对分类模型的检验
加载数据
1 %matplotlib notebook 2 import numpy as np 3 import pandas as pd 4 import seaborn as sns 5 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 6 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split 7 from sklearn.datasets import load_digits 8 9 dataset = load_digits() 10 X, y = dataset.data, dataset.target 11 #统计每个种类的个数 12 for class_name, class_count in zip(dataset.target_names, np.bincount(dataset.target)): 13 print(class_name,class_count)
0 178 1 182 2 177 3 183 4 181 5 182 6 181 7 179 8 174 9 180
1 # 进行一个数据之间的转换 2 # Negative class (0) is 'not digit 1' 3 # Positive class (1) is 'digit 1' 4 y_binary_imbalanced = y.copy() 5 y_binary_imbalanced[y_binary_imbalanced != 1] = 0 6 7 print('Original labels: ', y[1:30]) 8 print('New binary labels: ', y_binary_imbalanced[1:30])
Original labels: [1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9] New binary labels: [1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]
1 #np.bincount:用于统计每个索引的总个数 2 np.bincount(y_binary_imbalanced) # Negative class (0) is the most frequent class
array([1615, 182])
(索引为0的个数为:1615,索引为1的个数为:182,在这种情况下,比例完全不平衡,inbalanced classes)
使用RBF核函数SVM来建立分类模型
1 X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y_binary_imbalanced, random_state=0) 2 3 # Accuracy of Support Vector Machine classifier 4 from sklearn.svm import SVC 5 6 svm = SVC(kernel='rbf', C=1).fit(X_train, y_train) 7 svm.score(X_test, y_test)
0.90888888888888886
DummyClassifier是一个使用简单规则进行预测的分类器,它可以用作与实际分类器进行比较
的基准,尤其是对于不平衡的类。不能用于实际问题。
1 from sklearn.dummy import DummyClassifier 2 3 # Negative class (0) is most frequent 4 #使用策略(strategy)大频率来进行拟合 5 dummy_majority = DummyClassifier(strategy = 'most_frequent').fit(X_train, y_train) 6 # Therefore the dummy 'most_frequent' classifier always predicts class 0 7 y_dummy_predictions = dummy_majority.predict(X_test) 8 9 y_dummy_predictions
array([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0])
1 dummy_majority.score(X_test, y_test)
0.9044444444444445
1 svm = SVC(kernel='linear', C=1).fit(X_train, y_train) 2 svm.score(X_test, y_test)
0.97777777777777775
混淆矩阵
1 from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix 2 3 # Negative class (0) is most frequent 4 dummy_majority = DummyClassifier(strategy = 'most_frequent').fit(X_train, y_train) 5 y_majority_predicted = dummy_majority.predict(X_test) 6 #产生混淆矩阵 7 confusion = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_majority_predicted) 8 9 print('Most frequent class (dummy classifier) ', confusion)
1 from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix 2 3 # Negative class (0) is most frequent 4 dummy_majority = DummyClassifier(strategy = 'most_frequent').fit(X_train, y_train) 5 y_majority_predicted = dummy_majority.predict(X_test) 6 #产生混淆矩阵 7 confusion = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_majority_predicted) 8 9 print('Most frequent class (dummy classifier) ', confusion)
Most frequent class (dummy classifier) [[407 0] [ 43 0]]
1 # produces random predictions w/ same class proportion as training set 2 dummy_classprop = DummyClassifier(strategy='stratified').fit(X_train, y_train) 3 y_classprop_predicted = dummy_classprop.predict(X_test) 4 confusion = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_classprop_predicted) 5 6 print('Random class-proportional prediction (dummy classifier) ', confusion)
Random class-proportional prediction (dummy classifier) [[361 46] [ 39 4]]
1 svm = SVC(kernel='linear', C=1).fit(X_train, y_train) 2 svm_predicted = svm.predict(X_test) 3 confusion = confusion_matrix(y_test, svm_predicted) 4 5 print('Support vector machine classifier (linear kernel, C=1) ', confusion)
Support vector machine classifier (linear kernel, C=1) [[402 5] [ 5 38]]
1 from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression 2 3 lr = LogisticRegression().fit(X_train, y_train) 4 lr_predicted = lr.predict(X_test) 5 confusion = confusion_matrix(y_test, lr_predicted) 6 7 print('Logistic regression classifier (default settings) ', confusion)
Logistic regression classifier (default settings) [[401 6] [ 6 37]]
1 from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier 2 3 dt = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=2).fit(X_train, y_train) 4 tree_predicted = dt.predict(X_test) 5 confusion = confusion_matrix(y_test, tree_predicted) 6 7 print('Decision tree classifier (max_depth = 2) ', confusion)
二元分类的评估
1 from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, precision_score, recall_score, f1_score 2 # Accuracy = TP + TN / (TP + TN + FP + FN) 3 # Precision = TP / (TP + FP) 4 # Recall = TP / (TP + FN) Also known as sensitivity, or True Positive Rate 5 # F1 = 2 * Precision * Recall / (Precision + Recall) 6 print('Accuracy: {:.2f}'.format(accuracy_score(y_test, tree_predicted))) 7 print('Precision: {:.2f}'.format(precision_score(y_test, tree_predicted))) 8 print('Recall: {:.2f}'.format(recall_score(y_test, tree_predicted))) 9 print('F1: {:.2f}'.format(f1_score(y_test, tree_predicted)))
Accuracy: 0.95 Precision: 0.79 Recall: 0.60 F1: 0.68
综合报告
1 # Combined report with all above metrics 2 from sklearn.metrics import classification_report 3 4 print(classification_report(y_test, tree_predicted, target_names=['not 1', '1']))
precision recall f1-score support
not 1 0.96 0.98 0.97 407
1 0.79 0.60 0.68 43
avg / total 0.94 0.95 0.94 450
1 print('Random class-proportional (dummy) ', 2 classification_report(y_test, y_classprop_predicted, target_names=['not 1', '1'])) 3 print('SVM ', 4 classification_report(y_test, svm_predicted, target_names = ['not 1', '1'])) 5 print('Logistic regression ', 6 classification_report(y_test, lr_predicted, target_names = ['not 1', '1'])) 7 print('Decision tree ', 8 classification_report(y_test, tree_predicted, target_names = ['not 1', '1']))
Random class-proportional (dummy)
precision recall f1-score support
not 1 0.90 0.89 0.89 407
1 0.08 0.09 0.09 43
avg / total 0.82 0.81 0.82 450
SVM
precision recall f1-score support
not 1 0.99 0.99 0.99 407
1 0.88 0.88 0.88 43
avg / total 0.98 0.98 0.98 450
Logistic regression
precision recall f1-score support
not 1 0.99 0.99 0.99 407
1 0.86 0.86 0.86 43
avg / total 0.97 0.97 0.97 450
Decision tree
precision recall f1-score support
not 1 0.96 0.98 0.97 407
1 0.79 0.60 0.68 43
avg / total 0.94 0.95 0.94 450
Decision functions(类似cost functions,用于评价样本预测)
1 X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y_binary_imbalanced, random_state=0) 2 y_scores_lr = lr.fit(X_train, y_train).decision_function(X_test) 3 y_score_list = list(zip(y_test[0:20], y_scores_lr[0:20])) 4 5 # show the decision_function scores for first 20 instances 6 y_score_list
[(0, -23.172292973469549), (0, -13.542576515500066), (0, -21.717588760007864), (0, -18.903065133316442), (0, -19.733169947138638), (0, -9.7463217496747667), (1, 5.2327155658831117), (0, -19.308012306288916), (0, -25.099330209728528), (0, -21.824312362996), (0, -24.143782750720494), (0, -19.578811099762504), (0, -22.568371393280199), (0, -10.822590225240777), (0, -11.907918741521936), (0, -10.977026853802803), (1, 11.206811164226373), (0, -27.644157619807473), (0, -12.857692102545419), (0, -25.848149140240199)]
#predict_proba()预测为1的可能性
1 X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y_binary_imbalanced, random_state=0) 2 y_proba_lr = lr.fit(X_train, y_train).predict_proba(X_test) 3 y_proba_list = list(zip(y_test[0:20], y_proba_lr[0:20,1])) 4 5 # show the probability of positive class for first 20 instances 6 y_proba_list
[(0, 8.6377579220606466e-11), (0, 1.3138118599563736e-06), (0, 3.6997386039099659e-10), (0, 6.1730972504865241e-09), (0, 2.6914925394345074e-09), (0, 5.8506057771143608e-05), (1, 0.99468934644404694), (0, 4.1175302368500096e-09), (0, 1.2574750894253029e-11), (0, 3.3252290754668869e-10), (0, 3.269552979937297e-11), (0, 3.1407283576084996e-09), (0, 1.5800864117150149e-10), (0, 1.9943442430612578e-05), (0, 6.7368003023859777e-06), (0, 1.7089540581641637e-05), (1, 0.9999864188091131), (0, 9.8694940340196163e-13), (0, 2.6059983600823614e-06), (0, 5.9469113009063784e-12)]
Precision-recall curves
1 from sklearn.metrics import precision_recall_curve 2 3 precision, recall, thresholds = precision_recall_curve(y_test, y_scores_lr) 4 closest_zero = np.argmin(np.abs(thresholds)) 5 closest_zero_p = precision[closest_zero] 6 closest_zero_r = recall[closest_zero] 7 8 plt.figure() 9 plt.xlim([0.0, 1.01]) 10 plt.ylim([0.0, 1.01]) 11 plt.plot(precision, recall, label='Precision-Recall Curve') 12 plt.plot(closest_zero_p, closest_zero_r, 'o', markersize = 12, fillstyle = 'none', c='r', mew=3) 13 plt.xlabel('Precision', fontsize=16) 14 plt.ylabel('Recall', fontsize=16) 15 plt.axes().set_aspect('equal') 16 plt.show()

ROC curves, Area-Under-Curve (AUC)
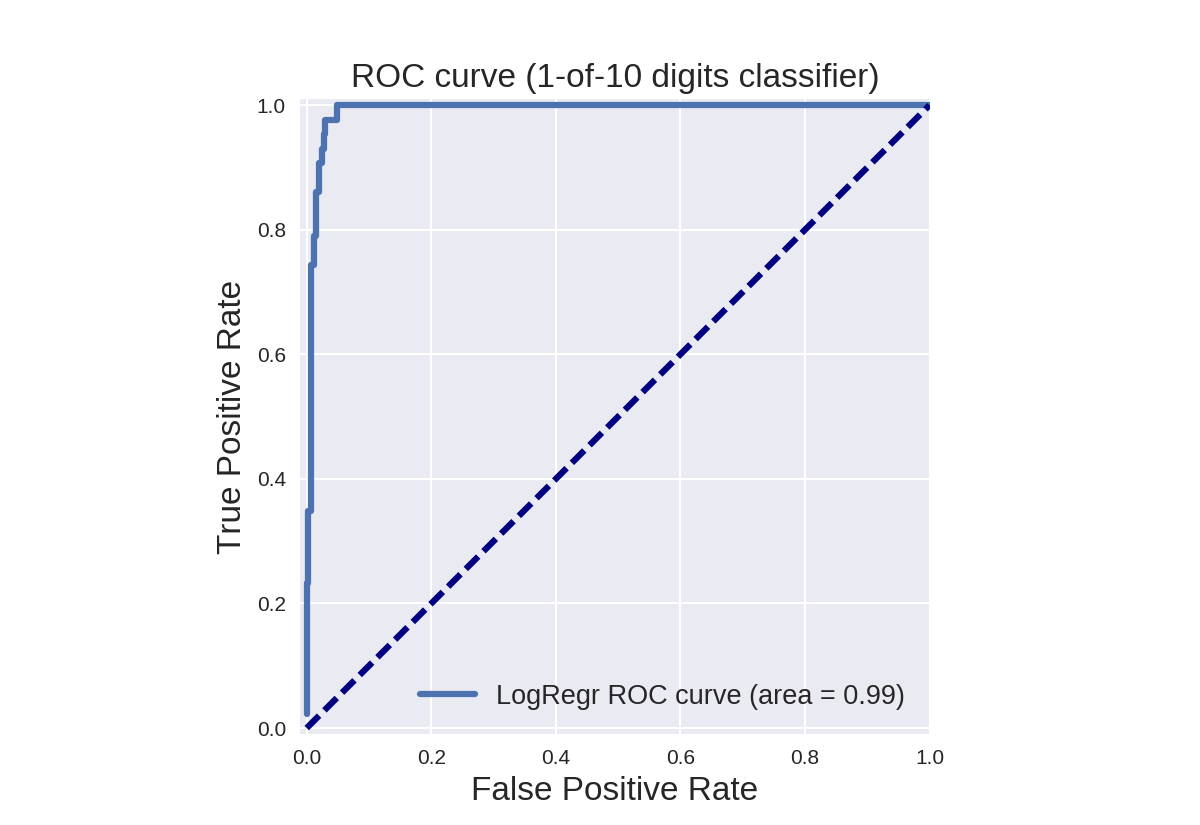
1 from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve, auc 2 3 X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y_binary_imbalanced, random_state=0) 4 5 y_score_lr = lr.fit(X_train, y_train).decision_function(X_test) 6 fpr_lr, tpr_lr, _ = roc_curve(y_test, y_score_lr) 7 roc_auc_lr = auc(fpr_lr, tpr_lr) 8 9 plt.figure() 10 plt.xlim([-0.01, 1.00]) 11 plt.ylim([-0.01, 1.01]) 12 plt.plot(fpr_lr, tpr_lr, lw=3, label='LogRegr ROC curve (area = {:0.2f})'.format(roc_auc_lr)) 13 plt.xlabel('False Positive Rate', fontsize=16) 14 plt.ylabel('True Positive Rate', fontsize=16) 15 plt.title('ROC curve (1-of-10 digits classifier)', fontsize=16) 16 plt.legend(loc='lower right', fontsize=13) 17 plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], color='navy', lw=3, linestyle='--') 18 plt.axes().set_aspect('equal') 19 plt.show()
1 from matplotlib import cm 2 3 X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y_binary_imbalanced, random_state=0) 4 5 plt.figure() 6 plt.xlim([-0.01, 1.00]) 7 plt.ylim([-0.01, 1.01]) 8 for g in [0.01, 0.1, 0.20, 1]: 9 svm = SVC(gamma=g).fit(X_train, y_train) 10 y_score_svm = svm.decision_function(X_test) 11 fpr_svm, tpr_svm, _ = roc_curve(y_test, y_score_svm) 12 roc_auc_svm = auc(fpr_svm, tpr_svm) 13 accuracy_svm = svm.score(X_test, y_test) 14 print("gamma = {:.2f} accuracy = {:.2f} AUC = {:.2f}".format(g, accuracy_svm, 15 roc_auc_svm)) 16 plt.plot(fpr_svm, tpr_svm, lw=3, alpha=0.7, 17 label='SVM (gamma = {:0.2f}, area = {:0.2f})'.format(g, roc_auc_svm)) 18 19 plt.xlabel('False Positive Rate', fontsize=16) 20 plt.ylabel('True Positive Rate (Recall)', fontsize=16) 21 plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], color='k', lw=0.5, linestyle='--') 22 plt.legend(loc="lower right", fontsize=11) 23 plt.title('ROC curve: (1-of-10 digits classifier)', fontsize=16) 24 plt.axes().set_aspect('equal') 25 26 plt.show()

对多分类模型的验证方法
多分类模型的混淆矩阵
1 dataset = load_digits() 2 X, y = dataset.data, dataset.target 3 X_train_mc, X_test_mc, y_train_mc, y_test_mc = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=0) 4 5 6 svm = SVC(kernel = 'linear').fit(X_train_mc, y_train_mc) 7 svm_predicted_mc = svm.predict(X_test_mc) 8 confusion_mc = confusion_matrix(y_test_mc, svm_predicted_mc) 9 df_cm = pd.DataFrame(confusion_mc, 10 index = [i for i in range(0,10)], columns = [i for i in range(0,10)]) 11 12 plt.figure(figsize=(5.5,4)) 13 sns.heatmap(df_cm, annot=True) 14 plt.title('SVM Linear Kernel Accuracy:{0:.3f}'.format(accuracy_score(y_test_mc, 15 svm_predicted_mc))) 16 plt.ylabel('True label') 17 plt.xlabel('Predicted label') 18 19 20 svm = SVC(kernel = 'rbf').fit(X_train_mc, y_train_mc) 21 svm_predicted_mc = svm.predict(X_test_mc) 22 confusion_mc = confusion_matrix(y_test_mc, svm_predicted_mc) 23 df_cm = pd.DataFrame(confusion_mc, index = [i for i in range(0,10)], 24 columns = [i for i in range(0,10)]) 25 26 plt.figure(figsize = (5.5,4)) 27 sns.heatmap(df_cm, annot=True) 28 plt.title('SVM RBF Kernel Accuracy:{0:.3f}'.format(accuracy_score(y_test_mc, 29 svm_predicted_mc))) 30 plt.ylabel('True label') 31 plt.xlabel('Predicted label');
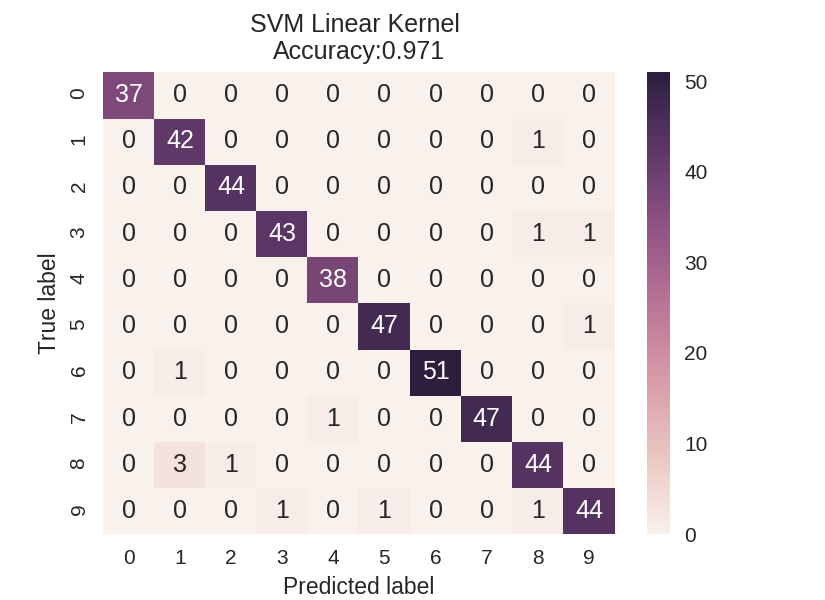
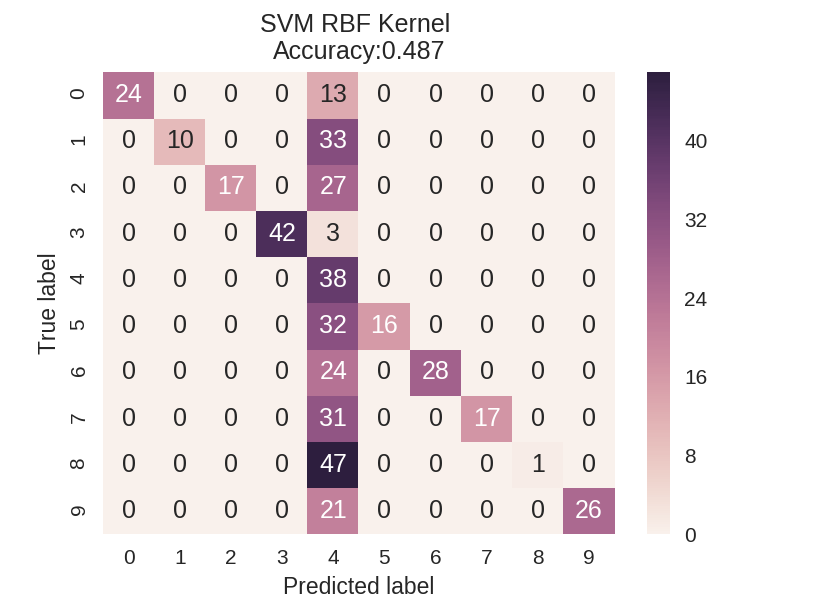
多分类模型的报告
1 print(classification_report(y_test_mc, svm_predicted_mc))
precision recall f1-score support
0 1.00 0.65 0.79 37
1 1.00 0.23 0.38 43
2 1.00 0.39 0.56 44
3 1.00 0.93 0.97 45
4 0.14 1.00 0.25 38
5 1.00 0.33 0.50 48
6 1.00 0.54 0.70 52
7 1.00 0.35 0.52 48
8 1.00 0.02 0.04 48
9 1.00 0.55 0.71 47
avg / total 0.93 0.49 0.54 450
微观平均指标与宏观平均指标
1 print('Micro-averaged precision = {:.2f} (treat instances equally)' 2 .format(precision_score(y_test_mc, svm_predicted_mc, average = 'micro'))) 3 print('Macro-averaged precision = {:.2f} (treat classes equally)' 4 .format(precision_score(y_test_mc, svm_predicted_mc, average = 'macro')))
Micro-averaged precision = 0.49 (treat instances equally) Macro-averaged precision = 0.91 (treat classes equally)
1 print('Micro-averaged f1 = {:.2f} (treat instances equally)' 2 .format(f1_score(y_test_mc, svm_predicted_mc, average = 'micro'))) 3 print('Macro-averaged f1 = {:.2f} (treat classes equally)' 4 .format(f1_score(y_test_mc, svm_predicted_mc, average = 'macro')))
Micro-averaged f1 = 0.49 (treat instances equally) Macro-averaged f1 = 0.54 (treat classes equally)
回归模型评估指标
1 %matplotlib notebook 2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 3 import numpy as np 4 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split 5 from sklearn import datasets 6 from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression 7 from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, r2_score 8 from sklearn.dummy import DummyRegressor 9 10 diabetes = datasets.load_diabetes() 11 12 X = diabetes.data[:, None, 6] 13 y = diabetes.target 14 15 X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=0) 16 17 lm = LinearRegression().fit(X_train, y_train) 18 lm_dummy_mean = DummyRegressor(strategy = 'mean').fit(X_train, y_train) 19 20 y_predict = lm.predict(X_test) 21 y_predict_dummy_mean = lm_dummy_mean.predict(X_test) 22 23 print('Linear model, coefficients: ', lm.coef_) 24 print("Mean squared error (dummy): {:.2f}".format(mean_squared_error(y_test, 25 y_predict_dummy_mean))) 26 print("Mean squared error (linear model): {:.2f}".format(mean_squared_error(y_test, y_predict))) 27 print("r2_score (dummy): {:.2f}".format(r2_score(y_test, y_predict_dummy_mean))) 28 print("r2_score (linear model): {:.2f}".format(r2_score(y_test, y_predict))) 29 30 # Plot outputs 31 plt.scatter(X_test, y_test, color='black') 32 plt.plot(X_test, y_predict, color='green', linewidth=2) 33 plt.plot(X_test, y_predict_dummy_mean, color='red', linestyle = 'dashed', 34 linewidth=2, label = 'dummy') 35 36 plt.show()
Linear model, coefficients: [-698.80206267] Mean squared error (dummy): 4965.13 Mean squared error (linear model): 4646.74 r2_score (dummy): -0.00 r2_score (linear model): 0.06
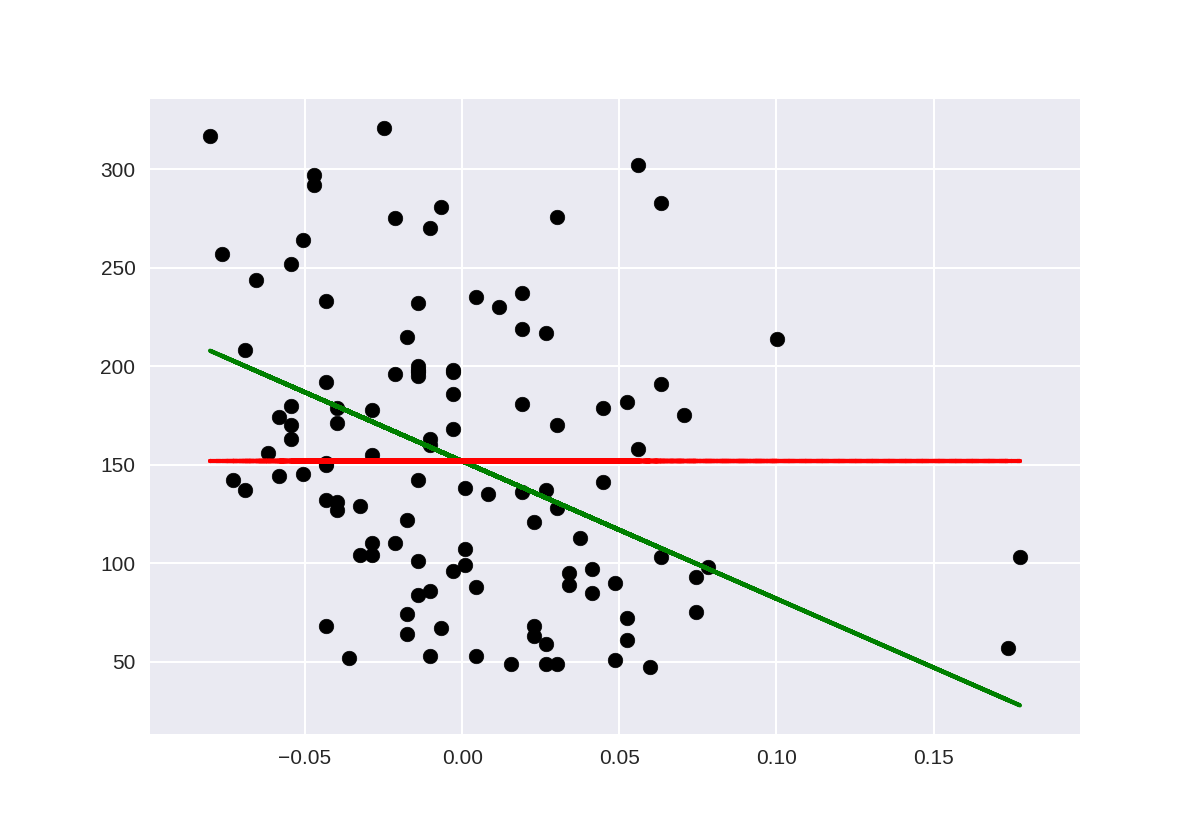
使用评估指标进行模型选择
交叉验证例子
1 from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score 2 from sklearn.svm import SVC 3 4 dataset = load_digits() 5 # again, making this a binary problem with 'digit 1' as positive class 6 # and 'not 1' as negative class 7 X, y = dataset.data, dataset.target == 1 8 clf = SVC(kernel='linear', C=1) 9 10 # accuracy is the default scoring metric 11 print('Cross-validation (accuracy)', cross_val_score(clf, X, y, cv=5)) 12 # use AUC as scoring metric 13 print('Cross-validation (AUC)', cross_val_score(clf, X, y, cv=5, scoring = 'roc_auc')) 14 # use recall as scoring metric 15 print('Cross-validation (recall)', cross_val_score(clf, X, y, cv=5, scoring = 'recall'))
Cross-validation (accuracy) [ 0.91944444 0.98611111 0.97214485 0.97493036 0.96935933] Cross-validation (AUC) [ 0.9641871 0.9976571 0.99372205 0.99699002 0.98675611] Cross-validation (recall) [ 0.81081081 0.89189189 0.83333333 0.83333333 0.83333333]
网格搜索示例
1 from sklearn.svm import SVC 2 from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV 3 from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score 4 5 dataset = load_digits() 6 X, y = dataset.data, dataset.target == 1 7 X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=0) 8 9 clf = SVC(kernel='rbf') 10 grid_values = {'gamma': [0.001, 0.01, 0.05, 0.1, 1, 10, 100]} 11 12 # default metric to optimize over grid parameters: accuracy 13 grid_clf_acc = GridSearchCV(clf, param_grid = grid_values) 14 grid_clf_acc.fit(X_train, y_train) 15 y_decision_fn_scores_acc = grid_clf_acc.decision_function(X_test) 16 17 print('Grid best parameter (max. accuracy): ', grid_clf_acc.best_params_) 18 print('Grid best score (accuracy): ', grid_clf_acc.best_score_) 19 20 # alternative metric to optimize over grid parameters: AUC 21 grid_clf_auc = GridSearchCV(clf, param_grid = grid_values, scoring = 'roc_auc') 22 grid_clf_auc.fit(X_train, y_train) 23 y_decision_fn_scores_auc = grid_clf_auc.decision_function(X_test) 24 25 print('Test set AUC: ', roc_auc_score(y_test, y_decision_fn_scores_auc)) 26 print('Grid best parameter (max. AUC): ', grid_clf_auc.best_params_) 27 print('Grid best score (AUC): ', grid_clf_auc.best_score_)
Grid best parameter (max. accuracy): {'gamma': 0.001}
Grid best score (accuracy): 0.996288047513
Test set AUC: 0.999828581224
Grid best parameter (max. AUC): {'gamma': 0.001}
Grid best score (AUC): 0.99987412783
1 #Evaluation metrics supported for model selection 2 from sklearn.metrics.scorer import SCORERS 3 4 print(sorted(list(SCORERS.keys())))
['accuracy', 'adjusted_rand_score', 'average_precision', 'f1', 'f1_macro', 'f1_micro',
'f1_samples', 'f1_weighted', 'log_loss', 'mean_absolute_error', 'mean_squared_error',
'median_absolute_error', 'neg_log_loss', 'neg_mean_absolute_error', 'neg_mean_square
d_error', 'neg_median_absolute_error', 'precision', 'precision_macro', 'precision_mic
ro', 'precision_samples', 'precision_weighted', 'r2', 'recall', 'recall_macro',
'recall_micro', 'recall_samples', 'recall_weighted', 'roc_auc']
使用数字数据集的双特征分类示例
使用不同的评估指标优化分类器
1 from sklearn.datasets import load_digits 2 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split 3 from adspy_shared_utilities import plot_class_regions_for_classifier_subplot 4 from sklearn.svm import SVC 5 from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV 6 7 8 dataset = load_digits() 9 X, y = dataset.data, dataset.target == 1 10 X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=0) 11 12 # Create a two-feature input vector matching the example plot above 13 # We jitter the points (add a small amount of random noise) in case there are areas 14 # in feature space where many instances have the same features. 15 jitter_delta = 0.25 16 X_twovar_train = X_train[:,[20,59]]+ np.random.rand(X_train.shape[0], 2) - jitter_delta 17 X_twovar_test = X_test[:,[20,59]] + np.random.rand(X_test.shape[0], 2) - jitter_delta 18 19 clf = SVC(kernel = 'linear').fit(X_twovar_train, y_train) 20 grid_values = {'class_weight':['balanced', {1:2},{1:3},{1:4},{1:5},{1:10},{1:20},{1:50}]} 21 plt.figure(figsize=(9,6)) 22 for i, eval_metric in enumerate(('precision','recall', 'f1','roc_auc')): 23 grid_clf_custom = GridSearchCV(clf, param_grid=grid_values, scoring=eval_metric) 24 grid_clf_custom.fit(X_twovar_train, y_train) 25 print('Grid best parameter (max. {0}): {1}' 26 .format(eval_metric, grid_clf_custom.best_params_)) 27 print('Grid best score ({0}): {1}' 28 .format(eval_metric, grid_clf_custom.best_score_)) 29 plt.subplots_adjust(wspace=0.3, hspace=0.3) 30 plot_class_regions_for_classifier_subplot(grid_clf_custom, X_twovar_test, y_test, None, 31 None, None, plt.subplot(2, 2, i+1)) 32 33 plt.title(eval_metric+'-oriented SVC') 34 plt.tight_layout() 35 plt.show()

Grid best parameter (max. precision): {'class_weight': {1: 2}}
Grid best score (precision): 0.5379994354058584
Grid best parameter (max. recall): {'class_weight': {1: 50}}
Grid best score (recall): 0.921184706893106
Grid best parameter (max. f1): {'class_weight': {1: 3}}
Grid best score (f1): 0.5079935126308859
Grid best parameter (max. roc_auc): {'class_weight': {1: 20}}
Grid best score (roc_auc): 0.8889416320163174
默认SVC分类器的精确召回曲线(平衡类别权重)
1 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split 2 from sklearn.metrics import precision_recall_curve 3 from adspy_shared_utilities import plot_class_regions_for_classifier 4 from sklearn.svm import SVC 5 6 dataset = load_digits() 7 X, y = dataset.data, dataset.target == 1 8 X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=0) 9 10 # create a two-feature input vector matching the example plot above 11 jitter_delta = 0.25 12 X_twovar_train = X_train[:,[20,59]]+ np.random.rand(X_train.shape[0], 2) - jitter_delta 13 X_twovar_test = X_test[:,[20,59]] + np.random.rand(X_test.shape[0], 2) - jitter_delta 14 15 clf = SVC(kernel='linear', class_weight='balanced').fit(X_twovar_train, y_train) 16 17 y_scores = clf.decision_function(X_twovar_test) 18 19 precision, recall, thresholds = precision_recall_curve(y_test, y_scores) 20 closest_zero = np.argmin(np.abs(thresholds)) 21 closest_zero_p = precision[closest_zero] 22 closest_zero_r = recall[closest_zero] 23 24 plot_class_regions_for_classifier(clf, X_twovar_test, y_test) 25 plt.title("SVC, class_weight = 'balanced', optimized for accuracy") 26 plt.show() 27 28 plt.figure() 29 plt.xlim([0.0, 1.01]) 30 plt.ylim([0.0, 1.01]) 31 plt.title ("Precision-recall curve: SVC, class_weight = 'balanced'") 32 plt.plot(precision, recall, label = 'Precision-Recall Curve') 33 plt.plot(closest_zero_p, closest_zero_r, 'o', markersize=12, fillstyle='none', c='r', mew=3) 34 plt.xlabel('Precision', fontsize=16) 35 plt.ylabel('Recall', fontsize=16) 36 plt.axes().set_aspect('equal') 37 plt.show() 38 print('At zero threshold, precision: {:.2f}, recall: {:.2f}' 39 .format(closest_zero_p, closest_zero_r))
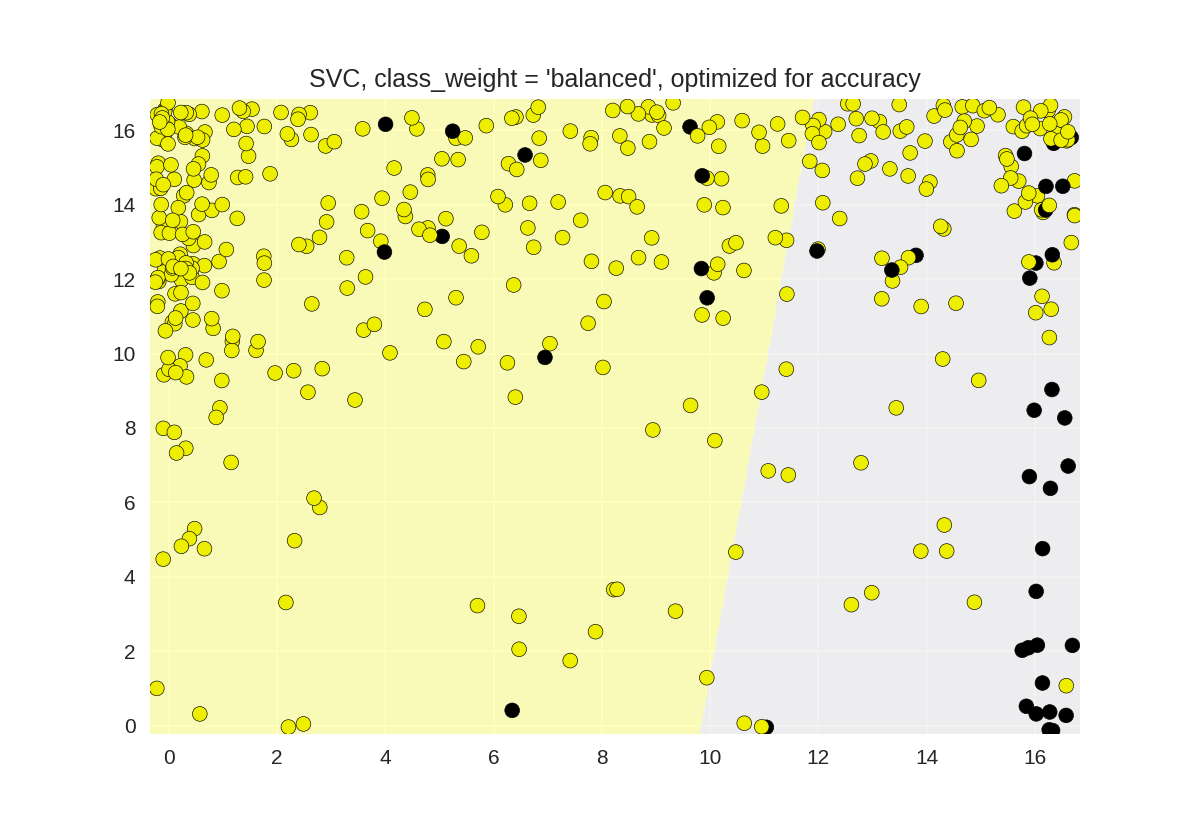
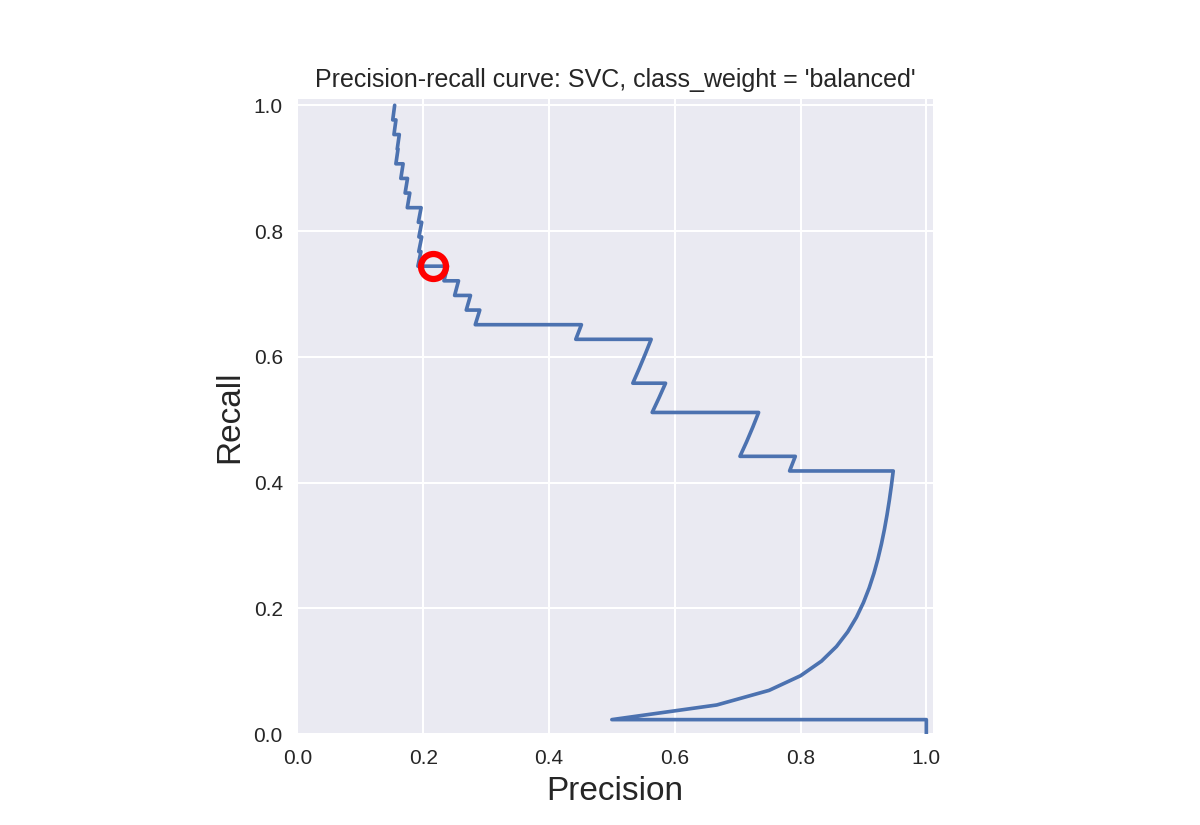
At zero threshold, precision: 0.22, recall: 0.74