下载:wget http://webpy.org/static/web.py-0.38.tar.gz
解压并进入web.py-0.38文件夹
安装:easy_install web.py
这是一个如何使用python快速构建简单restful风格webservice的应用教程。
1.分析rest路由规则
rest风格的服务通常使用web.py来创建服务器端脚本,一般情况下包含两个url路径:
一个是为了查询所有用户,一个是为了查询单个用户。
例如下面的url:
http://localhost:8080/users
http://localhost:8080/users/{id}
2.搭建web.py环境
首先你应该安装web.py模块到你的python环境下。如果你之前没有的话请执行下面的脚本。
sudo easy_install web.py
3.提供数据源
下面是一个提供数据的XML文件
user_data.xml
<users>
<user id="1" name="Rocky" age="38"/>
<user id="2" name="Steve" age="50"/>
<user id="3" name="Melinda" age="38"/>
</users>
4.提供服务器端程序
代码清单一:提供一个简单rest服务的python代码
rest.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Date : 2014-08-04 14:03:19
# @Author : pinghailinfeng (pinghailinfeng79@gmail.com)
# @Link : http://my.oschina.net/dlpinghailinfeng
# @Version : $Id$
import web
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
tree = ET.parse('users.xml')
root = tree.getroot()
urls=(
'/users','list_users',
'/users/(.*)','get_user'
)
app = web.application(urls,globals())
class list_users:
def GET(self):
output = 'users:[';
for child in root:
print 'child',child.tag,child.attrib
output +=str(child.attrib)+','
output += ']';
return output
class get_user:
def GET(self,user):
for child in root:
if child.attrib['id']==user:
return str(child.attrib)
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run()
5.运行脚本
接下来运行这个脚本
./rest.py
6.访问url
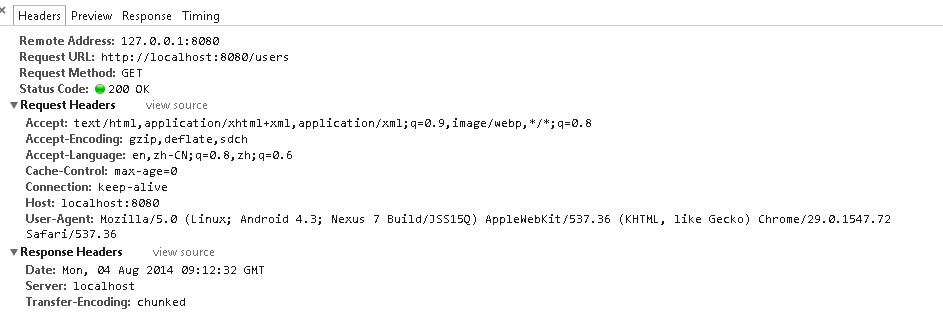
默认是在8080端口提供可以访问的service服务。这个API服务返回的是json数据,你可以使用下面任意一个URL路径访问,例如:
http://localhost:8080/users
http://localhost:8080/users/1
http://localhost:8080/users/2
http://localhost:8080/users/3
7.结果

至此,一个简单的restful风格的webservice应用建立完毕。
我的接口:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Date : 2018-01-04
# @Author : zhangmingcheng
import web
from PIL import Image
import imagehash
import glob
import json
import os,sys
urls=(
'/images/getImagesDhash','get_imagesdhash',
'/images/getImageDhash','get_imagedhash',
)
app = web.application(urls,globals())
class Dhash(object):
def __init__(self, name, dhash):
self.name = name
self.dhash = dhash
class get_imagesdhash:
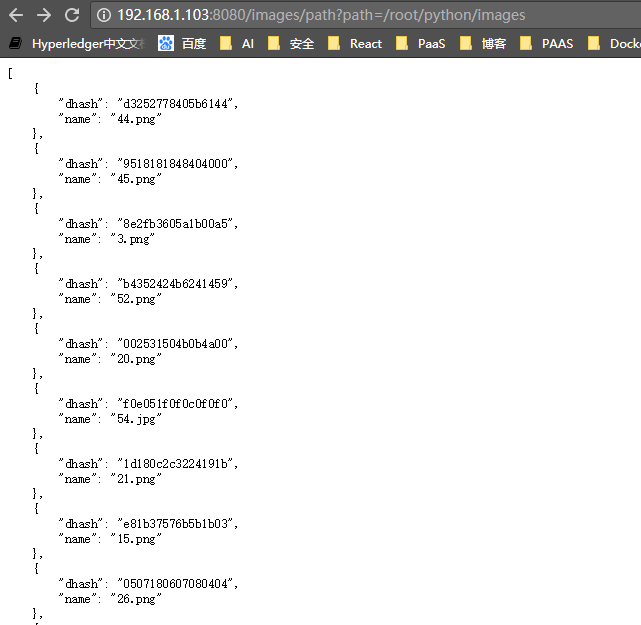
def GET(self):
path = web.input().path
dhashs = []
for imagePath in glob.glob(path + "/*.*"):
image = Image.open(imagePath)
h = str(imagehash.dhash(image))
filename = imagePath[imagePath.rfind("/") + 1:]
dhash = Dhash(filename,h)
dhashs.append(dhash)
return json.dumps(dhashs, default=lambda o: o.__dict__, sort_keys=True, indent=4)
class get_imagedhash:
def GET(self):
path = web.input().path
image = Image.open(path)
h = str(imagehash.dhash(image))
return h
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run()
~