集合
1、集合和数组的区别
(1)长度:
集合长度可变,数组长度固定。
(2)存储的元素类型:
- 集合中存储的只能是引用数据类型,数组可以是基本数据类型和引用数据类型(类、接口类型、数组类型、枚举类型、注解类型,字符串型),但是只能存储一种类型的数据。
- 集合在没有指定泛型之前,默认保存的是任意类型的元素(Object类型),指定泛型之后可以保存对应类型的元素
- 数组存储引用类型的数据较为繁琐,使用集合更简洁
- 数组比较适合保存基本类型的元素,集合比较适合保存引用类型的元素
2、集合的体系
(1)集合的体系
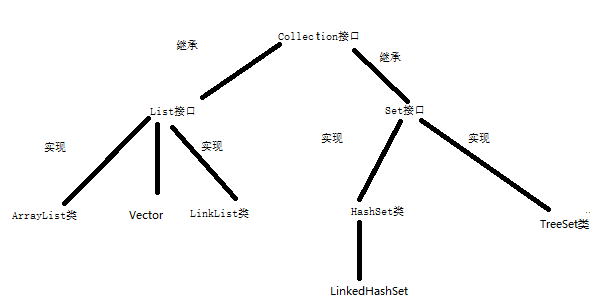
List接口与Set接口的不同:
- List可以存储相同的元素,Set不能存储相同的元素。
- Set元素无序,List有序
java的集合分为collection接口(单列集合)和Map(双列集合)两种体系,list和set是继承自collection的接口,map是一个独立的接口
list接口和set接口都有自己的实现类,因为接口是没有具体实现的,接口是一个规范,实现类在规范的基础上有自己的特性。在接口的实现上可以体现出面向对象编程的多态的特性。
(2)Collection 和 Collections的区别
- Collections是个java.util下的类,它包含有各种有关集合操作的静态方法
排序:
public static void main(String[] args) { List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>(); list.add(123); list.add(1); list.add(122); list.add(22); Collections.sort(list); for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {//类中的size方法 System.out.println(list.get(i)); } }
1 22 122 123
求最大值:
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>(); list.add(123); list.add(1); list.add(122); list.add(22); System.out.println( Collections.max(list)); } }
123
Collection是个java.util下的接口,它是各种集合结构的父接口,如:list、set、map
(3)Map接口

ArrayList集合
ArratList集合:查找快,增删慢的可变大小。
1、基本数据类型和引用数据类型的对应关系
因为集合只能存储引用数据类型,所以要注意基本数据类型和引用数据类型的对应关系:
与基本数据类型不同的是,基本数据类型所对应的包装类封装的有自己的方法,因此,功能上更加强大。

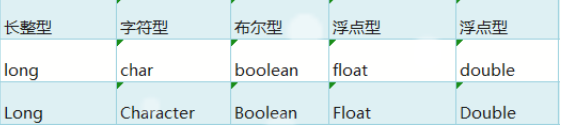
2、ArrayList类中的常用方法



3、Arraylist集合的运用
创建Person类:
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
if (age >= 0 || age <= 200)
this.age = age;
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
用add、get方法实现添加和获取集合元素,结合size方法,实现集合的遍历:
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Way {
public void addPerson(ArrayList<Person> array) {
Person p1 = new Person("张三", 12);
Person p2 = new Person("李明", 14);
Person p3 = new Person("李华", 23);
Person p4 = new Person("吴佩佩", 2);
Person p5 = new Person("王涛", 15);
array.add(p1);//类中的add方法
array.add(p2);
array.add(p3);
array.add(p4);
array.add(p5);
}
// 运用一般的get()方法遍历集合
public void printPerson(ArrayList<Person> array) {
for (int i = 0; i < array.size(); i++) {//类中的size方法
Person p = array.get(i);//get方法
System.out.println(p.getName() + " " + p.getAge());
}
}
}
测试类:
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ArrayListDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Person> array=new ArrayList<Person>();
Way way=new Way();
way.addPerson(array);
way.printPerson(array);
}
}

LinkedList集合
LinkedList集合的存储结构为链表,添加、删除快,查找慢,LinkedList和ArrayList的父类都是List接口,因此他们有很多相同的方法。
1、List共有方法
创建Person类:
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
if (age >= 0 || age <= 200)
this.age = age;
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
写遍历集合的方法:
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class Way {
public void addPerson(LinkedList<Person> array) {
Person p1 = new Person("张三", 12);
Person p2 = new Person("李明", 14);
Person p3 = new Person("李华", 23);
Person p4 = new Person("吴佩佩", 2);
Person p5 = new Person("王涛", 15);
array.add(p1);//类中的add方法
array.add(p2);
array.add(p3);
array.add(p4);
array.add(p5);
}
// 运用一般的get()方法遍历集合
public void printPerson(LinkedList<Person> link) {
for (int i = 0; i < link.size(); i++) {//类中的size方法
Person p = link.get(i);//get方法
System.out.println(p.getName() + " " + p.getAge());
}
}
}
测试类:
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class LinkedListDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<Person> link=new LinkedList<Person>();
Way way=new Way();
way.addPerson(link);
way.printPerson(link);
}
}

2、特有方法
由于LinkedList具有查询慢,增删快的特性,为了充分利用它的特点,LinkedList集合还有很多特有的方法。
(1)addFirst方法:
package pers.zhb.LinkedList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class Way {
public void LinkedListPrint(LinkedList<Integer> link) {
System.out.println("迭代器方法遍历集合:");
Iterator<Integer> linkIt = link.iterator();// 获取集合的实现类对象,并调用集合的iterator()
while (linkIt.hasNext()) {
Integer in = linkIt.next();
System.out.print(in);
}
}
public void linkedListadd(LinkedList<Integer> link) {
Integer it1 = new Integer(1);
Integer it2 = new Integer(2);
Integer it3 = new Integer(3);
Integer it4 = new Integer(4);
link.addFirst(it1);
link.addFirst(it2);
link.addFirst(it3);
link.addFirst(it4);
}
}
package pers.zhb.LinkedList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class LinkedListDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<Integer> link = new LinkedList<Integer>();
Way way = new Way();
way.linkedListadd(link);
way.LinkedListPrint(link);
}
}
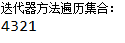
由结果可知,LinkedList集合的addFirst集合符合“后进先出”的规则,具有栈的特点。
(2)removeFirst()与getFirst():
package pers.zhb.LinkedList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class LinkedListDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<Integer> link = new LinkedList<Integer>();
Way way = new Way();
way.linkedListadd(link);
link.removeFirst();// 方法removeFirst();
System.out.println("集合中的第一个元素为:" + link.getFirst());// 方法getFirst();
way.LinkedListPrint(link);
}
}

(3)pop()、push()、isEmpty()方法的使用:
package pers.zhb.LinkedList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class LinkedListDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<Integer> link = new LinkedList<Integer>();
Way way = new Way();
way.linkedListadd(link);
System.out.println("栈顶插入元素前,栈中的元素为:");
way.LinkedListPrint(link);
link.push(5);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("弹出栈顶的元素:" + link.pop());
System.out.println("栈顶弹出元素后,栈中的元素为:");
way.LinkedListPrint(link);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("是否为空:" + link.isEmpty());
}
}
HashSet集合
HashSet集合的底层数据结构为哈希表,当存储已有类型的数据时,不需要重写equals和hashcode方法,如果存储自定义类型的数据需要将两个方法重写。存储过程中,先调用hashcode方法产生哈希值,根据哈希值寻找存储位置,如果两个数的哈希值相同,则调用equals方法,如果返回true则第二个元素不予存储(已经重复),否则,将其存储到哈希表中。
1、存储已经定义的数据:
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class HashSetDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet<String> hs = new HashSet<String>();
hs.add("qwe");
hs.add("123qwe");
hs.add("q23we");
hs.add("qw1e");
hs.add("qwe");
Iterator<String> it = hs.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
String s = it.next();
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}

由运行结果可知,不用重写equals和hashcode方法,即可去除重复元素。
2、存储自定义类型的数据(重写equals和hashcode方法)
创建Person类,重写equals和hashcode方法:
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
if (age >= 0 || age <= 200)
this.age = age;
}
public int hashCode() {//哈希值
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + age;
result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());
return result;
}
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (!(obj instanceof Person)) {
System.out.println("类型错误");
return false;
}
Person other = (Person) obj;
return this.age == other.age && this.name.equals(other.name);
}
}
hashCode的重写原则:
- 和属性相关、属性一样的话要求哈希值一样
- 如果hashCode方法的重写有失误会造成哈希值一样的元素增多,那么就会造成equals执行的次数增加,使得程序的执行效率降低,因此,在属性不一样的情况下要尽最大努力让哈希值不一样
- 选择系数的时候要尽量选择较大的系数,因为如果计算出来的hash地址越大冲突就会减少,查找起来的效率就会越高
- 31占5bit,相乘造成数据溢出的概率较小
- i*31可以转化为位移运算和减法运算,可以提高算法效率
创建Way类,添加数据、遍历集合:
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class Way {
// 添加元素
public void addHash(HashSet<Person> hash) {
Person p1 = new Person();
Person p2 = new Person();
Person p3 = new Person();
Person p4 = new Person();
Person p5 = new Person();
Person p6 = new Person();
Person p7 = new Person();
p1.setAge(12);
p1.setName("张敏");
p2.setAge(11);
p2.setName("吴喜爱");
p3.setAge(14);
p3.setName("小猫咪");
p4.setAge(67);
p4.setName("吴长春");
p5.setAge(34);
p5.setName("Tom");
p6.setAge(67);
p6.setName("吴长春");
p7.setAge(34);
p7.setName("Tom");
hash.add(p1);
hash.add(p2);
hash.add(p3);
hash.add(p4);
hash.add(p5);
hash.add(p6);
hash.add(p7);
}
// 运用迭代器方法遍历集合
public void iteratorPrint(HashSet<Person> hash) {
System.out.println("迭代器方法遍历集合:");
Iterator<Person> hashIt = hash.iterator();// 获取集合的实现类对象,病调用集合的iterator()
while (hashIt.hasNext()) {
Person per = hashIt.next();
System.out.println(per.getName() + " " + per.getAge());
}
}
}
创建测试类:
import java.util.HashSet;
public class HashDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet<Person> hash = new HashSet<Person>();
Way way = new Way();
way.addHash(hash);
way.iteratorPrint(hash);
}
}
重写两个方法后,可以将姓名与年龄相同的对象,只保留一个,即不存储重复的元素。
LinkedHashSet集合
LinkedHashSet集合与HashSet集合的最大区别在于,LinkedHashSet集合存入和取出的顺序相同,而HashSet集合存取顺序不一定相同:
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
public class HashSetDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet<String> hs = new HashSet<String>();
hs.add("qwe");
hs.add("123qwe");
hs.add("q23we");
hs.add("qw1e");
hs.add("qwe");
Iterator<String> it = hs.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
String s = it.next();
System.out.println(s);
}
System.out.println("----------------------------");
LinkedHashSet<String> lhs = new LinkedHashSet<String>();
lhs.add("qwe");
lhs.add("123qwe");
lhs.add("q23we");
lhs.add("qw1e");
lhs.add("qwe");
Iterator<String> ite = lhs.iterator();
while (ite.hasNext()) {
String s = ite.next();
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
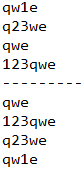
HashMap集合
collection接口下的List和Set集合,存储的都是单个元素。而Map接口下的集合,存储的是键值对,键值对中,值可以相同,但是键必须不同。
1、HashMap中的常用方法:




import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class HashMapDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
map.put("河南", "郑州");
map.put("北京", "北京");
System.out.println(map);
System.out.println(map.get("河南"));
System.out.println(map.remove("河南") + "已被移除");
System.out.println(map);
System.out.println(map.size());
}
}

2、HashMap的遍历:

import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
public class HashMapDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
map.put("河南", "郑州");
map.put("北京", "北京");
Set<String> keySet = map.keySet();
// 遍历存放所有key的Set集合
Iterator<String> it = keySet.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
// 得到每一个key
String key = it.next();
// 通过key获取对应的value
String value = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key + "=" + value);
}
}
}
