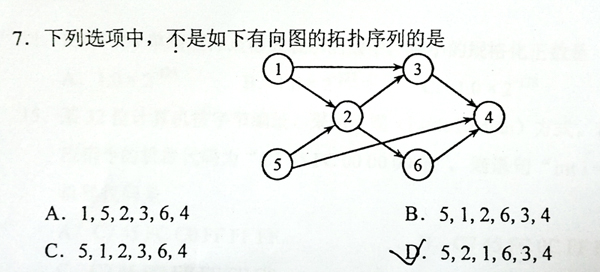
This is a problem given in the Graduate Entrance Exam in 2018: Which of the following is NOT a topological order obtained from the given directed graph? Now you are supposed to write a program to test each of the options.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line gives two positive integers N (≤ 1,000), the number of vertices in the graph, and M (≤ 10,000), the number of directed edges. Then M lines follow, each gives the start and the end vertices of an edge. The vertices are numbered from 1 to N. After the graph, there is another positive integer K (≤ 100). Then K lines of query follow, each gives a permutation of all the vertices. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
Print in a line all the indices of queries which correspond to "NOT a topological order". The indices start from zero. All the numbers are separated by a space, and there must no extra space at the beginning or the end of the line. It is graranteed that there is at least one answer.
Sample Input:
6 8
1 2
1 3
5 2
5 4
2 3
2 6
3 4
6 4
5
1 5 2 3 6 4
5 1 2 6 3 4
5 1 2 3 6 4
5 2 1 6 3 4
1 2 3 4 5 6
Sample Output:
3 4思路
定义一个count数组,保存每个结点对应的指向它的弧的个数,如上图中,count[1]=count[5]=0,count[2]=2,然后对
待检验序列进行遍历,对遍历到的每个结点:
如果当前结点的count数组值不等于0,则返回false
否则,对与该结点连接的每个结点的count值都减1
#include<iostream> #include<vector> #include<algorithm> #include<queue> #include<string> #include<map> #include<set> #include<stack> #include<string.h> #include<cstdio> #include<cmath> using namespace std; vector<vector<int>> num; bool check(int a[],int n,vector<int>& cnt) { for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { int temp=a[i]; if(cnt[temp]!=0) return false; for(auto &va:num[temp]) { cnt[va]--; // cout<<va<<" "<<cnt[va]<<endl; } } return true; } int main() { int n,m; scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); num.resize(n+1); vector<int> cnt(n+1,0); // cnt=(n+1,0); for(int i=0;i<m;i++) { int start,endL; cin>>start>>endL; num[start].push_back(endL); cnt[endL]++; } int k; cin>>k; int a[n]; vector<int>result; vector<int>temp(n+1); for(int i=0;i<k;i++) { for(int j=0;j<n;j++) { temp[j+1]=cnt[j+1]; cin>>a[j]; } if(!check(a,n,temp)) result.push_back(i); } cout<<result[0]; for(int i=1;i<result.size();i++) cout<<" "<<result[i]; return 0; }