-
Difficulty: Medium
-
Related Topics: Hash Table, Linked List
-
Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/copy-list-with-random-pointer/
Description
A linked list is given such that each node contains an additional random pointer which could point to any node in the list or null.
给定一个单链表,单链表的每个节点都有一个新增的随机指针,该指针会随机指向链表中的任何一个节点(或者 null)。
Return a deep copy of the list.
返回该链表的深拷贝。
The Linked List is represented in the input/output as a list of n nodes. Each node is represented as a pair of [val, random_index] where:
输入/输出的链表表示为一个长度为 n 的节点数组,每个节点
val: an integer representingNode.val
val:一个整数,表示Node.valrandom_index: the index of the node (range from0ton-1) where random pointer points to, ornullif it does not point to any node.
random_index:节点的下标(范围是0到n-1)表示该指针指向的节点,如果不指向任何节点,则以null表示。
Examples
Example 1
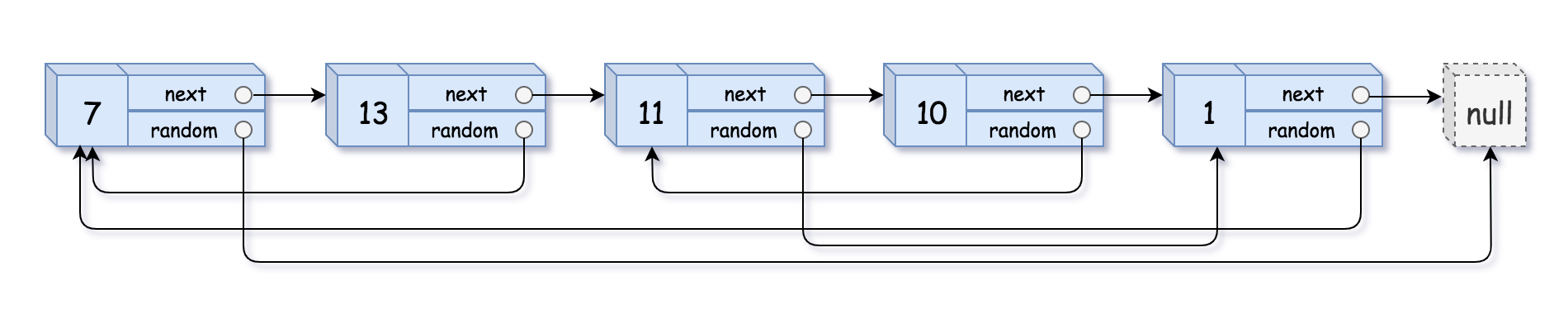
Input: head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
Output: [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
Example 2
Input: head = [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
Output: [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
Example 3
Input: head = []
Output: []
Explanation: Given linked list is empty (null pointer), so return null.
Constraints
-10000 <= Node.val <= 10000Node.randomis null or pointing to a node in the linked list.- The number of nodes will not exceed 1000.
Hints
-
Just iterate the linked list and create copies of the nodes on the go. Since a node can be referenced from multiple nodes due to the random pointers, make sure you are not making multiple copies of the same node.
-
You may want to use extra space to keep old node ---> new node mapping to prevent creating multiples copies of same node.
-
We can avoid using extra space for old node ---> new node mapping, by tweaking the original linked list. Simply interweave the nodes of the old and copied list. For e.g.
Old List: A --> B --> C --> D
InterWeaved List: A --> A' --> B --> B' --> C --> C' --> D --> D' -
The interweaving is done using next pointers and we can make use of interweaved structure to get the correct reference nodes for random pointers.
Solution
含有随机指针的链表,它首先是个链表,我们肯定是有办法复制出这个链表的所有节点的,复制出来后,再处理随机指针就很容易了。只要建立一个从旧节点到新节点的映射,维护这个映射即可,代码如下:
class Solution {
fun copyRandomList(node: Node?): Node? {
if (node == null) {
return null
}
val oldToNew = hashMapOf<Node, Node>()
// dummy 头节点,便于复制
val dummy = Node(-1)
var p = node
var q: Node? = dummy
// 第一次复制,复制出完整的链表结构
while (p != null) {
val newNode = Node(p.`val`)
q?.next = newNode
oldToNew[p] = newNode
p = p.next
q = q?.next
}
p = node
q = dummy.next
// 第二次复制,复制 random 结构
while (p != null) {
p.random?.let { q?.random = oldToNew[it] }
p = p.next
q = q?.next
}
return dummy.next
}
}
如果所使用的语言没有 map 这样的数据结构支持,也可以试试提示 3 和 4 所说的常数额外空间的解法,代码如下:
/**
* Example:
* var ti = Node(5)
* var v = ti.`val`
* Definition for a Node.
* class Node(var `val`: Int) {
* var next: Node? = null
* var random: Node? = null
* }
*/
class Solution {
fun copyRandomList(node: Node?): Node? {
if (node == null) {
return null
}
var p = node
// 第一次遍历,复制链表结构
// 确保每个原节点的后面是该节点的复制节点
while (p != null) {
val newNode = Node(p.`val`)
newNode.next = p.next
p.next = newNode
p = p.next?.next
}
p = node
var q = node.next
// 第二次遍历,复制 random 指针
// 原节点的 random 的 next 为 random 的复制节点
while (p != null) {
p.random?.let {
q?.random = it.next
}
p = p.next?.next
q = q?.next?.next
}
val result = node.next
p = node
q = node.next
// 第三次遍历,将复制节点从原节点中分离出来
while (p != null) {
p.next = q?.next
q?.next = p.next?.next
p = p.next
q = q?.next
}
return result
}
}