这两节开始做个简单的图书管理系统(基于43节课程学的原生Django使用原生SQL操作):
主要实现如下功能:图书查看(包括详情)、添加和删除:
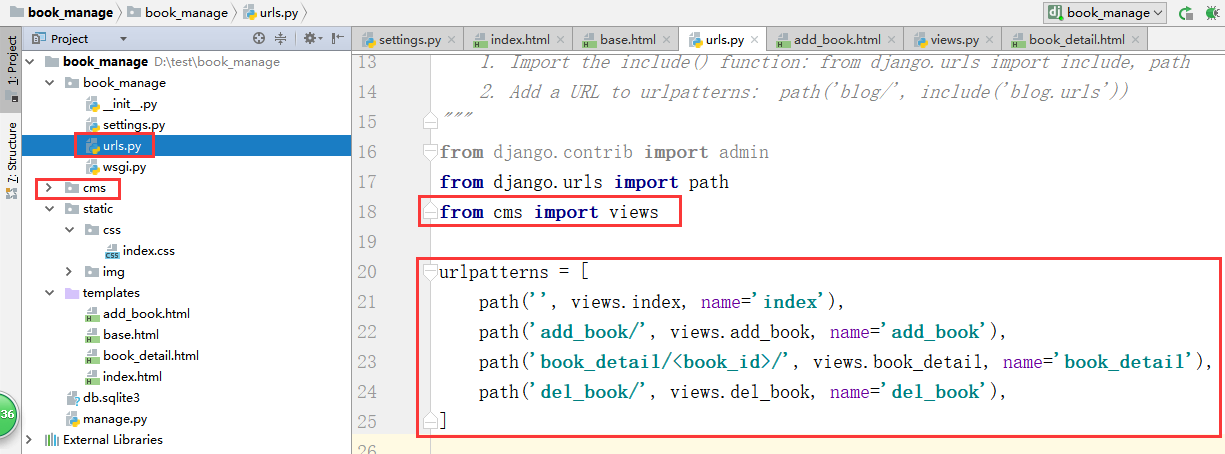
1、创建一个book_manage工程(使用pycharm创建时,同时创建一个APP——cms),url情况:
2、setting.py中静态文件加载,MySQL数据库配置,同时关闭中间件的csrf功能:
STATICFILES_DIRS = ( os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'static'), )
注释:MIDDLEWARE 中间件的csrf:
# 'django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddleware',
#MySQL 数据库配置
DATABASES = {
'default': {
'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.mysql',
'NAME': 'test',
'USER': 'root',
'PASSWORD': '123456789',
'HOST': '127.0.0.1',
'PORT': '3306'
}
}
3、静态文件模板——base.html:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="/static/css/index.css"> </head> <body> <nav> <ul class="nav"> <li><a href="/">首页</a></li> <li><a href="{% url 'add_book' %}">发布图书</a></li> </ul> </nav> {% block content %}{% endblock %} </body> </html>
4、index.css 内容:
* { margin: 0; padding: 0; } .nav{ background: #3a3a3a; height: 65px; overflow: hidden; } .nav li{ float: left; list-style: none; margin: 0 20px; line-height: 65px; } .nav li a{ color: #fff; text-decoration: none; } .nav li a:hover{ color: lightblue; }
5、首页文件内容:
{% extends 'base.html' %} {% block content %} <table> <thead> <tr> <td>序号</td> <td>书名</td> <td>作者</td> </tr> </thead> <tbody> {% for book in books %} <tr> <td>{{ forloop.counter }}</td> <td><a href="{% url 'book_detail' book_id=book.0 %}">{{ book.1 }}</a></td> <td>{{ book.2 }}</td> </tr> {% endfor %} </tbody> </table> {% endblock %}
6、views.py文件内容:
from django.shortcuts import render, redirect, reverse from django.db import connection # Create your views here. def get_cursor(): return connection.cursor() def index(request): cursor = get_cursor() cursor.execute("select * from book") books = cursor.fetchall() return render(request, 'index.html', {'books': books}) def add_book(request): if request.method == 'GET': return render(request, 'add_book.html') else: name = request.POST.get('name') author = request.POST.get('author') cursor = get_cursor() cursor.execute("insert into book (name, auther) VALUES ('%s', '%s')" % (name, author)) return redirect(reverse('index')) def book_detail(request, book_id): cursor = get_cursor() cursor.execute("select * from book where id=%s" % book_id) book = cursor.fetchone() # print(book[0],book[1],book[2]) print(type(book)) return render(request, 'book_detail.html', {'book': book}) def del_book(request): if request.method == "POST": book_id = request.POST.get("book_id") cursor = get_cursor() cursor.execute("delete from book where id=%s" % book_id) return redirect(reverse(index)) else: raise RuntimeError("删除图书失败!!!")
7、add_book.html文件内容:
{% extends 'base.html' %} {% block content %} <form action="" method="post"> <table> <tbody> <tr> <td>书名:</td> <td><input type="text" name="name"></td> </tr> <tr> <td>作者:</td> <td><input type="text" name="author"></td> </tr> <tr> <td></td> <td><input type="submit" value="添加"></td> </tr> </tbody> </table> </form> {% endblock %}
8、book_detail.html文件内容:
{% extends 'base.html' %} {% block content %} <p>书名:{{ book.1 }}</p> <p>作者:{{ book.2 }}</p> <form action="{% url 'del_book' %}" method="post"> <input type="hidden" name="book_id" value="{{ book.0 }}"> <input type="submit" value="删除"> </form> {% endblock %}