---恢复内容开始---
一、目标:
1、掌握Service的生命周期
2、了解Service的常用方法
3、掌握通过启动模式创建和使用Service
4、掌握通过绑定模式创建和使用Service
二、什么是Service
1、Service是运行在Android应用后台的组件
2、没有用户界面,不需要和用户交互
三、Service的用途
1、一种是执行长时间运行的好事操作
a、如网络下载,音乐播放
b、文件系统监控等
2、另一种是负责组件间的交互
a、将某些功能以Service组件形式封装,然后提供给其他组件使用
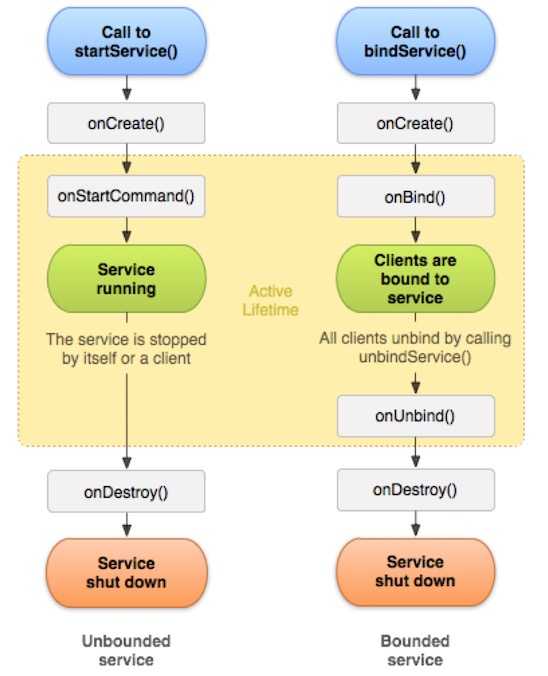
四、Service的生命周期
1、Service不能自己启动,必须由其他应用组件来调用
2、根据调用方式不同,分为两种运行模式:
a、启动模式
b、绑定模式
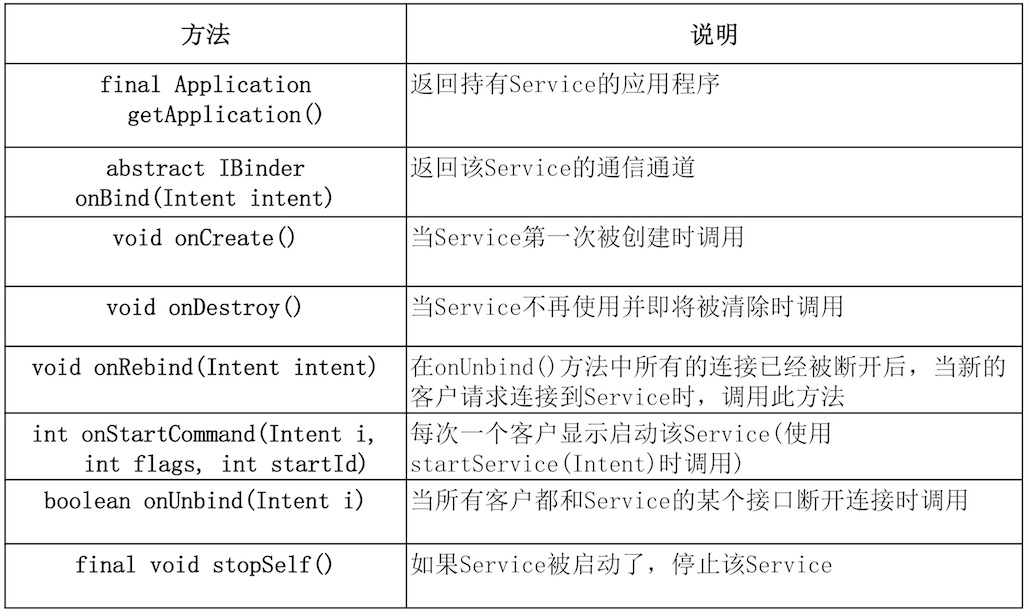
五、Service常用方法
六、启动模式下的Service
1、创建启动模式运行的Service组件
a、创建Service类,继承android.app.Service类
b、在Service类中实现onStartCommand等生命周期方法
public class CountService extends Service {
@Overrid
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent,int flag,int startid) {
}
...
}
c、在AndroidManifest.xml文件中配置Service组件
<service android:name=".CountService" />
d、在Acitivity中启动Service
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
this.startService(new Intent(this, CountService.class));
}
e、在Acitivity中停止Service
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
this.stopService(new Intent(this, CountService.class));
}
f、主要逻辑在onStartCommand方法中实现,该方法的返回值决定了不同的Service运行模式。
I、START_NOT_STICKY:在Service意外被终止后停止。适用场景:网上下载数据
II、START_REDELIVER_INTENT:在Service意外被终止后将停止将自动重新运行并保证Intent被处理。适用场景:关键业务处理。
III、START_STICKY:确保Service一直保持启动状态,但不保证Intent执行。适用场景:后台播放音乐。
七、IntentService
1、Service组件经常涉及多线程以及同步问题
2、使用IntentService帮助开发人员解决多线程同步问题
a、创建一个工作队列,每次将一个Intent传递屌onHandleIntent()方法,无需担心多线程同步问题。
八、绑定模式下的Service
创建绑定模式运行的Service组件
1、创建 Service类,继承android.app.Service类
2、在Service类中实现一个内部类,它继承Binder类。并在Service类的onBind()生命方法中返回内部类对象
public class BindService extends Service {
@Override
public IBinderonBind(Intent intent) {
return myBinder;
}
public class MyBinder extends Binder{
public BindServicegetService(){
return BindService.this;
}
}
.....
}
3、在AndroidManifest.xml文件中配置Service组件
<service android:name=".BindService" />
4、Activity使用bindService()方法绑定服务
Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this,BindService.class);
bindService(intent, conn, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
1、第二个参数ServiceConnection对象代表当前组件到Service组件的链接
5、Activity使用unbindService(ServiceConnection conn)方法取消Service组件的绑定
6、ServiceConnection对象如果链接成功,在生命周期方法onServiceConnected()中,可以获取Service组件的onBind()方法返回Binder对象,通过它可以实现Service组件的调用。
private ServiceConnection conn = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName n, IBinder service) {
MyBinder binder = (MyBinder)service;
BindServicebindService = binder.getService();//获取Service组件
bindService.MyMethod();//调用service组件的方法
}
} ;
九、使用系统服务
1、在Activity中可以通过getSystemService方法获取应用框架提供的系统服务
2、在Android SDK的android.content.Context类中定义了系统服务的ID
*@see #WINDOW_SERVICE
* @see android.view.WindowManager
* @see #LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE
* @see android.view.LayoutInflater
* @see #ACTIVITY_SERVICE
* @see android.app.ActivityManager
...
public abstract Object getSystemService(String name);