变量以及类型
变量:存储程序运行中的数据,变量有3个要素:变量名、变量类型、变量值。python属于弱类型语言,不需要声明变量类型。
[root@localhost python]# ipython3 In [1]: a=1 //变量名=变量值;在堆内存中的一个区域存了一个值为1,内存分为堆内存和栈内存,栈内存的是引用。指向堆内存中的值。 In [4]: b=88 In [5]: c=a+b In [7]: c Out[7]: 89 In [8]: a Out[8]: 1 In [9]: type(a) Out[9]: int In [10]: type(c) Out[10]: int In [11]: str="hello" In [12]: str Out[12]: 'hello' In [13]: x,y=1,2 In [14]: x Out[14]: 1 In [15]: y Out[15]: 2 In [16]: In [16]: type(str) Out[16]: str
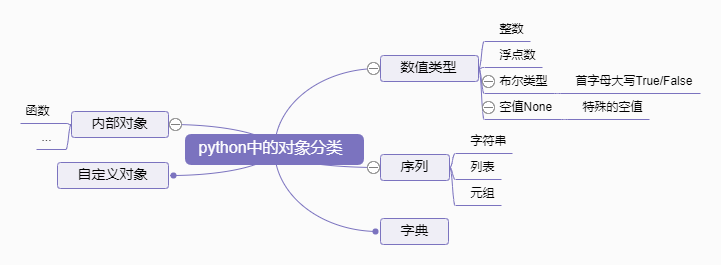
变量类型
标识符:自定义的一些符号和名称,标识符是自己定义的,如变量名、函数名等。
规则:由字母、下划线和数字组成,且不能以数字开头;不能包含一些有特殊意义的符号,如#.&!()等;同时区分大小写。
大小写规则:
驼峰命名法:如小驼峰:userName / userLoginFlag 大驼峰:UserName;类的名字一般首字母大写。
下划线规则:user_name user_login_flag
保留字/关键字:在计算机中有特殊含义的单词。
In [1]: import keyword In [2]: keyword.kwlist Out[2]: ['False', 'None', 'True', 'and', 'as', 'assert', 'break', 'class', 'continue', 'def', 'del', 'elif', 'else', 'except', 'finally', 'for', 'from', 'global', 'if', 'import', 'in', 'is', 'lambda', 'nonlocal', 'not', 'or', 'pass', 'raise', 'return', 'try', 'while', 'with', 'yield'] In [3]:
输出和输出格式
In [4]: print('hello','world','zyj','hello') //输出多个变量 hello world zyj hello In [5]: print(111+222) //输出表达式 333 In [6]: exit [root@localhost python]#vim 3.py 1 a=35 2 print("my age is:%d"%a ) //变量替换 [root@localhost python]# python3 3.py my age is:35 [root@localhost python]#vim 3.py 1 a=35 2 b=10 3 print("my age is:%d"%a+b) [root@localhost python]# python3 3.py Traceback (most recent call last): File "3.py", line 3, in <module> print("my age is:%d"%a+b) //错误行 TypeError: must be str, not int //错误类型 [root@localhost python]#vim 3.py 1 a=35 2 b=10 3 print("my age is:%d"%(a+b)) //表达式需要用括号括起来 [root@localhost python]# python3 3.py my age is:45 [root@localhost python]#vim 3.py 1 a=35 2 b=10 3 my_name="zyj" 4 print("my age is:%d,my name is:%s" %(a+b,my_name)) //如果需要多个变量替换也要加小括号,并且每个变量用逗号隔开,%d代表整数类型替换,%s代表所有的类型变量替换,可以只记住%s [root@localhost python]# python3 3.py my age is:45,my name is:zyj [root@localhost python]# vim 3.py 1 a=35 2 b=10 3 my_name="zyj" 4 print("my age is:%d,my name is:%s" %(a+b,my_name)) 5 money=2 6 print("I have money:%04d" %money)//不够4位前面用0填充 7 w=3.1415926 8 print("w is:%.2f"%w) //输出的数字包含两位小数,如果没有用0填充 9 print("it's:%d%%"%a) //%表示占位符,%%第一个%表示转义符 [root@localhost python]# python3 3.py my age is:45,my name is:zyj I have money:0002 w is:3.14 it's:35%
输入和运算符:注意python2和python3中的一些区别。
输入:用户从电脑输入一些字符,可以让用户输入。
[root@localhost python]# vim 02输入.py 1 #encoding=UTF-8 2 #raw_input()只在python2中有,将输入内容作为字符串。 区别1 3 a=raw_input("请输入你的名字:") // [root@localhost python]# python 02输入.py 请输入你的名字:zyj [root@localhost python]#
[root@localhost python]# vim 02输入.py 4 #input函数在python2和python3中都有 5 #在python2中input函数输入的内容作为表达式,而不是字符串,在python3作为字符串。在python3中取消支持表达式,可以防止某些恶意脚本中包含大量的表达式,提升安全性。区别2 6 a=input("请输入姓名:") 7 print(a) [root@localhost python]# python3 02输入.py 请输入姓名:ZYJ ZYJ [root@localhost python]# python 02输入.py 请输入姓名:11+11 22
[root@localhost python]# vim 02输入.py 6 name=input("请输入姓名:") 7 print(name) 8 age=input("请输入年龄:") 9 print("你输入的姓名:%s,你输入的年龄:%s" %(name,age)) [root@localhost python]# python3 02输入.py 请输入姓名:zyj zyj 请输入年龄:18 [root@localhost python]# vim 02输入.py 6 name=input("请输入姓名:") 7 print(name) 8 age=input("请输入年龄:") 9 print(type(age)) 10 age=age+2 //年龄加2岁 11 print("你输入的姓名:%s,你输入的年龄:%s" %(name,age)) <class 'str'> Traceback (most recent call last): File "02输入.py", line 10, in <module> age=age+2 TypeError: must be str, not int //age为字符串,第10行只能字符串相加 [root@localhost python]# vim 02输入.py 6 name=input("请输入姓名:") 7 print(name) 8 age=input("请输入年龄:") 9 print(type(age)) 10 age=int(age)+2 //转换类型后进行相加 11 print("你输入的姓名:%s,你输入的年龄:%s" %(name,age)) [root@localhost python]# python3 02输入.py 请输入姓名:zyj zyj 请输入年龄:18 <class 'str'> 你输入的姓名:zyj,输入的年龄:20
运算符:
赋值运算符=:把=右边的结果给左边的变量。注意区别与==,==为数学中的等于号;
+-*/%//** 加减乘除取余取整除幂
In [1]: 3**2 Out[1]: 9 In [2]: 3//2 Out[2]: 1 In [3]: 3/2 Out[3]: 1.5 In [4]: 3%2 Out[4]: 1
复合赋值运算符:前后先操作再赋值
+= -= *= /= %= **= //=
In [7]: a=3 In [9]: b=2 In [10]: b+=a //b=b+a In [11]: b Out[11]: 5
In [13]: a=6 In [14]: a*=23-21+34-7 //a=6*(29) In [15]: a Out[15]: 174
条件判断
if<条件判断1>: 执行1 elif<条件判断2>: 执行2 elif<条件判断3>: 执行3 else: 执行4
举例:
[root@localhost python]# vim 04.py 1 age=input("age:") 2 age=int(age) 3 sex=input("sex:") 4 # and or not 5 if age >=18 and sex == "man" : 6 print('you can do it') 7 elif age <18 or sex == "woman" : 8 print("you can't do it") 9 elif not (sex == "man" or sex == "woman"):#sex != "woman" and sex != "man" //<>也是不等于 10 print("人妖") 11 else: 12 pass #以后填充代码,为了保证不出现语法错误,当由else:又没有写其他的时候会出现语法错误 [root@localhost python]# python3 04.py age:19 sex:man you can do it [root@localhost python]# python3 04.py age:14 sex:woman you can't do it [root@localhost python]# vim 04.py [root@localhost python]# python3 04.py age:13 sex:dsfdsf you can't do it [root@localhost python]# python3 04.py age:19 sex:dfdsf 人妖
小技巧:age:dfsdfsdf^H^H^H^H^H^H^H 当键盘输入删除符时会当作字符,此时需要按ctrl+backspace键可以删除。
特殊的真和假
真:非0
假:0 “” None [] () {}
[root@localhost python]# vim 05.py 1 age=int(input('age:')) 2 if age: 3 print("age不为0") 4 else: 5 print("age为0") 6 name="" 7 if name: 8 print("name 不是空字符串") 9 else: 10 print("name 是空字符串") [root@localhost python]# python3 05.py age:0 age为0 name 是空字符串
练习:
1、根据BMI公式(体重除以身高的平方)计算输入人的BMI指数,低于18.5过轻,18.5-25正常,25-28过重,高于32严重肥胖,用if-elif输出打印出来
[root@localhost python]# vim 06.py 1 h=float(input("input your height:")) 2 w=float(input("input your weight:")) 3 print("your height is %.2f,weight is %.2f"%(h,w)) 4 BMI=w/(h**2) 5 if BMI <18.5 : 6 print("you are too light") 7 elif BMI >=18.5 and BMI <25: 8 print("you are nomal") 9 10 elif BMI >=25 and BMI <32: 11 print("you are weight") 12 13 else: 14 print("you are too weight") 15 print("your BMI is:%.2f"%BMI) [root@localhost python]# python3 06.py input your height:1.50 input your weight:48 your height is 1.50,weight is 48.00 you are nomal your BMI is:21.33 [root@localhost python]#
2、情节描述:输入公交卡余额,超过2元就可以上车,如果空位置数量大于0,就可以坐下;
[root@localhost python]# vim 07.py 1 b=float(input("please input your balance:")) 2 s=int(input("please input the number of the empty seat:")) 3 print("your balance is:%.2f,the empty seat is:%d"%(b,s)) 4 if b >= 2 and s > 0: 5 print("please get on and you have a seat") 6 elif b >= 2 and s <= 0: //第一次忘记写:号,第二次调式的时候与预期不一致,忘记写=号,输入0时没有匹配到。边界值测试 7 print("you can get on but there is no seat for you") 8 else: 9 print("sorry you can't get on,because your balance is too short") 10 print("goodluck to you") [root@localhost python]# python3 07.py File "07.py", line 6 elif b >= 2 and s < 0 ^ SyntaxError: invalid syntax [root@localhost python]# vim 07.py 6 //进去后光标在报错行 #运行测试,查看结果 [root@localhost python]# python3 07.py please input your balance:2 #边界值测试 please input the number of the empty seat:0 #边界值 your balance is:2.00,the empty seat is:0 you can get on but there is no seat for you goodluck to you [root@localhost python]# python3 07.py please input your balance:1 #正常值测试 please input the number of the empty seat:3 #正常值 your balance is:1.00,the empty seat is:3 sorry you can't get on,because your balance is too short goodluck to you [root@localhost python]# python3 07.py please input your balance:0 please input the number of the empty seat:0 your balance is:0.00,the empty seat is:0 sorry you can't get on,because your balance is too short goodluck to you [root@localhost python]# python3 07.py please input your balance:10 please input the number of the empty seat:10 your balance is:10.00,the empty seat is:10 please get on and you have a seat goodluck to you [root@localhost python]# python3 07.py please input your balance:-1 #非法值测试 please input the number of the empty seat:-1#非法值测试 your balance is:-1.00,the empty seat is:-1 sorry you can't get on,because your balance is too short goodluck to you [root@localhost python]# python3 07.py please input your balance:1000000000000000000000000 #超大值测试 please input the number of the empty seat:1000000000000000000000000 your balance is:999999999999999983222784.00,the empty seat is:1000000000000000000000000 please get on and you have a seat goodluck to you [root@localhost python]#
使用if嵌套实现,更符合正常逻辑。
[root@localhost python]# python3 07.py 1 m = float(input("money:")) 2 s = int(input("seat:")) 3 if m >= 2: 4 print("you can get on") 5 if s > 0: 6 print("there is a seat for you") 7 else: 8 print("sorry there is no seat for you") 9 else: 10 print("sorry,you can't get on ") [root@localhost python]# python3 08.py #边界值测试 money:2 seat:0 you can get on sorry there is no seat for you [root@localhost python]# python3 08.py #正常值测试 money:2 seat:1 you can get on there is a seat for you [root@localhost python]# python3 08.py #非法值测试 money:-1 seat:-1 sorry,you can't get on [root@localhost python]# python3 08.py #较大的值测试 money:100000000000000 seat:1000000000000000000000 you can get on there is a seat for you
循环:在程序中做相同的事情,需要使用循环。
while循环
while 条件: 条件满足时,做的事情1 条件满足时,做的事情2 条件满足时,做的事情3 .......
举例:
求1加到100的和:
[root@localhost python]# vim 09.py 1 i = 1 2 s = 0 3 while i <= 100: #满足条件的才进入while循环 4 s += i 5 #i++ python不支持这种写法 6 i+=1 #如果i不变的时候,一直为1,则会一直循环,出现死循环。 7 print("从1加到100的和为:%d" %s) [root@localhost python]# python3 09.py 从1加到100的和为:5050
求1-100之间偶数的和,包含1和100。
[root@localhost python]# vim 10.py 1 i=1 2 s=0 3 while i <= 100: 4 even = i % 2 5 if even == 0 : 6 s+=i 7 else: 8 pass 9 i+=1 10 print("1和100之间的偶数和为:%d" %s) [root@localhost python]# python3 10.py 1和100之间的偶数和为:2550
打印下面的图形:
[root@localhost python]# vim 12.py 1 i=1 2 while i <= 5 : 3 print(i*"*") 4 i+=1 [root@localhost python]# python3 12.py * ** *** **** *****
1 i=1 2 while i <= 10 : 3 print(10*"*") 4 i+=1 [root@localhost python]# python3 12.py ********** ********** ********** ********** ********** ********** ********** ********** ********** **********
while循环嵌套
while 条件1: 条件1满足时,做的事情1 条件1满足时,做的事情2 条件1满足时,做的事情3 ....... while 条件2: 条件2满足时,做的事情1 条件2满足时,做的事情2 条件2满足时,做的事情3 ......
举例:用星号打印矩形
版本1:按照逻辑初次编写
1 x=1 #x为矩形长 2 y=1 #y为矩形宽 3 4 while y <= 10 :#输出10行 5 while x <= 10 :#在一行中输出10个* 6 print("*") 7 x += 1 8 y += 1 9 print("pass") [root@localhost python]# python3 11.py * * * * * * * * * * pass #输出结果不符合预期
版本2:解决输出一行时,进行了换行的问题。
1 x=1 #x为矩形长 2 y=1 #y为矩形宽 3 4 while y <= 10 :#输出10行 5 while x <= 10 :#在一行中输出10个* 6 print("*",end="")#print函数默认输出后就会换行,如果不换行,end="" 7 x += 1 8 y += 1 9 print("pass")
[root@localhost python]# python3 11.py
**********pass #输出不符合预期
版本3:解决只打印了一行星号的问题。
1 x=1 #x为矩形长 2 y=1 #y为矩形宽 3 4 while y <= 10 :#输出10行 5 x=1 #每行执行完成后,x为11,若不重新赋值,则第二次大循环的时候不会进到小循环里面,因此只会输出一行*,因此这里需要重新赋值。 6 while x <= 10 :#在一行中输出10个* 7 print("*",end="")#print函数默认输出后就会换行,如果不换行,end="" 8 x += 1 9 y += 1 10 print("pass") [root@localhost python]# python3 11.py ****************************************************************************************************pass #还是不满足预期
版本4:解决多行星号没有换行的问题
1 x=1 #x为矩形长 2 y=1 #y为矩形宽 3 4 while y <= 10 :#输出10行 5 x=1 #每行执行完成后,x为11,若不重新赋值,则第二次大循环的时候不会进到小循环里面,因此只会输出一行* 6 while x <= 10 :#在一行中输出10个* 7 print("*",end="")#print函数默认输出后就会换行,如果不换行,end="" 8 x += 1 9 print("")#每行结束后输出一个换行,print函数默认会输出换行 10 y += 1 11 print("pass") [root@localhost python]# python3 11.py ********** ********** ********** ********** ********** ********** ********** ********** ********** ********** pass
说明:查看python中函数的帮助文档:
[root@localhost ~]# ipython3 In [1]: help(print) #查看print()函数的帮助文档。 Help on built-in function print in module builtins: print(...) print(value, ..., sep=' ', end=' ', file=sys.stdout, flush=False) #默认输出后由换行符。 Prints the values to a stream, or to sys.stdout by default. Optional keyword arguments: file: a file-like object (stream); defaults to the current sys.stdout. sep: string inserted between values, default a space. end: string appended after the last value, default a newline. flush: whether to forcibly flush the stream. (END)
练习2:打印九九乘法表
[root@localhost python]# vim 13.py 1 x = 1 #行数 2 while x <= 9 : #一共循环9次,才能打印9行,每行打印的列数和行号一样 3 y = 1 #代表列数 4 while y <= x: 5 print("%d*%d=%d "%(y,x,y*x),end="") 6 y+=1 7 print("") 8 x+=1 [root@localhost python]# python3 13.py 1*1=1 1*2=2 2*2=4 1*3=3 2*3=6 3*3=9 1*4=4 2*4=8 3*4=12 4*4=16 1*5=5 2*5=10 3*5=15 4*5=20 5*5=25 1*6=6 2*6=12 3*6=18 4*6=24 5*6=30 6*6=36 1*7=7 2*7=14 3*7=21 4*7=28 5*7=35 6*7=42 7*7=49 1*8=8 2*8=16 3*8=24 4*8=32 5*8=40 6*8=48 7*8=56 8*8=64 1*9=9 2*9=18 3*9=27 4*9=36 5*9=45 6*9=54 7*9=63 8*9=72 9*9=81
循环要点:
1、循环次数:while中循环次数由条件决定;如九九乘法表中循环9次;
2、循环体:在循环过程中做什么,如打印一行九九乘法表;
3、变量怎么变化:如变量增加或者递减
break和continue
在循环中,break语句可以提前退出循环;
1 age = int(input("please input your age:")) 2 i = 1 3 while True : 4 if i == age: 5 print("your age is %d" %i) 6 break #不知道要循环几次的时候,可以使用break防止死循环。 7 else: 8 print("wrong") 9 i += 1 [root@localhost python]# python3 14.py please input your age:3 wrong wrong your age is 3
在循环过程中,continue语句,可以跳过当前的这次循环,直接开始下一次循环。终止当前的循环,开启下次循环。
1 i = 0 2 while i < 10 : 3 i += 1 4 if i % 2 == 0: 5 print("%d is enev" %i) #i是偶数的时候打印 6 continue 7 print("i is %d" %i) #i不是偶数的时候打印 8 else: 9 print("else 表示不满足条件时调试的代码,这时i为%d" %i) #不满足条件的时候执行else,注意while和这里的else是一个整体,这种方式不常用。 10 print("结束") [root@localhost python]# python3 15.py i is 1 2 is enev i is 3 4 is enev i is 5 6 is enev i is 7 8 is enev i is 9 10 is enev else 表示不满足条件时调试的代码,这时i为10 结束
练习:使用*打印倒等边三角形,并且行号由用户输入。
1 i = int(input("请输入行数:")) 2 3 a = 0 4 while a < i :#假设i=4,打印4行, 5 b = 0 #定义空格 6 while b < a :#打印当前行前面的空格,第一行不打印空格,第二行打印1个,后面增加一个; 7 print(" ",end="") 8 b += 1 9 c = i-a 10 while c > 0 : #打印星号,第一行打印4个*,后面的行减1 11 print("*",end=" ")#打印*不换行,后面跟一个空格 12 c -= 1 13 print("") 14 a += 1
[root@localhost python]# python3 16.py 请输入行数:3 * * * * * * [root@localhost python]# python3 16.py 请输入行数:4 * * * * * * * * * * [root@localhost python]# python3 16.py 请输入行数:5 * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * [root@localhost python]# [root@localhost python]# python3 16.py 请输入行数:10 * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * [root@localhost python]#
1 i = int(input("请输入行数:")) 2 a = 1 #控制行数,打印i行,初始值根据规律选择0或者1都可以。 3 while a <= i : 4 b = i - a #定义空格 5 while b > 0 : 6 print(" ",end="") 7 b -= 1 8 c = 0 #定义星号 9 while c < a : 10 print("*",end=" ") 11 c += 1 12 a += 1 13 print("") [root@localhost python]# python3 17.py 请输入行数:4 * * * * * * * * * *
for循环
for 临时变量 in 集合或字符串等: 循环满足条件时执行的代码 else: 循环不满足条件时执行的代码
举例1:
1 for i in "abcdefg": 2 print(i) 3 else: 4 print("没有内容") [root@localhost python]# python3 19.py a b c d e f g 没有内容 [root@localhost python]#
举例2:
7 for i in range(1,10): 8 print(i) 9 else: 10 print("没有内容") [root@localhost python]# python3 19.py 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 没有内容 [root@localhost python]#