SpringMVC执行流程源码分析
我们先来看张图片,帮助我们理解整个流程
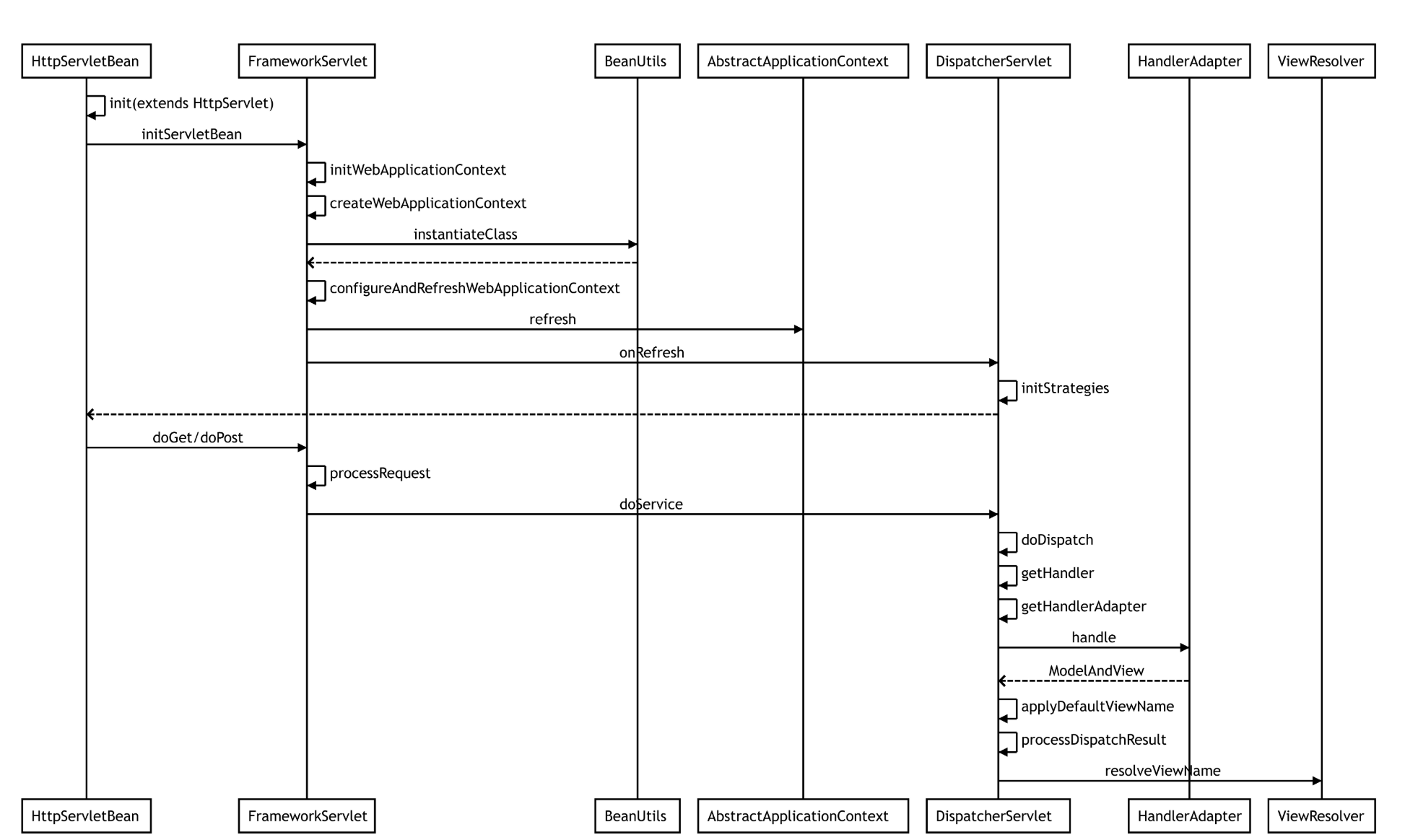
然后我们开始来解析
首先SpringMVC基于Servlet来运行 那么我们首先来看HttpServletBean这个类 他继承HttpServlet,所以这个HttpServletBean为一个Servlet,我们直接看Init方法,因为init方法在Servlet初始化的时候会执行的一个方法
public final void init() throws ServletException { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Initializing servlet '" + getServletName() + "'"); } // 在Web.xml中读取配置文件. PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties); if (!pvs.isEmpty()) { try { //通过BeanWrapper代理器创建DispatcherServlet BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this); ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext()); bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment())); initBeanWrapper(bw); //设置DispatcherServlet属性 bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true); } catch (BeansException ex) { if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) { logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex); } throw ex; } } // 该类为空实现,由他的子类实现也就是FrameworkServlet initServletBean(); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Servlet '" + getServletName() + "' configured successfully"); } }
那我们来看FrameworkServlet里的实现
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException { getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "'"); if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) { this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization started"); } long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); try { this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext(); initFrameworkServlet(); } catch (ServletException ex) { this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex); throw ex; } catch (RuntimeException ex) { this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex); throw ex; } if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) { long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime; this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization completed in " + elapsedTime + " ms"); } }
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
可以看到在这里进行webApplicationContext的初始化,initFrameworkServlet()也可也为空方法,此方法将在设置任何bean属性之后调用,已加载WebApplicationContext,默认实现为空,子类可以覆盖此方法来执行它们需要的任何初始化.
我们点进initWebApplicationContext详细来看
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() { WebApplicationContext rootContext = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext()); WebApplicationContext wac = null; if (this.webApplicationContext != null) { // A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it wac = this.webApplicationContext; if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) { ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac; if (!cwac.isActive()) { // The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as // setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc if (cwac.getParent() == null) { // The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set // the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent cwac.setParent(rootContext); } configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac); } } } if (wac == null) { // No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one // has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is assumed // that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the // user has performed any initialization such as setting the context id wac = findWebApplicationContext(); } if (wac == null) { // No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext); } if (!this.refreshEventReceived) { // Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh // support or the context injected at construction time had already been // refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here. onRefresh(wac); } if (this.publishContext) { // Publish the context as a servlet context attribute. String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName(); getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac); if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) { this.logger.debug("Published WebApplicationContext of servlet '" + getServletName() + "' as ServletContext attribute with name [" + attrName + "]"); } } return wac; }
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ApplicationContext parent) { Class<?> contextClass = getContextClass(); if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) { this.logger.debug("Servlet with name '" + getServletName() + "' will try to create custom WebApplicationContext context of class '" + contextClass.getName() + "'" + ", using parent context [" + parent + "]"); } if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) { throw new ApplicationContextException( "Fatal initialization error in servlet with name '" + getServletName() + "': custom WebApplicationContext class [" + contextClass.getName() + "] is not of type ConfigurableWebApplicationContext"); } ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass); wac.setEnvironment(getEnvironment()); wac.setParent(parent); wac.setConfigLocation(getContextConfigLocation()); //刷新并配置web应用上下文 configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac); return wac;
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
可以看到通过反射实例化Web上下文,我们继续来看configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac);
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac) { if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) { // The application context id is still set to its original default value // -> assign a more useful id based on available information if (this.contextId != null) { wac.setId(this.contextId); } else { // Generate default id... wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX + ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(getServletContext().getContextPath()) + '/' + getServletName()); } } wac.setServletContext(getServletContext()); wac.setServletConfig(getServletConfig()); wac.setNamespace(getNamespace()); wac.addApplicationListener(new SourceFilteringListener(wac, new ContextRefreshListener())); // The wac environment's #initPropertySources will be called in any case when the context // is refreshed; do it eagerly here to ensure servlet property sources are in place for // use in any post-processing or initialization that occurs below prior to #refresh ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment(); if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) { ((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(getServletContext(), getServletConfig()); } postProcessWebApplicationContext(wac); applyInitializers(wac); wac.refresh(); }
我们注意最后一个调用方法 wac.refresh(); 在这里面可以看到IOC的初始化流程 。我们现在继续回到刚刚说的onRefresh他没有实现 而让他的子类DispatchServlet实现
//DispatchServlet protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) { initStrategies(context); }
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) { // 初始化文件上传处理 initMultipartResolver(context); //初始化本地化处理 initLocaleResolver(context); //初始化主题处理 initThemeResolver(context); // 初始化处理器映射器(用来保存controller中配置的RequestMapping与Method对应关系) initHandlerMappings(context); // 初始化处理器适配器(用来动态匹配Method参数 包括类转换 动态赋值) initHandlerAdapters(context); // 初始化处理器异常处理 initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context); // 初始化请求至视图名转换 initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context); // 初始化视图解析器 initViewResolvers(context); // 初始化flash映射管理器 initFlashMapManager(context); }
我们再来看DispatcherServlet的配置文件DispatcherServlet.properties
org.springframework.web.servlet.LocaleResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver org.springframework.web.servlet.ThemeResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.theme.FixedThemeResolver org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerMapping=org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping, org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerAdapter=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.HttpRequestHandlerAdapter, org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter, org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExceptionResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.AnnotationMethodHandlerExceptionResolver, org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.ResponseStatusExceptionResolver, org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.support.DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver org.springframework.web.servlet.RequestToViewNameTranslator=org.springframework.web.servlet.view.DefaultRequestToViewNameTranslator org.springframework.web.servlet.ViewResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver org.springframework.web.servlet.FlashMapManager=org.springframework.web.servlet.support.SessionFlashMapManager
这个是DispatcherServlet策略接口的默认实现类。
protected final void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { processRequest(request, response); }
protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); Throwable failureCause = null; LocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext(); LocaleContext localeContext = buildLocaleContext(request); RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes(); ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes); WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new RequestBindingInterceptor()); initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes); try { //执行请求 doService(request, response); } catch (ServletException ex) { failureCause = ex; throw ex; } catch (IOException ex) { failureCause = ex; throw ex; } catch (Throwable ex) { failureCause = ex; throw new NestedServletException("Request processing failed", ex); } finally { resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes); if (requestAttributes != null) { requestAttributes.requestCompleted(); } if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { if (failureCause != null) { this.logger.debug("Could not complete request", failureCause); } else { if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { logger.debug("Leaving response open for concurrent processing"); } else { this.logger.debug("Successfully completed request"); } } } publishRequestHandledEvent(request, response, startTime, failureCause); } }
我们点进doService(request, response);这时又到我们的DispatcherServlet类
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { String resumed = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).hasConcurrentResult() ? " resumed" : ""; logger.debug("DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'" + resumed + " processing " + request.getMethod() + " request for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "]"); } // Keep a snapshot of the request attributes in case of an include, // to be able to restore the original attributes after the include. Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null; if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) { attributesSnapshot = new HashMap<String, Object>(); Enumeration<?> attrNames = request.getAttributeNames(); while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) { String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement(); if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PREFIX)) { attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName)); } } } // Make framework objects available to handlers and view objects. request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext()); request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver); request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver); request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource()); FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response); if (inputFlashMap != null) { request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap)); } request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap()); request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager); try { doDispatch(request, response); } finally { if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { // Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include. if (attributesSnapshot != null) { restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot); } } } }
我们点进 doDispatch(request, response);
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request; HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null; boolean multipartRequestParsed = false; WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); try { ModelAndView mv = null; Exception dispatchException = null; try { // 如果是MultipartContent类型则转换为MultiHttpServletRequest类型的request processedRequest = checkMultipart(request); multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request); // 确定当前请求的处理程序,根据request寻找对应的handler mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest); if (mappedHandler == null || mappedHandler.getHandler() == null) { noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response); return; } // // 根据处理器获取handler适配器 HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler()); // Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler. String method = request.getMethod(); boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method); if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) { long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "] is: " + lastModified); } if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) { return; } } // 拦截器postHandle方法处理 if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) { return; } // Actually invoke the handler. mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { return; } // 结果视图对象的处理 applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv); // 拦截器postHandle方法处理 mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv); } catch (Exception ex) { dispatchException = ex; } catch (Throwable err) { // As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well, // making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios. dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err); } // 处理最终结果 渲染视图等 processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException); } catch (Exception ex) { triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex); } catch (Throwable err) { triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err)); } finally { if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { // 请求成功响应之后的方法 if (mappedHandler != null) { mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response); } } else { // Clean up any resources used by a multipart request. if (multipartRequestParsed) { cleanupMultipart(processedRequest); } } } }
我们来看getHandler()方法
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { for (HandlerMapping hm : this.handlerMappings) { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace( "Testing handler map [" + hm + "] in DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'"); } HandlerExecutionChain handler = hm.getHandler(request); if (handler != null) { return handler; } } return null; }
我们继续看hm.getHandler(request);方法的实现来自于HandlerMapping这个接口由AbstractHandlerMapping来实现
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { // 根据request获取handler Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request); // 没有查找到使用默认handler if (handler == null) { handler = getDefaultHandler(); } if (handler == null) { return null; } // 如果handler是字符串类型 说明是bean名称 需要获取handler bean对象 if (handler instanceof String) { String handlerName = (String) handler; handler = getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName); } // 封装handler执行链 HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request); if (CorsUtils.isCorsRequest(request)) { CorsConfiguration globalConfig = this.globalCorsConfigSource.getCorsConfiguration(request); CorsConfiguration handlerConfig = getCorsConfiguration(handler, request); CorsConfiguration config = (globalConfig != null ? globalConfig.combine(handlerConfig) : handlerConfig); executionChain = getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(request, executionChain, config); } return executionChain; }
我们继续来看getHandlerInternal
//AbstractHandlerMethodMapping protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { // 获取request中的url 用来匹配handler String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Looking up handler method for path " + lookupPath); } this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock(); try { // 根据路径寻找handler HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { if (handlerMethod != null) { logger.debug("Returning handler method [" + handlerMethod + "]"); } else { logger.debug("Did not find handler method for [" + lookupPath + "]"); } } return (handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null); } finally { this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock(); } }
protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { List<Match> matches = new ArrayList<Match>(); // 直接匹配 List<T> directPathMatches = this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByUrl(lookupPath); // 存在匹配 则添加到匹配列表中 if (directPathMatches != null) { addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request); } // 没有匹配 遍历所有处理方法查找 if (matches.isEmpty()) { // No choice but to go through all mappings... addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), matches, request); } // 存在匹配 if (!matches.isEmpty()) { Comparator<Match> comparator = new MatchComparator(getMappingComparator(request)); Collections.sort(matches, comparator); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Found " + matches.size() + " matching mapping(s) for [" + lookupPath + "] : " + matches); } // 排序之后获取第一个 Match bestMatch = matches.get(0); // 有多个匹配 会找出第二个进行比较 if (matches.size() > 1) { if (CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) { return PREFLIGHT_AMBIGUOUS_MATCH; } Match secondBestMatch = matches.get(1); if (comparator.compare(bestMatch, secondBestMatch) == 0) { Method m1 = bestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod(); Method m2 = secondBestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod(); throw new IllegalStateException("Ambiguous handler methods mapped for HTTP path '" + request.getRequestURL() + "': {" + m1 + ", " + m2 + "}"); } } // 设置request参数 handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, lookupPath, request); // 返回匹配的url处理方法 return bestMatch.handlerMethod; } else { return handleNoMatch(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), lookupPath, request); } }
我们回到 getHandlerExecutionChain继续来看
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandlerExecutionChain(Object handler, HttpServletRequest request) { // // 如果当前handler不是执行链类型 则创建一个新的执行链封装 HandlerExecutionChain chain = (handler instanceof HandlerExecutionChain ? (HandlerExecutionChain) handler : new HandlerExecutionChain(handler)); // 当前url String lookupPath = this.urlPathHelper.getLookupPathForRequest(request); // 遍历拦截器 与当前url匹配的添加至执行链中 for (HandlerInterceptor interceptor : this.adaptedInterceptors) { if (interceptor instanceof MappedInterceptor) { MappedInterceptor mappedInterceptor = (MappedInterceptor) interceptor; if (mappedInterceptor.matches(lookupPath, this.pathMatcher)) { chain.addInterceptor(mappedInterceptor.getInterceptor()); } } else { chain.addInterceptor(interceptor); } } return chain; }
private void processDispatchResult(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler, ModelAndView mv, Exception exception) throws Exception { boolean errorView = false; if (exception != null) { if (exception instanceof ModelAndViewDefiningException) { logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered", exception); mv = ((ModelAndViewDefiningException) exception).getModelAndView(); } else { Object handler = (mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null); mv = processHandlerException(request, response, handler, exception); errorView = (mv != null); } } // Did the handler return a view to render? if (mv != null && !mv.wasCleared()) { //渲染 render(mv, request, response); if (errorView) { WebUtils.clearErrorRequestAttributes(request); } } else { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Null ModelAndView returned to DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "': assuming HandlerAdapter completed request handling"); } } if (WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { // Concurrent handling started during a forward return; } if (mappedHandler != null) { mappedHandler.triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null); } }
点进render来看
protected void render(ModelAndView mv, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { // Determine locale for request and apply it to the response. Locale locale = this.localeResolver.resolveLocale(request); response.setLocale(locale); View view; if (mv.isReference()) { // 解析视图名获取视图对象 view = resolveViewName(mv.getViewName(), mv.getModelInternal(), locale, request); if (view == null) { throw new ServletException("Could not resolve view with name '" + mv.getViewName() + "' in servlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'"); } } else { // No need to lookup: the ModelAndView object contains the actual View object. view = mv.getView(); if (view == null) { throw new ServletException("ModelAndView [" + mv + "] neither contains a view name nor a " + "View object in servlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'"); } } // Delegate to the View object for rendering. if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Rendering view [" + view + "] in DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'"); } try { if (mv.getStatus() != null) { response.setStatus(mv.getStatus().value()); } view.render(mv.getModelInternal(), request, response); } catch (Exception ex) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Error rendering view [" + view + "] in DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'", ex); } throw ex; } }
好的 到这里我们解析结束.