动手动脑1:
请运行以下示例代码StringPool.java,查看其输出结果。如何解释这样的输出结果?从中你能总结出什么?

在Java中,内容相同的字串常量(“Hello”)只保存一份以节约内存,所以s0,s1,s2实际上引用的是同一个对象。编译器在编译s2一句时,会去掉“+”号,直接把两个字串连接起来得一个字串(“Hello”)。这种优化工作由Java编译器自动完成。当直接使用new关键字创建字符串对象时,虽然值一致(都是“Hello”),但仍然是两个独立的对象。==在此比较是它们的地址,因为开辟空间,初始化的不同,所以地址不同,所以结果是False;

从上述代码中可得到:
给字串变量赋值意味着:两个变量(s1,s2)现在引用同一个字符串对象“a”!
String对象的内容是只读的,使用“+”修改s1变量的值,实际上是得到了一个新的字符串对象,其内容为“ab”,它与原先s1所引用的对象”a”无关,所以,s1==s2返回false;
代码中的“ab”字符串是一个常量,它所引用的字符串与s1所引用的“ab”对象无关。
String.equals()方法可以比较两个字符串的内容。
动手动脑 2::
String.equal() jdk源代码的源代码如下:

使用说明:
用于判断两个字符串的值是否相等
阅读笔记:
方法体实质上是先比较两个字符串的长度是否相等,然后,在将字符串转化为字符数组,通过比较对应位置的字符是否相同,进而来判断两个字符串值是否相同。
该方法首先判断this == anObject ?,也就是说判断要比较的对象和当前对象是不是同一个对象,如果是直接返回 true,如不是再继续比较,然后在判断
anObject 是不是 String类型的,如果不是,直接返回 false,如果是他还是先比较了两个数组的长度,不一样直接返回 false,一样再逐一比较字符数组的值。
动手动脑 3:
每当一个对象创建后,Java虚拟机会给这个对象分配一个引用自身的指针,这个指针的名字就是 this。因此,this只能在类中的非静态方法中使用,静态方法和静态的代码块中绝对不能出现this的用法。因为这里需要实现级联调用特性,所以将方法返回值设为对象类型(以该类作类型),即方法本身可再调用方法。
String.concat()函数
将字符串与字符串连接起来。创建新的字符数组,新的length=两字符串长度之和,将长度,首元赋给字符数组
String.trim()函数
去掉字符串首尾的空格,为防止不必要的空格产生的错误,该方法返回字符串对象的一个副本。
String.toUpperCase()函数
string.toUpperCase()为将字符串string中字符变为大写。
所以实现级调的实例如下:
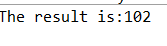
1 package String; 2 public class MyCounter { 3 int num; 4 public MyCounter increase(int j)//public是对别的类公开,该方法需要返回MyCounter对象,所以应用this指针,下面同理 5 { 6 num+=j; 7 return this; 8 9 } 10 public MyCounter decrease(int n) 11 { 12 num-=n; 13 return this; 14 } 15 MyCounter(int k) 16 { 17 num=k; 18 } 19 public static void main(String[] args) { 20 MyCounter counter1=new MyCounter(1); 21 MyCounter counter2=counter1.increase(100).decrease(2).increase(3); 22 System.out.println("The result is:"+counter2.num); 23 } 24 }
执行结果:
Java中String类的length()、charAt()、getChars()、replace()、toUpperCase()、toLowerCase()、trim()、toCharArray()使用说明
在Java语言中String类有很多以处理函数,例如length()、charAt()、getChars()、replace()、toUpperCase()、toLowerCase()、trim()、toCharArray()等,用法如下:
1 string.length()是用来求字符串的长度,返回值为字符串的长度。
2 string.charAt()为取该字符串某个位置的字符,从0开始,例如string.charAt(0)就会返回该字符串的第一个字符。
3 string.getChars()为将这个字符串中的字符复制到目标字符数组。
4 string.replace()为将原string 中的元素或子串替换。返回替换后的string。
5 string.toUpperCase()为将字符串string中字符变为大写。
6 string.toLowerCase()为将字符串string中字符变为小写。
7 string.trim()为去除字符串的头为空格。
8 string.toCharArray()为将字符串转换为字符数组。
举个例子:
1 public class Example 2 3 { 4 public static void main(String args[]) 5 { 6 String s1=new String("you are a student"); 7 String s2=new String("HOW ARE YOU"); 8 String s3=new String(" Hello "); 9 10 //string.length()求长度 11 System.out.println("length of string is:"+s1.length()); 12 13 //string.charAt()取指定位置字符 14 System.out.println("the first char of string::"+s1.charAt(0)); 15 16 //string.getChars()为将这个字符串中的字符复制到目标字符数组。 17 char[] c = new char[s1.length()]; 18 s1.getChars(0, s1.length(), c, 0); 19 System.out.print("输出数组:"); 20 for(int i=0;i<s1.length()-1; i++) 21 { 22 System.out.print(" "+c[i]); 23 } 24 25 //string.replace()为将原string 中的元素或子串替换。返回替换后的string。 26 System.out.println(" s1替换为s2后是:"+s1.replace(s1, s2)); 27 28 //string.toUpperCase()为将字符串string中字符变为大写。 29 System.out.println("s1变为大写后为:"+s1.toUpperCase()); 30 31 //string.toLowerCase()为将字符串string中字符变为小写。 32 System.out.println("s2变为小写后为:"+s2.toLowerCase()); 33 34 //string.trim()为去除字符串的头为空格。 35 System.out.println("s1变为大写后为:"+s3.trim()); 36 37 //string.toCharArray()为将字符串转换为字符数组 38 char a[]=s1.toCharArray(); 39 System.out.println("转换为数组a后a[1]= "+a[1]); 40 41 } 42 }
结果截图:

各方法的源码如下:
1.String.length()
1 public int length() { 2 return value.length; 3 }
2.String.charAt()
1 public char charAt(int index) { 2 if ((index < 0) || (index >= value.length)) { 3 throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(index); 4 } 5 return value[index]; 6 }
3.String.getChars()
1 void getChars(char dst[], int dstBegin) { 2 System.arraycopy(value, 0, dst, dstBegin, value.length); 3 }
1.//将value从srcBegin到srcEnd的字符串复制到dst的dstBegin处 2.public void getChars(int srcBegin, int srcEnd, char[] dst, int dstBegin) 3.{ 4. if (srcBegin < 0) 5. throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(srcBegin); 6. if ((srcEnd < 0) || (srcEnd > count)) 7. throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(srcEnd); 8. if (srcBegin > srcEnd) 9. throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException("srcBegin > srcEnd"); 10. //将value从srcBegin起的(srcEnd-srcBegin)个字符复制到dst的dstBegin位置处 11. System.arraycopy(value, srcBegin, dst, dstBegin, srcEnd - srcBegin); }
4.String.replace()方法
- replace 的参数是 char 和 CharSequence,即可以支持字符的替换, 也支持字符串的替换, 把源字符串中的某一字符或字符串全部换成指定的字符或字符串
1.public AbstractStringBuilder replace(int start, int end, String str) { 2. if (start < 0) 3. throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(start); 4. if (start > count) 5. throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException("start > length()"); 6. if (start > end) 7. throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException("start > end"); 8. if (end > count) 9. end = count; 10. int len = str.length(); 11. //计算新长度 12. int newCount = count + len - (end - start); 13. //扩容 14. ensureCapacityInternal(newCount); 15. //复制,实际上是删除start到end间的字符串 16. System.arraycopy(value, end, value, start + len, count - end); 17. //复制 18. str.getChars(value, start); 19. //更新长度 20. count = newCount; 21. return this; 22.}
1 public String replace(char oldChar, char newChar) { 2 if (oldChar != newChar) { 3 int len = value.length; 4 int i = -1; 5 char[] val = value; /* avoid getfield opcode */ 6 7 while (++i < len) { 8 if (val[i] == oldChar) { 9 break; 10 } 11 } 12 if (i < len) { 13 char buf[] = new char[len]; 14 for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) { 15 buf[j] = val[j]; 16 } 17 while (i < len) { 18 char c = val[i]; 19 buf[i] = (c == oldChar) ? newChar : c; 20 i++; 21 } 22 return new String(buf, true); 23 } 24 } 25 return this; 26 }
- 5. String.toUpperCase()
1 public String toUpperCase() { 2 return toUpperCase(Locale.getDefault()); 3 } 4 public String toUpperCase(Locale locale) { 5 if (locale == null) { 6 throw new NullPointerException(); 7 } 8 9 int firstLower; 10 final int len = value.length; 11 12 /* Now check if there are any characters that need to be changed. */ 13 scan: { 14 for (firstLower = 0 ; firstLower < len; ) { 15 int c = (int)value[firstLower]; 16 int srcCount; 17 if ((c >= Character.MIN_HIGH_SURROGATE) 18 && (c <= Character.MAX_HIGH_SURROGATE)) { 19 c = codePointAt(firstLower); 20 srcCount = Character.charCount(c); 21 } else { 22 srcCount = 1; 23 } 24 int upperCaseChar = Character.toUpperCaseEx(c); 25 if ((upperCaseChar == Character.ERROR) 26 || (c != upperCaseChar)) { 27 break scan; 28 } 29 firstLower += srcCount; 30 } 31 return this; 32 } 33 34 /* result may grow, so i+resultOffset is the write location in result */ 35 int resultOffset = 0; 36 char[] result = new char[len]; /* may grow */ 37 38 /* Just copy the first few upperCase characters. */ 39 System.arraycopy(value, 0, result, 0, firstLower); 40 41 String lang = locale.getLanguage(); 42 boolean localeDependent = 43 (lang == "tr" || lang == "az" || lang == "lt"); 44 char[] upperCharArray; 45 int upperChar; 46 int srcChar; 47 int srcCount; 48 for (int i = firstLower; i < len; i += srcCount) { 49 srcChar = (int)value[i]; 50 if ((char)srcChar >= Character.MIN_HIGH_SURROGATE && 51 (char)srcChar <= Character.MAX_HIGH_SURROGATE) { 52 srcChar = codePointAt(i); 53 srcCount = Character.charCount(srcChar); 54 } else { 55 srcCount = 1; 56 } 57 if (localeDependent) { 58 upperChar = ConditionalSpecialCasing.toUpperCaseEx(this, i, locale); 59 } else { 60 upperChar = Character.toUpperCaseEx(srcChar); 61 } 62 if ((upperChar == Character.ERROR) 63 || (upperChar >= Character.MIN_SUPPLEMENTARY_CODE_POINT)) { 64 if (upperChar == Character.ERROR) { 65 if (localeDependent) { 66 upperCharArray = 67 ConditionalSpecialCasing.toUpperCaseCharArray(this, i, locale); 68 } else { 69 upperCharArray = Character.toUpperCaseCharArray(srcChar); 70 } 71 } else if (srcCount == 2) { 72 resultOffset += Character.toChars(upperChar, result, i + resultOffset) - srcCount; 73 continue; 74 } else { 75 upperCharArray = Character.toChars(upperChar); 76 } 77 78 /* Grow result if needed */ 79 int mapLen = upperCharArray.length; 80 if (mapLen > srcCount) { 81 char[] result2 = new char[result.length + mapLen - srcCount]; 82 System.arraycopy(result, 0, result2, 0, i + resultOffset); 83 result = result2; 84 } 85 for (int x = 0; x < mapLen; ++x) { 86 result[i + resultOffset + x] = upperCharArray[x]; 87 } 88 resultOffset += (mapLen - srcCount); 89 } else { 90 result[i + resultOffset] = (char)upperChar; 91 } 92 } 93 return new String(result, 0, len + resultOffset); 94 }
6.String.toLowerCase()
1 public String toLowerCase() { 2 return toLowerCase(Locale.getDefault()); 3 } 4 5 public String toLowerCase(Locale locale) { 6 if (locale == null) { 7 throw new NullPointerException(); 8 } 9 10 int firstUpper; 11 final int len = value.length; 12 13 /* Now check if there are any characters that need to be changed. */ 14 scan: { 15 for (firstUpper = 0 ; firstUpper < len; ) { 16 char c = value[firstUpper]; 17 if ((c >= Character.MIN_HIGH_SURROGATE) 18 && (c <= Character.MAX_HIGH_SURROGATE)) { 19 int supplChar = codePointAt(firstUpper); 20 if (supplChar != Character.toLowerCase(supplChar)) { 21 break scan; 22 } 23 firstUpper += Character.charCount(supplChar); 24 } else { 25 if (c != Character.toLowerCase(c)) { 26 break scan; 27 } 28 firstUpper++; 29 } 30 } 31 return this; 32 } 33 34 char[] result = new char[len]; 35 int resultOffset = 0; /* result may grow, so i+resultOffset 36 * is the write location in result */ 37 38 /* Just copy the first few lowerCase characters. */ 39 System.arraycopy(value, 0, result, 0, firstUpper); 40 41 String lang = locale.getLanguage(); 42 boolean localeDependent = 43 (lang == "tr" || lang == "az" || lang == "lt"); 44 char[] lowerCharArray; 45 int lowerChar; 46 int srcChar; 47 int srcCount; 48 for (int i = firstUpper; i < len; i += srcCount) { 49 srcChar = (int)value[i]; 50 if ((char)srcChar >= Character.MIN_HIGH_SURROGATE 51 && (char)srcChar <= Character.MAX_HIGH_SURROGATE) { 52 srcChar = codePointAt(i); 53 srcCount = Character.charCount(srcChar); 54 } else { 55 srcCount = 1; 56 } 57 if (localeDependent || 58 srcChar == 'u03A3' || // GREEK CAPITAL LETTER SIGMA 59 srcChar == 'u0130') { // LATIN CAPITAL LETTER I WITH DOT ABOVE 60 lowerChar = ConditionalSpecialCasing.toLowerCaseEx(this, i, locale); 61 } else { 62 lowerChar = Character.toLowerCase(srcChar); 63 } 64 if ((lowerChar == Character.ERROR) 65 || (lowerChar >= Character.MIN_SUPPLEMENTARY_CODE_POINT)) { 66 if (lowerChar == Character.ERROR) { 67 lowerCharArray = 68 ConditionalSpecialCasing.toLowerCaseCharArray(this, i, locale); 69 } else if (srcCount == 2) { 70 resultOffset += Character.toChars(lowerChar, result, i + resultOffset) - srcCount; 71 continue; 72 } else { 73 lowerCharArray = Character.toChars(lowerChar); 74 } 75 76 /* Grow result if needed */ 77 int mapLen = lowerCharArray.length; 78 if (mapLen > srcCount) { 79 char[] result2 = new char[result.length + mapLen - srcCount]; 80 System.arraycopy(result, 0, result2, 0, i + resultOffset); 81 result = result2; 82 } 83 for (int x = 0; x < mapLen; ++x) { 84 result[i + resultOffset + x] = lowerCharArray[x]; 85 } 86 resultOffset += (mapLen - srcCount); 87 } else { 88 result[i + resultOffset] = (char)lowerChar; 89 } 90 } 91 return new String(result, 0, len + resultOffset); 92 }
7.String.trim()
1 public String trim() { 2 int len = value.length; 3 int st = 0; 4 char[] val = value; /* avoid getfield opcode */ 5 6 while ((st < len) && (val[st] <= ' ')) { 7 st++; 8 } 9 while ((st < len) && (val[len - 1] <= ' ')) { 10 len--; 11 } 12 return ((st > 0) || (len < value.length)) ? substring(st, len) : this; 13 }
8.String.toCharArray()
1 public char[] toCharArray() { 2 // Cannot use Arrays.copyOf because of class initialization order issues 3 char result[] = new char[value.length]; 4 System.arraycopy(value, 0, result, 0, value.length); 5 return result; 6 }
9.String.concat()函数
创建新的字符数组,新的length=两字符串长度之和,将长度,首元赋给字符数组
1 public String concat(String str) { 2 int otherLen = str.length(); 3 if (otherLen == 0) { 4 return this; 5 } 6 int len = value.length; 7 char buf[] = Arrays.copyOf(value, len + otherLen); 8 str.getChars(buf, len); 9 return new String(buf, true); 10 }