debug = True开启debug模式 当你的代码在界面增减之后不用刷新界面自动更新
app.logger.error("这是error模式") app.logger.info("这是info模式") app.logger.debug("这是debug模式")
生产环境中一般都是用error模式
methods
我们可以在路由中设置你的methods就是你的路由所支持的所有的请求类型,默认的是get请求 如果你想要修改支持其他请求 也必须要带上get请求
@app.route("/",methods=["post","get"]) #methods是表示支持的请求类型默认是get
def index():
return "您好"
|
request.query_string |
表示你的url中的所有的数据 |
| request.form | 请求体中的数据在form中 |
配置文件:
因为你的主分区的功能会有很多那么你的所有的定义都放入其中吗?NO,我们可以把一起配置放入一个文件内 然后导入进来使用增加解耦性
你的配置文件放在的文件中需要是一个类中
设置你的配置文件
class Settings(object): DEBUG = True SECRET_KEY = "dasb" SERVER_NAME = "www.baidu.com:9980"
导入你的配置文件用:app.config.form_object(你的配置文件)
from settings import Settings,STUDENT_DICT #导入你的 配置文件 app = Flask(__name__)# 实例化一个flask对象 app.config.from_object(Settings) # 配置你的导入的文件中的类 这个类中放置的是你的配置信息
app.secret_key = "" # 开启你的session 给你的session赋值 开启session
from flask import Flask,render_template from one.settings import Settings,dict # 导入配置文件类 同时也要导入你的配置文件类中的要引用的内容 不然无法使用 app = Flask(__name__) app.config.from_object(Settings) #接收你的配置文件 @app.route("/") def one(): return "hello world" @app.route("/set") def set(): return str(dict) # 使用你的配置文件类中的内容 if __name__ == "__main__": app.run("127.0.0.1",9867,debug = True)
然后你的 setting的配置中的类中的信息 不需要再次进行导入就可以直接使用了 这样相当于已经把信息导入了进行
今天我们就来了解下 什么是Flask的路由系统
Falsk的路由系统其实我们并不陌生就是在你的请求执行的函数上加上一个类似于装饰器的路由
@app.route("要请求的url")
@app.route("/",methods=["POST","GET"])
这个就类似于一个装饰器把你的函数给包裹了 但是这个也是你的路由的写法,methods是你的允许请求的方式 默认为GET
路由的匹配模式:strict_slashes 可以修改这个模式让它是严格模式还是一般模式
@app.route("/index/",strict_slashes= True) # strict_slashes是严格匹配模式 就是你的url信息如果这里面输入的是什么浏览器也要是什么 必须是和这个一致 一个/ 都不能少
如果你的strict_slashes事等于True然后你的请求的url后面没有加上/那么会一直报错 因为你的浏览器会默认补上那个后面的/
url别名:endpoint 给你的url地址起一个别名,url_for反向生成一个url 可以通过url_for()来反向查找这个别名
@app.route("/index/",strict_slashes= True,endpoint="r_index")
可以通过url_for()来打印这个别名 反向生成
from flask import url_for #导入url_for @app.route("/index/",strict_slashes= True,endpoint="r_index") def index(): print(url_for("r_index")) #/index/ btn = "<a href='/add_stu'>添加信息</a>" btn = Markup(btn) return render_template("index.html",stu=STUDENT_DICT,btn = btn)
url_for:
@app.route("/") def one(): url = url_for("set") # 找到你的对应的方法的路径 return "hello world"+url #然后把这个路径也给返回出去 @app.route("/seet") def set(): return str(dict) # 使用你的配置文件类中的内容
显示的就是:
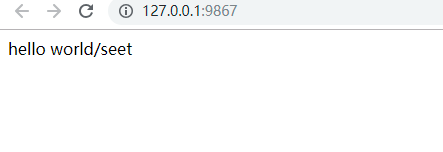
就把你的获取的这个方法url给显示出来
defaults : 视图函数的参数默认值{"nid":1}
@app.route("/index/",strict_slashes= True,endpoint="r_index",defaults={"nid":100}) def index(nid): # 这里必须要接收你的defaults内传递进来的参数 print(nid) #打印这个参数 btn = "<a href='/add_stu'>添加信息</a>" btn = Markup(btn) return render_template("index.html",stu=STUDENT_DICT,btn = btn)
redirect_to : url地址重定向
@app.route("/index/",strict_slashes= True,endpoint="r_index",defaults={"nid":100},redirect_to="/index_to/") # redirect_to 跳转到你的这个后面输入的url def index(nid): # 这里必须要接收你的defaults内传递进来的参数 print(nid) #打印这个参数 btn = "<a href='/add_stu'>添加信息</a>" btn = Markup(btn) return render_template("index.html",stu=STUDENT_DICT,btn = btn) @app.route("/index_to/",strict_slashes=True) #严格匹配模式 def index_one(): return "二狗子"
动态参数路由:
@app.route("/info/<int:nid>",endpoint="r_info") def info(nid): print(nid) print(url_for("r_info",nid=1)) #反向生成的时候也要给一个值 return "动态参数"
