1、HashMap的数据存储结构
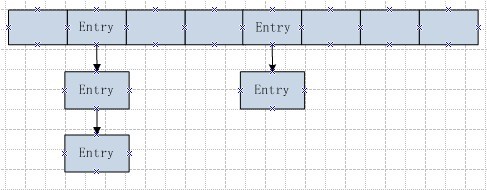
如上图,HashMap由一个数组和一系列的链表组成,存储的数据类型为Entry,一个HashMap的内部类
Entry{hash,key,value,next}。
数组的长度为2的n次方,默认值为16,如果自己设置的值不为2的n次方,则由hashmap自己处理为2的n次方,比如说:
HashMap<String,String> hsm = new HashMap<String,String>(13);
源码如下:

public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) { if (initialCapacity < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " + initialCapacity); if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY; if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " + loadFactor); // Find a power of 2 >= initialCapacity int capacity = 1; while (capacity < initialCapacity) capacity <<= 1; this.loadFactor = loadFactor; threshold = (int)(capacity * loadFactor); table = new Entry[capacity]; init(); }
传入13,实际数组大小为16。
2、存储数据的逻辑
看源码:

public V put(K key, V value) { if (key == null) //如果key为null,执行特殊存储操作,在问题3中详细回答 return putForNullKey(value); int hash = hash(key.hashCode()); //再次hash int i = indexFor(hash, table.length); //查找在数组中的存储位置 for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) { //如果数组当前位置不为null,循环数组对应位置的链表 Object k; if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) { //如果存在符合hash和key的条件的entry V oldValue = e.value; e.value = value; e.recordAccess(this); //啥也没干 return oldValue; } } modCount++; addEntry(hash, key, value, i); //如果数组当前位置为null,则插入当前entry return null; }
查找在数组中的存储位置,源码:

static int indexFor(int h, int length) { return h & (length-1); }
如果length为2的n次方,则length-1的二进制为1111...,比如现在(16-1)为1111,经过计算后返回值一定在数组长度范围内。
新增Entry到数组中,源码:

void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) { Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex]; //new一个新的Entry,并存储在数组的bucketIndex位置上 table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, e); //判断数组是否需要扩容 if (size++ >= threshold) resize(2 * table.length); }
3、key为null是怎么存储的
源码:

private V putForNullKey(V value) { //static final Object NULL_KEY = new Object(); //如果key为null,则用默认的NULL_KEY的hashcode来查找数组中位置 //我还看过不用indexFor(),直接 i=0 的实现 int hash = hash(NULL_KEY.hashCode()); int i = indexFor(hash, table.length); for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) { if (e.key == NULL_KEY) { V oldValue = e.value; e.value = value; e.recordAccess(this); return oldValue; } }
4、怎么根据key取数据的
源码:

public V get(Object key) { if (key == null)//key为null则用特殊方法取value return getForNullKey(); int hash = hash(key.hashCode()); //根据key的hash值取数组位置 //如果不为null,则循环挂靠在该位置上的链表 for (Entry<K,V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)]; e != null; e = e.next) { Object k; //如果找到则返回value值 if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) return e.value; } return null; } private V getForNullKey() { //取默认NULL_KEY的hash值,查找数组位置 int hash = hash(NULL_KEY.hashCode()); int i = indexFor(hash, table.length); Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; while (true) { if (e == null) return null; if (e.key == NULL_KEY) return e.value; e = e.next; } modCount++; addEntry(hash, (K) NULL_KEY, value, i); return null; }
5、为什么初始容量必须是2的n次方
看源码:

static int indexFor(int h, int length) { return h & (length-1); }
所有的存储和查找都是通过这个方法查找数组中的位置的。
举个不是2的n次方的例子,如果长度为13会发生什么情况?
13-1的二进制为: 1100
也就是说hash值以...1100、...1101、 ...1110、 ...1111为结尾的一系列的key都会落到数组[12]的位置上,换句话说这个位置的链表会很长,通过hash散列的效果差,查找效率会低。
