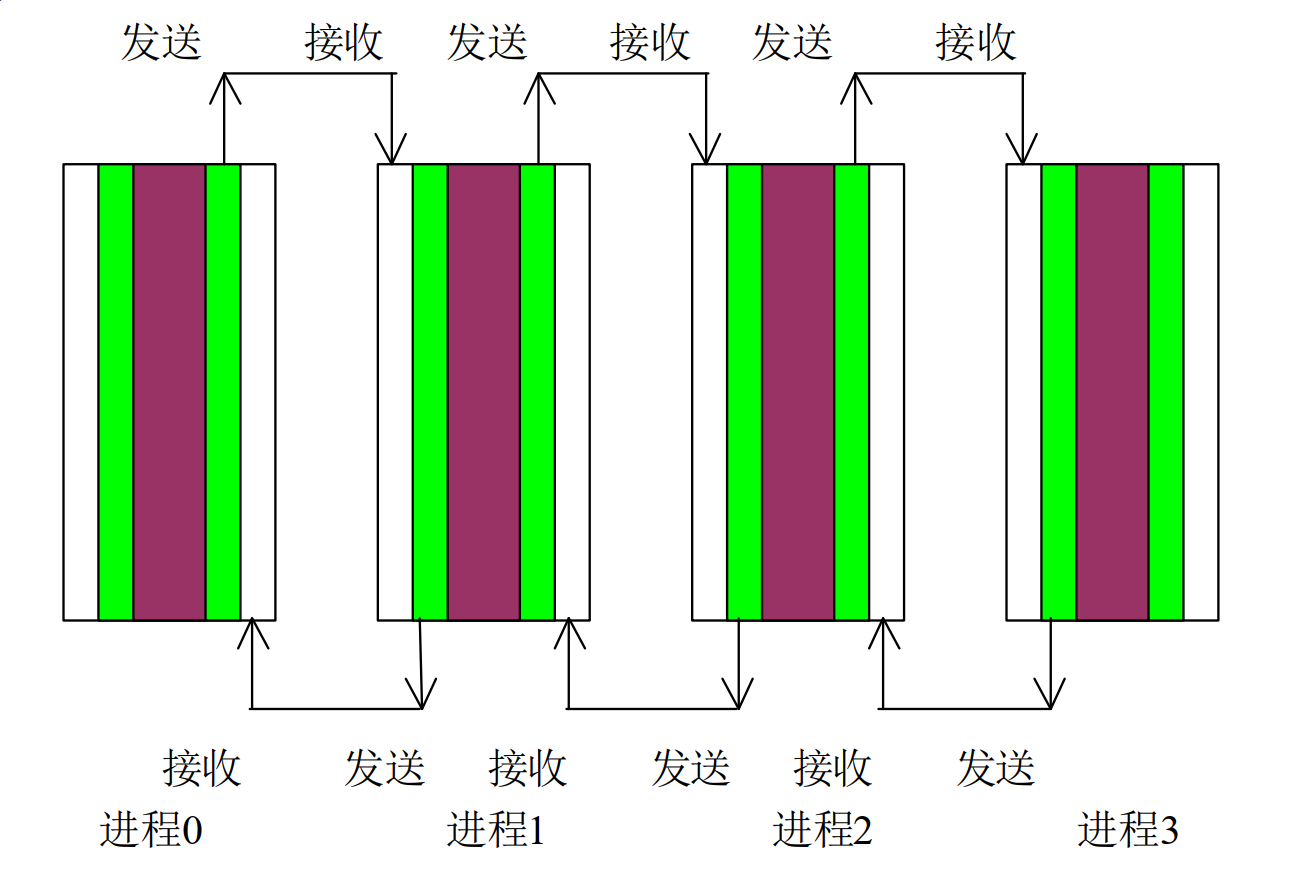
一、Jacobi迭代
#include<stdio.h>
#include<mpi.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define totalsize 16
#define mysize totalsize / 4
#define steps 10
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
int rank, size, i, j, begin_col, end_col;
//除分块大小外,还包括左右两边各一列
float a[totalsize][mysize + 2], b[totalsize][mysize + 2];
float temp[totalsize];//临时数组
MPI_Status status;
MPI_Init(&argc, &argv);
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &size);
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &rank);
printf("Process %d of %d is alive
", rank, size);
//数组初始化
for (i = 0; i < totalsize; i++)
for (j = 0; j < mysize + 2; j++)
a[i][j] = 0;
if (rank == 0)
{
for (i = 0; i < totalsize; i++)
a[i][1] = 8.0;
}
if (rank == 3)
{
for (i = 0; i < totalsize; i++)
a[i][mysize] = 8.0;
}
for (i = 1; i < mysize + 1; i++)
{
a[0][i] = 8.0;
a[totalsize - 1][i] = 8.0;
}
//Jacobi 迭代
for (int n = 1; n <= steps; n++)
{
//从右边的邻居得到数据
if (rank < 3)
{
MPI_Recv(&temp[0], totalsize, MPI_FLOAT, rank + 1, 10, MPI_COMM_WORLD, &status);
for (i = 0; i < totalsize; i++)
a[i][mysize + 1] = temp[i];
}
//向左侧的邻居发送数据
if (rank > 0)
{
for (i = 0; i < totalsize; i++)
temp[i] = a[i][1];
MPI_Send(&temp[0], totalsize, MPI_FLOAT, rank - 1, 10, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
}
//向右侧的邻居发送数据
if (rank < 3)
{
for (i = 0; i < totalsize; i++)
temp[i] = a[i][mysize];
MPI_Send(&temp[0], totalsize, MPI_FLOAT, rank + 1, 10, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
}
//从左侧的邻居得到数据
if (rank > 0)
{
MPI_Recv(&temp[0], totalsize, MPI_FLOAT, rank - 1, 10, MPI_COMM_WORLD, &status);
for (i = 0; i < totalsize; i++)
a[i][0] = temp[i];
}
begin_col = 1;
end_col = mysize;
if (rank == 0) begin_col = 2;
if (rank == 3) end_col = mysize - 1;
for (i = 1; i < totalsize - 1; i++)
for (j = begin_col; j <= end_col; j++)
b[i][j] = 0.25 * (a[i][j + 1] + a[i][j - 1] + a[i + 1][j] + a[i - 1][j]);
for (i = 1; i < totalsize - 1; i++)
for (j = begin_col; j <= end_col; j++)
a[i][j] = b[i][j];
}
MPI_Barrier(MPI_COMM_WORLD);
printf("Process %d:
", rank);
for (i = 0; i < totalsize; i++)
{
for (j = 1; j <= mysize; j++)
printf("%.2fP%d ", a[i][j], rank);
printf("
");
}
MPI_Finalize();
return 0;
}
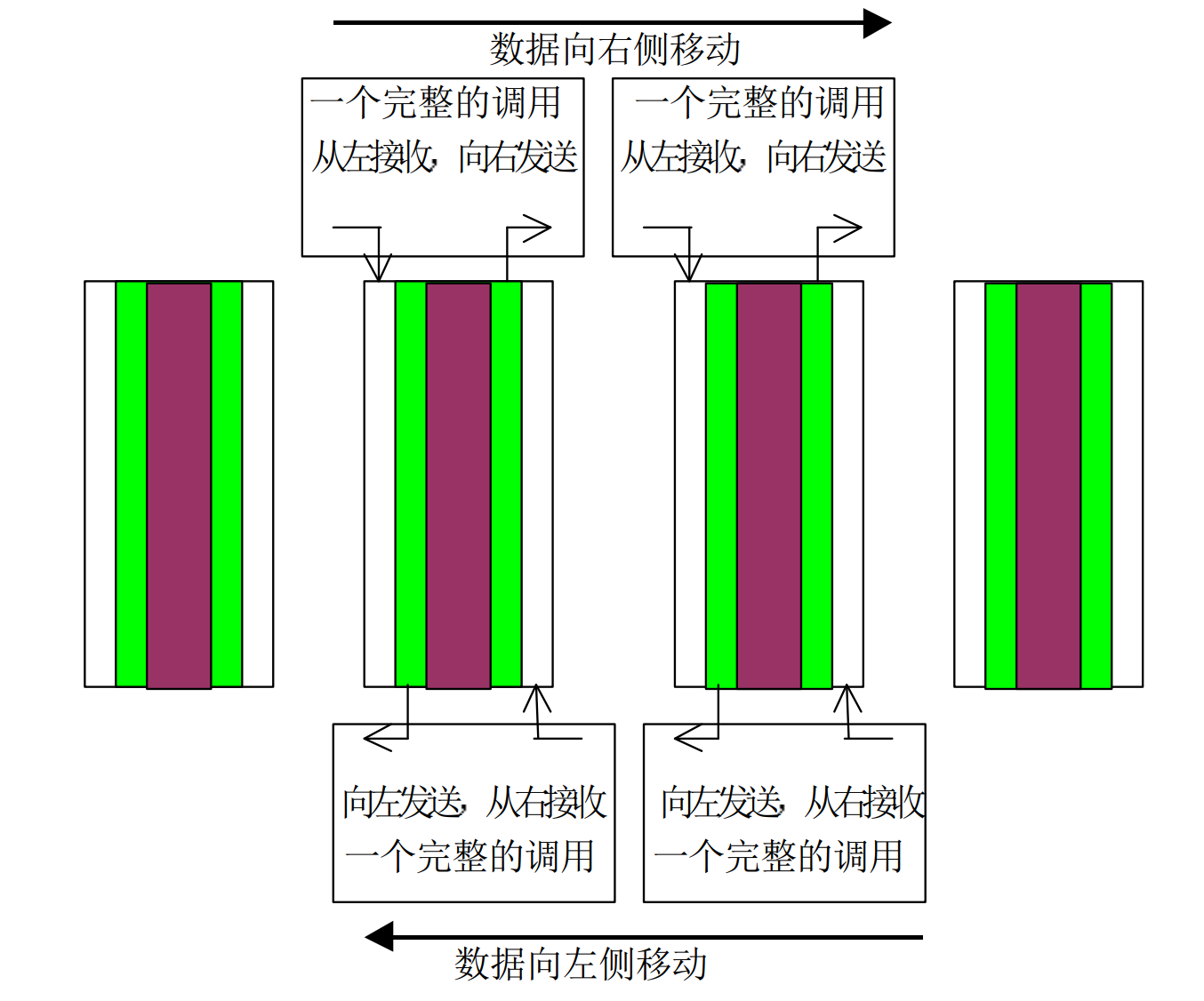
二、用捆绑发送接收实现Jacobi 迭代
#include<stdio.h>
#include<mpi.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define totalsize 16
#define mysize totalsize / 4
#define steps 10
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
int rank, size, i, j, begin_col, end_col;
//除分块大小外,还包括左右两边各一列
float a[totalsize][mysize + 2], b[totalsize][mysize + 2];
float temp[totalsize],temp1[totalsize];//临时数组
MPI_Status status;
MPI_Init(&argc, &argv);
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &size);
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &rank);
printf("Process %d of %d is alive
", rank, size);
//数组初始化
for (i = 0; i < totalsize; i++)
for (j = 0; j < mysize + 2; j++)
a[i][j] = 0;
if (rank == 0)
{
for (i = 0; i < totalsize; i++)
a[i][1] = 8.0;
}
if (rank == 3)
{
for (i = 0; i < totalsize; i++)
a[i][mysize] = 8.0;
}
for (i = 1; i < mysize + 1; i++)
{
a[0][i] = 8.0;
a[totalsize - 1][i] = 8.0;
}
//Jacobi 迭代
for (int n = 1; n <= steps; n++)
{
//从左向右平移数据
if (rank == 0)
{
for (i = 0; i < totalsize; i++)
temp[i] = a[i][mysize];
MPI_Send(&temp[0], totalsize, MPI_FLOAT, rank + 1, 10, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
}
else if (rank == 3)
{
MPI_Recv(&temp[0], totalsize, MPI_FLOAT, rank - 1, 10, MPI_COMM_WORLD, &status);
for (i = 0; i < totalsize; i++)
a[i][1] = temp[i];
}
else
{
for (i = 0; i < totalsize; i++)
temp[i] = a[i][1];
MPI_Sendrecv(&temp[0], totalsize, MPI_FLOAT, rank - 1, 10, &temp1[0], totalsize, MPI_FLOAT,
rank + 1, 10, MPI_COMM_WORLD, &status);
for (i = 0; i < totalsize; i++)
a[i][1] = temp1[i];
}
//从右向左平移数据
if (rank == 0)
{
MPI_Recv(&temp[0], totalsize, MPI_FLOAT, rank + 1, 10, MPI_COMM_WORLD, &status);
for (i = 0; i < totalsize; i++)
a[i][mysize] = temp[i];
}
else if (rank == 3)
{
for (i = 0; i < totalsize; i++)
temp[i] = a[i][1];
MPI_Send(&temp, totalsize, MPI_FLOAT, rank - 1, 10, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
}
else
{
for (i = 0; i < totalsize; i++)
temp[i] = a[i][1];
MPI_Sendrecv(&temp[0], totalsize, MPI_FLOAT, rank + 1, 10, &temp1[0], totalsize, MPI_FLOAT,
rank - 1, 10, MPI_COMM_WORLD, &status);
for (i = 0; i < totalsize; i++)
a[i][mysize] = temp1[i];
}
begin_col = 1;
end_col = mysize;
if (rank == 0) begin_col = 2;
if (rank == 3) end_col = mysize - 1;
for (i = 1; i < totalsize - 1; i++)
for (j = begin_col; j <= end_col; j++)
b[i][j] = 0.25 * (a[i][j + 1] + a[i][j - 1] + a[i + 1][j] + a[i - 1][j]);
for (i = 1; i < totalsize - 1; i++)
for (j = begin_col; j <= end_col; j++)
a[i][j] = b[i][j];
}
MPI_Barrier(MPI_COMM_WORLD);
printf("Process %d:
", rank);
for (i = 0; i < totalsize; i++)
{
for (j = 1; j <= mysize; j++)
printf("%.2fP%d ", a[i][j], rank);
printf("
");
}
MPI_Finalize();
return 0;
}
矩阵乘
#include <stdio.h>
#include "mpi.h"
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <time.h>
#define SIZE 5
//生成随机矩阵
int** generate_matrix(int size)
{
int num = 0, m;
int** matrix;
matrix = (int**)malloc(sizeof(int*) * size);
for (m = 0; m < size; m++)
matrix[m] = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * size);
int i, j;
srand(time(NULL) + rand());
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < size; j++)
{
matrix[i][j] = rand() % 20;
}
}
return matrix;
}
//输出矩阵
void print_matrx(int** a, int size)
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < size; j++)
{
printf("%d ", a[i][j]);
}
printf("
");
}
printf("
");
}
//矩阵相乘([参考](https://blog.csdn.net/qq_35614920/article/details/80570839))
int* Multiplication(int** a, int b[], int size)
{
int* result;
result = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * size);
int i, m, n, sum = 0;
for (m = 0; m < size; m++)
{
for (n = 0; n < size; n++)
{
sum += a[n][m] * b[n];
}
result[m] = sum;
sum = 0;
}
return result;
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
int size, rank, dest;
MPI_Comm comm = MPI_COMM_WORLD;
MPI_Status status;
MPI_Init(&argc, &argv);
MPI_Comm_size(comm, &size);
MPI_Comm_rank(comm, &rank);
int** matrix1;
int** matrix2;
int send_buff[SIZE* SIZE];
matrix1 = generate_matrix(size);
matrix2 = generate_matrix(size);
if (rank == 0)
{
printf("matrix1 is :
");
print_matrx((int**)matrix1, size);
printf("matrix2 is :
");
print_matrx((int**)matrix2, size);
int j, k, tmp = 0;
for (j = 0; j < size; j++)
for (k = 0; k < size; k++)
{
send_buff[tmp] = matrix1[j][k];
tmp++;
}
}
int rbuf[SIZE];
int* result;
result = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * size);
//分发列
MPI_Scatter(send_buff, size, MPI_INT, rbuf, size, MPI_INT, 0, comm);
result = Multiplication((int**)matrix2, rbuf, size);
MPI_Barrier(comm);//等待所有进程计算结束
int* recv_buff;
recv_buff = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * size * size);
MPI_Barrier(comm);
MPI_Gather(result, size, MPI_INT, recv_buff, size, MPI_INT, 0, comm);//收集各列数据
//根进程进行输出
if (rank == 0)
{
printf("
result is :
");
int m, n, tmp = 0;
for (m = 0; m < size; m++)
{
for (n = 0; n < size; n++)
{
printf("%d ", recv_buff[tmp]);
tmp++;
}
printf("
");
}
printf("
");
}
MPI_Finalize();
return 0;
}

