一:环境
1、服务端:Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server release 6.4 (Santiago)
2、客户端:windows7旗舰版64位
3、同步对象:测试数据
4、Rsync介绍:rsync是linux系统下的数据镜像备份工具。使用快速增量备份工具Remote Sync可以远程同步,支持本地复制,或者与其他SSH、rsync主机同步。是一款非常理想的数据同步工具
Rsync的好处:支持增量备份,对于很多大的数据文件来说用rsync是一个很理想的工具,既能节省磁盘空间还能提高备份相率
5、注意事项:此种同步方式仅限rsync的daemon模式
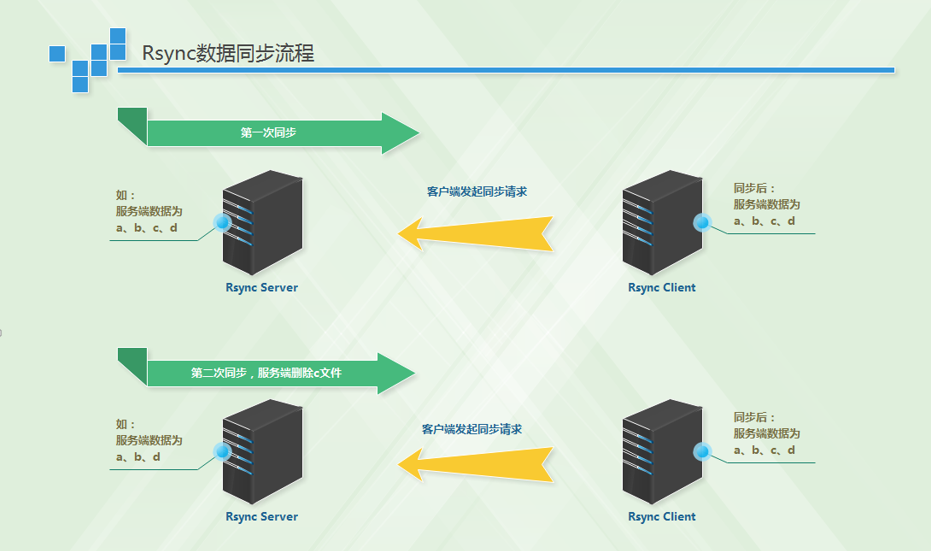
二:无差异同步示意图
三:服务端配置文件
1、 rsync配置文件:/etc/rsyncd.conf
uid = rsync # rsync用户,要是0的话代表所有用户
gid = rsync # rsync用户组
use chroot = no # 安全考虑,出现BUG可以把危险的数据定位到一个chroot目录下去,避免恶意攻击
max connections = 200 # 最大连接数
timeout = 300 # 超时时常
pid file = /var/run/rsyncd.pid # 服务端进程号
lock file = /var/run/rsync.lock # 服务端锁文件
log file = /var/log/rsyncd.log # 服务端后台日志
[test] # 模块名
path = /tmp/filesystem/ # 需要同步的目录内容
ignore errors # 忽略错误
read only = false # 取消只读
list = false # 客户端列出服务端的内容
hosts allow = 192.168.3.0/24 # 同步的主机地址
hosts deny = 0.0.0.0/32 # 需要阻止哪些地址登陆
auth users = test_rsync # rsync用户名
secrets file = /etc/rsync.password
2、rsync密码文件:/etc/rsync.password
[root@test ~]# cat /etc/rsync.password
test_rsync:test1234 #前面是rsync的虚拟用户,后者是rsync的密码
[root@test ~]# ll /etc/rsync.password
-rw------- 1 root root 17 Nov 26 14:46 /etc/rsync.password # 修改密码文件权限为600
3、修改服务端两个配置文件权限(/etc/rsyncd.conf、rsync.password)
[root@test ~]# chmod 600 /etc/rsyncd.conf
[root@test ~]# chmod 600 /etc/rsync.password
4、创建rsync用户
[root@test ~]# useradd rsync -s /sbin/nologin
5、启动服务器端rsync进程
[root@test ~]# rsync --daemon
6、检查进程状态以及进程端口(默认873)如下:说明服务端一切正常
[root@test ~]# netstat -lnutp | grep rsync
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:873 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 20509/rsync
tcp 0 0 :::873 :::* LISTEN 20509/rsync
[root@test ~]# ps -ef | grep rsync
root 20509 1 0 16:20 ? 00:00:00 rsync --daemon
root 22508 10881 0 17:12 pts/1 00:00:00 grep rsync
三:客户端准备
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1kHQSVEODxbtXpxxMnT1S2A
提取码:9q4m
四:安装rsync客户端



五:客户端配置
1、rsync家目录内容
2、配置客户端rsync
在bin目录下加入密码文件:rsync.password,注意此密码要和服务端的/etc/rsync.password里面的密码一致,服务端密码为:test1234,所以客户端密码文件也写成这个
3、修改客户端密码文件的属主:(不修改属主默认会提示错误)

4、同步服务端的数据到客户端指定位置
在客户端rsync目录的bin目录下执行:
rsync.exe -avz --password-file=rsync.password test_rsync@192.168.3.14::test /cygdrive/f/testdir >> syslog.log
5、参数解读
-avz参数说明:
-a:等于下图所有内容:

-v:可视化
-z:传输时进行压缩提高传输速率
--password-file:指定密码文件
test_rsync:服务端/etc/rsyncd.conf里面的rsync的虚拟用户
::test:这个是服务端/etc/rsyncd.conf里面的模块名,客户端会根据服务端的模块名去找服务端需要共同步数据的目录
/cygdrive/f/testdir:告诉rsync我的数据是同步到客户端f盘的testdir目录下
6、linux和linux系统之间同步客户端配置更简单★★★★
只需要在客户端上加入如下内容即可:
[root@rsync_client ~]# cat /etc/rsync.password
test1234
六:无差异备份实验
1、服务端数据
[root@rsync_server zwy]# ls
1 10 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
2、客户端数据
[root@rsync_client data]# pwd
/root/data
[root@rsync_client data]# ls # 客户端无数据
3、第一次同步
[root@rsync_client data]# rsync -avz --password-file=/etc/rsync.password test_rsync@192.168.3.14::test ~/data/
receiving incremental file list
./
1
10
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
sent 248 bytes received 539 bytes 1574.00 bytes/sec
total size is 0 speedup is 0.00
4、检查服务端数据是否同步正常
[root@rsync_client data]# ls
1 10 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
5、无差异同步,删除服务器端的1-5的数据,然后客户端拉取数据看看效果
[root@rsync_server zwy]# ls
1 10 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
[root@rsync_server zwy]# rm -f {1..5}
[root@rsync_server zwy]# ls
10 6 7 8 9
6、客户端用无差异备份的方式拉数据看看效果
[root@rsync_client data]# rsync -avz --delete --password-file=/etc/rsync.password test_rsync@192.168.3.14::test ~/data/
receiving incremental file list
deleting 5
deleting 4
deleting 3
deleting 2
deleting 1
./
10
6
7
8
9
sent 153 bytes received 333 bytes 972.00 bytes/sec
total size is 0 speedup is 0.00
[root@rsync_client data]# ls # 再看客户端数据发现1-5的数据已经被删除了
10 6 7 8 9
7、无差异备份要了解拉数据和推数据的流程,否则风险很大!!!!!
七:附rsync自启动脚本
1 [root@test ~]# cat /etc/init.d/tfrsync 2 #!/bin/sh 3 # 4 # 5 # rsync start/stop/status/restart 6 # 7 # chkconfig: 35 57 10 8 # description: rsync backup oa data 9 10 . /etc/init.d/functions 11 12 PID="/var/run/rsyncd.pid" 13 LOCK="/var/run/rsync.lock" 14 COUNT=`ps -ef | grep rsync | grep -vE "grep|vim|cat|more|sh" | wc -l` 15 STATUS_TRUE="action "$0" /bin/true" 16 STATUS_FALSE="action "$0" /bin/false" 17 18 case "$1" in 19 20 start) 21 22 if [ $COUNT -eq 1 ] 23 then 24 echo -ne "rsync is started " && $STATUS_FALSE 25 exit 1 26 else 27 /usr/bin/rsync --daemon && $STATUS_TRUE || $STATUS_FALSE 28 29 fi 30 31 ;; 32 33 stop) 34 35 cat $PID | xargs kill -9 2>/dev/null && $STATUS_TRUE && rm -f $PID $LOCK || $STATUS_FALSE 36 37 ;; 38 39 status) 40 41 [ $COUNT -eq 1 ] && echo "rsync is running." || echo "rsync is stoped." 42 43 ;; 44 45 restart) 46 47 if [ -f $PID ] 48 then 49 cat $PID | xargs kill -9 && $STATUS_TRUE && rm -rf $PID $LOCK && \ 50 /usr/bin/rsync --daemon && $STATUS_TRUE || $STATUS_FALSE 51 else 52 /usr/bin/rsync --daemon && $STATUS_TRUE || $STATUS_FALSE 53 fi 54 55 ;; 56 57 *) 58 echo "Usage:$0 {start|stop|status|restart}" 59 ;; 60 esac
脚本写的不好,还请大家多多包涵,谢谢!