.objects.all().aggregate(Min('ptice'))
res3 = models.Book.objects.all().aggregate(Sum('ptice'))
res4 = models.Book.objects.all().aggregate(Count('ptice'))
分组查询
关键字:annotate
最简单的规律:models后面点什么,就是按什么分组
# 1、统计每一本书的作者个数
from django.db.models import Max,Min,Count,Sum,Avg
res = models.Book.objects.annotate(author_num=Count('authors')).values('author_num')
print(res)
# annotate就自动按书分组
# 2、统计出每个出版社卖的最便宜的书的价格
res = models.Publish.objects.annotate(price_min=Min('book__price')).values('price__min')
print(res)
# 3、统计不止一个作者的图书
models.Book.objects.annotate(author_num=Count("author")).filter(author_num__gt=1).values('author_num')
F与Q查询
F查询
能够帮助你获取到表中字段所对应的数据
from django.db.models import F
# 1、查询出卖出数大于库存数的书籍
res = models.Book.objects.filter(maichu__gt=F('kucun'))
print(res)
# 2、将所有书的价格全部提高100元
models.Book.objects.update(price=F('price')+100)
# 将所有书的名字后面都加上爆款
from django.db.models.functions import Concat
from django.db.models import Value
ret = models.Product.objects.update(name=Concat(F('name'),Value('爆款')))
Q查询
filter() 等方法中逗号隔开的条件是与的关系。 如果你需要执行更复杂的查询(例如OR语句),你可以使用Q对象。
你可以组合& 和| 操作符以及使用括号进行分组来编写任意复杂的Q 对象。
from django.db.models import Q
# 查询书籍名称是python入门或者价格是544.44的书
modelsBook.objects.filter(Q(title='python入门')|Q(price=544.44))
同时,Q 对象可以使用" ~ "操作符取反,这允许组合正常的查询和取反(NOT/非) 查询。
# 查询书籍名称不是python入门或价格不是544.44的书
models.Book.objects.filter(~Q(title='python入门')|Q(price=54))
Q查询进阶
models.Book.objects.filter(Q(title="linux") | Q(price=123))
上面的方式查询条件只能是字段名。
如果我们只有字符串怎么写呢?
查询条件由用户输入决定
q = Q() # 实例化一个Q对象
q.connector = 'or' #将默认and,改为or
q.children.append(('title','python'))
q.children.append(('kucun',666))
res = models.Book.objects.filter(q)
ORM中常见字段及参数
常用字段
1、models.AutoField 自增列= int(11)
如果没有的话,默认会生成一个名称为 id 的列,如果要显示的自定义一个自增列,必须将给列设置为主键 primary_key=True。
2、models.CharField 字符串字段
必须 max_length 参数
3、models.BooleanField 布尔类型=tinyint(1)
不能为空,Blank=True
4、models.ComaSeparatedIntegerField 用逗号分割的数字=varchar
继承CharField,所以必须 max_lenght 参数
5、models.DateField 日期类型 date
对于参数,auto_now =True则每次更新都会更新这个时间;auto_now_add 则只是第一次创建添加,之后的更新不再改变。
6、models.DateTimeField 日期类型 datetime
同DateField的参数
7、models.DecimalField 十进制小数类型= decimal
必须指定整数位max_digits和小数位decimal_places
8、models.EmailField 字符串类型(正则表达式邮箱)=varchar
对字符串进行正则表达式
9、models.FloatField 浮点类型= double
10、models.IntegerField 整形
11、models.BigIntegerField 长整形
integer_field_ranges ={
'SmallIntegerField':(-32768,32767),
'IntegerField':(-2147483648,2147483647),
'BigIntegerField':(-9223372036854775808,9223372036854775807),
'PositiveSmallIntegerField':(0,32767),
'PositiveIntegerField':(0,2147483647),
}
12、models.IPAddressField 字符串类型(ip4正则表达式)
13、models.GenericIPAddressField 字符串类型(ip4和ip6是可选的)
参数protocol可以是:both、ipv4、ipv6
验证时,会根据设置报错
14、models.NullBooleanField 允许为空的布尔类型
15、models.PositiveIntegerFiel 正Integer
16、models.PositiveSmallIntegerField 正smallInteger
17、models.SlugField 减号、下划线、字母、数字
18、models.SmallIntegerField 数字
数据库中的字段有:tinyint、smallint、int、bigint
19、models.TextField 字符串=longtext
20、models.TimeField 时间 HH:MM[:ss[.uuuuuu]]
21、models.URLField 字符串,地址正则表达式
22、models.BinaryField 二进制
23、models.ImageField 图片
24、models.FilePathField 文件
ORM字段与MySQL字段对应关系:
'AutoField': 'integer AUTO_INCREMENT',
'BigAutoField': 'bigint AUTO_INCREMENT',
'BinaryField': 'longblob',
'BooleanField': 'bool',
'CharField': 'varchar(%(max_length)s)',
'CommaSeparatedIntegerField': 'varchar(%(max_length)s)',
'DateField': 'date',
'DateTimeField': 'datetime',
'DecimalField': 'numeric(%(max_digits)s, %(decimal_places)s)',
'DurationField': 'bigint',
'FileField': 'varchar(%(max_length)s)',
'FilePathField': 'varchar(%(max_length)s)',
'FloatField': 'double precision',
'IntegerField': 'integer',
'BigIntegerField': 'bigint',
'IPAddressField': 'char(15)',
'GenericIPAddressField': 'char(39)',
'NullBooleanField': 'bool',
'OneToOneField': 'integer',
'PositiveIntegerField': 'integer UNSIGNED',
'PositiveSmallIntegerField': 'smallint UNSIGNED',
'SlugField': 'varchar(%(max_length)s)',
'SmallIntegerField': 'smallint',
'TextField': 'longtext',
'TimeField': 'time',
'UUIDField': 'char(32)',
常用参数
1、null=True
数据库中字段是否可以为空
2、blank=True
django的Admin中添加数据时是否可允许空值
3、primary_key =False
主键,对AutoField设置主键后,就会代替原来的自增 id 列
4、auto_now 和 auto_now_add
auto_now 自动创建---无论添加或修改,都是当前操作的时间
auto_now_add 自动创建---永远是创建时的时间
5、choices
GENDER_CHOICE =(
(u'M', u'Male'),
(u'F', u'Female'),
)
gender = models.CharField(max_length=2,choices = GENDER_CHOICE) #字段模板展示
6、max_length 最大长度
7、default 默认值
8、verbose_name Admin中字段的显示名称
9、name|db_column 数据库中的字段名称
10、unique=True 不允许重复
11、db_index =True 数据库索引
12、editable=True 在Admin里是否可编辑
13、error_messages=None 错误提示
14、auto_created=False 自动创建
15、help_text 在Admin中提示帮助信息
16、validators=[] 验证器
17、upload-to 重定义上传文件的路径前缀
关系字段
(1)ForeignKey
(1)作用:
(1)外键类型在ORM中用来表示外键关联关系,一般把ForeignKey字段设置在 '一对多'中'多'的一方。
(2)ForeignKey可以和其他表做关联关系同时也可以和自身做关联关系。
(1)字段参数
(1)to
(1)作用:设置要关联的表
(1)to_field
(1)作用:设置要关联的表的字段
(1)on_delete
(1)作用:当删除关联表中的数据时,当前表与其关联的行的行为。
(1)models.CASCADE
(1)作用:删除关联数据,与之关联也删除
(1)db_constraint
(1)作用:是否在数据库中创建外键约束,默认为True。
其余字段参数:
models.DO_NOTHING
删除关联数据,引发错误IntegrityError
models.PROTECT
删除关联数据,引发错误ProtectedError
models.SET_NULL
删除关联数据,与之关联的值设置为null(前提FK字段需要设置为可空)
models.SET_DEFAULT
删除关联数据,与之关联的值设置为默认值(前提FK字段需要设置默认值)
models.SET
删除关联数据,
a. 与之关联的值设置为指定值,设置:models.SET(值)
b. 与之关联的值设置为可执行对象的返回值,设置:models.SET(可执行对象)
使用方式:
def func():
return 10
class MyModel(models.Model):
user = models.ForeignKey(
to="User",
to_field="id",
on_delete=models.SET(func)
)
(2)OneToOneField
(1)作用:
(1)一对一字段
(2)通常一对一字段用来扩展已有字段。(通俗的说就是一个人的所有信息不是放在一张表里面的,简单的信息一张表,隐私的信息另一张表,之间通过一对一外键关联)
(2)字段参数
(1)to
(1)作用:设置要关联的表。
to_field
(1)作用:设置要关联的字段。
on_delete
(1)作用:当删除关联表中的数据时,当前表与其关联的行的行为。(参考上面的例子)
自定义char字段
from django.db import models
#Django中没有对应的char类型字段,但是我们可以自己创建
class MyCharField(models.Field):
'''
自定义的char类型的字段类
'''
def __init__(self,max_length,*args,**kwargs):
self.max_length=max_length
super().__init__(max_length=max_length,*args,**kwargs)
def db_type(self, connection):
'''
限定生成的数据库表字段类型char,长度为max_length指定的值
:param connection:
:return:
'''
return 'char(%s)'%self.max_length
查询优化(面试比较喜欢问)
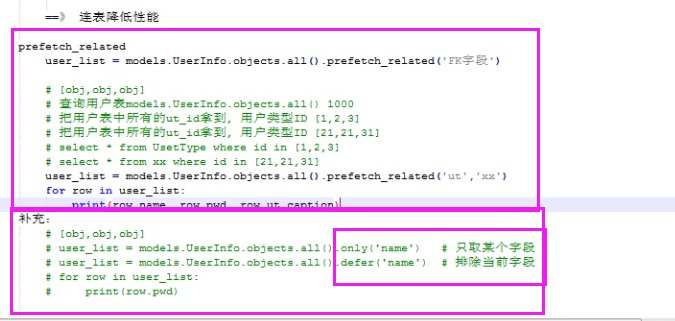
only与defer
res = models.Book.objects.only('title')
for r in res:
print(r.title) # 只走一次数据库
only会将括号内的字段对应的值,直接封装到返回给你的对象中,点该字段不需要再走数据库,一旦你点了不是括号内的字段,就会频繁的去走数据库查询
res = models.Book.objects.defer('title') # defer与only互为反关系
for r in res:
print(r.title) # 走多次数据库
defer会将括号内的字段排除之外将其他字段对应的值,直接封装到返回给你的对象中,点该其他字段,不需要再走数据库,一旦你点了括号内的字段,就会频繁的去走数据库查询
select_related与prefetch_related
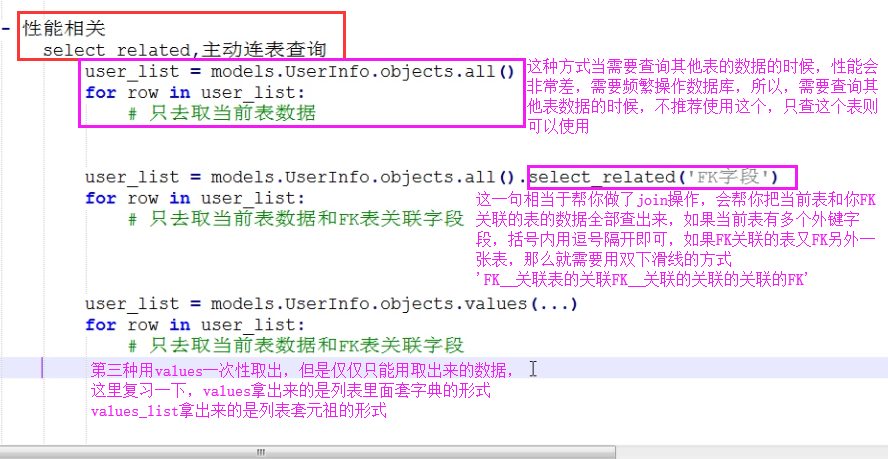
select_related
select_related() 会自动帮你做连表操作,然后将连表之后的数据全部查询出来封装给对象,然后就可以点字段查询。但要注意select_related() 括号内只能放外键字段,并且多对多字段不能放
如果括号内外键字段所关联的表中还有外键字段,还可以继续连表:select_related(外键字段__外键字段__外键字段...)
prefetch_related
prefetch_related() 看似连表操作,其实是类似于子查询,内部不做连表操作,消耗的资源就在查询次数上,括号内只能放外键字段
django orm中的事务操作
事务的特性:ACID:原子性、一致性、隔离性、持久性
django中如何开启事务
from django.db import transaction
with transaction.atomic()
# 在该代码块中所写的orm语句同属于一个事务
# 缩进出来之后自动结束
补充知识:
django2.x版本:在建数据库关系的时候需要手动指定2个参数,要告诉django级联更新,级联删除,是否建立外键约束
on_delete和db_constraint