一、前言
之前的List,讲了ArrayList、LinkedList,反映的是两种思想:
(1)ArrayList以数组形式实现,顺序插入、查找快,插入、删除较慢
(2)LinkedList以链表形式实现,顺序插入、查找较慢,插入、删除方便
那么是否有一种数据结构能够结合上面两种的优点呢?有,答案就是HashMap。
HashMap是一种非常常见、方便和有用的集合,是一种键值对(K-V)形式的存储结构。
四个关注点在HashMap上的答案

二、hashMap数据结构

说明:上图说明了hashMap的数据结构,由数组+链表+红黑树组成,链表为单向链表,桶中的结构可能是链表,也可能是红黑树,红黑树的引用是为了提高效率。
三、hashMap源码分析-属性及构造函数
3.1 类的继承关系
public class HashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable
可以看到HashMap继承自父类(AbstractMap),实现了Map、Cloneable、Serializable接口。其中,Map接口定义了一组通用的操作;Cloneable接口则表示可以进行拷贝,在HashMap中,实现的是浅层次拷贝,即对拷贝对象的改变会影响被拷贝的对象;Serializable接口表示HashMap实现了序列化,即可以将HashMap对象保存至本地,之后可以恢复状态。
3.2 类的属性
// 序列号 private static final long serialVersionUID = 362498820763181265L; // 默认的初始容量是16 static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // 最大容量 static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30; // 默认的加载因子是0.75 static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; // 当桶(bucket)上的结点数大于这个值时链表会转成红黑树 static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8; // 当桶(bucket)上的结点数小于这个值时红黑树转成链表 static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6; // 桶中结构转化为红黑树对应的table的最小大小 static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64; // 存储元素的数组,总是2的幂次倍 transient Node<k,v>[] table; // 存放具体元素的集 transient Set<map.entry<k,v>> entrySet; // 存放元素的个数,注意这个不等于数组的长度。 transient int size; // 每次扩容和更改map结构的计数器 transient int modCount; // 临界值 当实际大小size(容量*加载因子)超过该值时,会进行扩容 int threshold; // 加载因子 final float loadFactor;
说明:hashMap的属性比较多,这里说一下threshold和loadFactor这两个属性。hashMap的默认初始容量为16,默认加载因子为0.75,那么threshold = 16 * 0.75 = 12,当size > 12时,就会进行扩容。而加载因子越大,threshold越大,那么在扩容之前可以填充的元素就越多,空间利用率提高了,但是相应的就会比较容易造成hash冲突。而加载因子越小,threshold越小,那么在扩容之前可以填充的元素就越少,空间利用降低了,但是相应的就没那么容易造成hash冲突。
3.3 类的构造函数
1.、public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor)型
/** * Constructs an empty <tt>HashMap</tt> with the specified initial * capacity and load factor. * * @param initialCapacity the initial capacity * @param loadFactor the load factor * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative * or the load factor is nonpositive */ public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) { if (initialCapacity < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " + initialCapacity); if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY; if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " + loadFactor); this.loadFactor = loadFactor; this.threshold = tableSizeFor(initialCapacity); }
tableSizeFor函数返回大于等于initialCapacity最小的二次幂的值
/** * Returns a power of two size for the given target capacity. */ static final int tableSizeFor(int cap) { int n = cap - 1; n |= n >>> 1; n |= n >>> 2; n |= n >>> 4; n |= n >>> 8; n |= n >>> 16; return (n < 0) ? 1 : (n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : n + 1; }
说明:>>> 操作符表示无符号右移,高位取0。
2、public HashMap(int initialCapacity)型
/** * Constructs an empty <tt>HashMap</tt> with the specified initial * capacity and the default load factor (0.75). * * @param initialCapacity the initial capacity. * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative. */ public HashMap(int initialCapacity) { this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR); }
3、public HashMap()型
/** * Constructs an empty <tt>HashMap</tt> with the default initial capacity * (16) and the default load factor (0.75). */ public HashMap() { this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; // all other fields defaulted }
4、public HashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m)型
/** * Constructs a new <tt>HashMap</tt> with the same mappings as the * specified <tt>Map</tt>. The <tt>HashMap</tt> is created with * default load factor (0.75) and an initial capacity sufficient to * hold the mappings in the specified <tt>Map</tt>. * * @param m the map whose mappings are to be placed in this map * @throws NullPointerException if the specified map is null */ public HashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) { this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; putMapEntries(m, false); }
说明:putMapEntries(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m, boolean evict)函数将m的所有元素存入本HashMap实例中。
/** * Implements Map.putAll and Map constructor * * @param m the map * @param evict false when initially constructing this map, else * true (relayed to method afterNodeInsertion). */ final void putMapEntries(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m, boolean evict) { int s = m.size(); if (s > 0) { if (table == null) { // pre-size float ft = ((float)s / loadFactor) + 1.0F; int t = ((ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? (int)ft : MAXIMUM_CAPACITY); if (t > threshold) threshold = tableSizeFor(t); } else if (s > threshold) resize(); for (Map.Entry<? extends K, ? extends V> e : m.entrySet()) { K key = e.getKey(); V value = e.getValue(); putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, evict); } } }
四、hashMap源码分析-核心函数
JDK1.8以后的hashmap为什么在链表长度为8的时候变为红黑树
4.1 增:put和putVal函数----存储元素
/** * Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map. * If the map previously contained a mapping for the key, the old * value is replaced. * * @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated * @param value value to be associated with the specified key * @return the previous value associated with <tt>key</tt>, or * <tt>null</tt> if there was no mapping for <tt>key</tt>. * (A <tt>null</tt> return can also indicate that the map * previously associated <tt>null</tt> with <tt>key</tt>.) */ public V put(K key, V value) { return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true); }
putVal函数
/** * Implements Map.put and related methods * * @param hash hash for key * @param key the key * @param value the value to put * @param onlyIfAbsent if true, don't change existing value * @param evict if false, the table is in creation mode. * @return previous value, or null if none */ final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict) { HashMap.Node<K,V>[] tab; HashMap.Node<K,V> p; int n, i; //判断tab是否为空 if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) //为空,构建tab n = (tab = resize()).length; //(n - 1) & hash 按位与运算得到tab的索引值,判断该索引值处是否有元素 if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null) //该索引值处无元素,构建Node节点放入桶中(桶中的第一个元素,位于数组中),存储key-value tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null); else { //该索引值处有元素(对应桶中的第一个元素,位于tab数组中) HashMap.Node<K,V> e; K k; //比较桶中的第一个元素(数组中)与要存储的元素的hash值和key值 if (p.hash == hash && ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) //相等(key值相同),将桶中的第一个元素赋值给e e = p; //hash值不相等,存储在链表或是红黑树中 else if (p instanceof HashMap.TreeNode) //存储在红黑树中(此时p所在的桶中的那条链表(Node节点)已经转换成了红黑树(TreeNode节点)了) e = ((HashMap.TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value); else { //存储在链表中 for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) { //判断桶中的第一个元素是否有next节点 if ((e = p.next) == null) { //为null,没有next节点,构建Node,赋值给p.next(p关联起来形成链表结构) p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null); //链表中的节点数量大于阈值,将那条链表转换成红黑树 if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st treeifyBin(tab, hash); //跳出循环 break; } //判断链表中的节点的key值与要存储的key值是否相等 if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) //相等,跳出循环(此时e == p.next) break; //用于遍历链表中的节点,和e = p.next结合,可以遍历链表中的所有节点 p = e; } } if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key //要存储的key找到了对应的mapping,替换value并返回oldValue V oldValue = e.value; if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null) //onlyIfAbsent为false或者旧值为null,替换 e.value = value; //访问后回调 afterNodeAccess(e); //返回oldValue return oldValue; } } //结构性修改加一 ++modCount; //map中实际元素的大小大于阈值则进行扩容 if (++size > threshold) resize(); //插入后回调 afterNodeInsertion(evict); //no existing mapping for key,返回null值 return null; }
说明:HashMap并没有直接提供putVal接口给用户调用,而是提供的put函数,而put函数就是通过putVal来插入元素的。
举例:
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Map map = new HashMap(); map.put("zhangsan", "zhangsan"); map.put("lisi", "lisi"); map.put("wangwu", "wangwu"); map.put("zhaoliu", "zhaoliu"); map.put("caocao", "caocao"); map.put("liubei", "liubei"); map.put("sunquan", "sunquan"); map.put("guanyu", "guanyu"); map.put("zhangfei", "zhangfei"); map.put("zhugeliang", "zhugeliang"); map.put("zhubajie", "zhubajie"); map.put("sunwukong", "sunwukong"); map.put("tangseng", "tangseng"); map.put("shaseng", "shaseng"); System.out.println(map); } }
结果:
{lisi=lisi, zhangfei=zhangfei, shaseng=shaseng, zhaoliu=zhaoliu, liubei=liubei, tangseng=tangseng, sunquan=sunquan, sanzhang=sanzhang, zhugeliang=zhugeliang, sunwukong=sunwukong, zhubajie=zhubajie, guanyu=guanyu, wangwu=wangwu, caocao=caocao}
说明:可以看到,获取元素的顺序与put的顺序不一致。这里列出key值、hash(key)值和在数组tab中的索引index(i = (n - 1) & hash),并用图示说明上述元素在hashMap中的分布:
key hash(key) index(i = (n - 1) & hash) zhangsan -1432577304 8 lisi 3322017 1 wangwu -795083590 10 zhaoliu -323235449 7 caocao -1367733222 10 liubei -1102508889 7 sunquan -1856616245 11 guanyu -1235148906 6 zhangfei -1432573310 2 zhugeliang 466938860 12 zhubajie -871240751 1 sunwukong -1589103089 15 tangseng -556007510 10 shaseng 2054237254 6
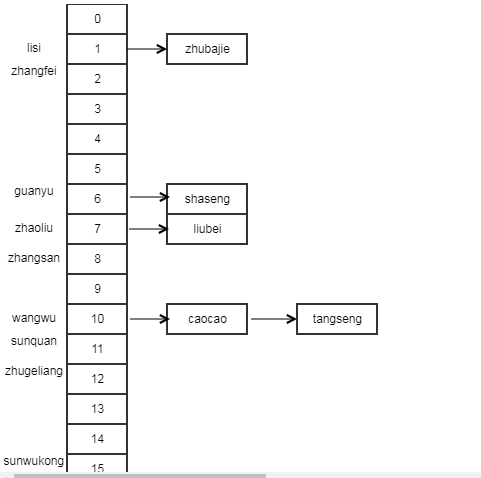
4.2 删:remove和removeNode函数----删除元素
/** * Removes the mapping for the specified key from this map if present. * * @param key key whose mapping is to be removed from the map * @return the previous value associated with <tt>key</tt>, or * <tt>null</tt> if there was no mapping for <tt>key</tt>. * (A <tt>null</tt> return can also indicate that the map * previously associated <tt>null</tt> with <tt>key</tt>.) */ public V remove(Object key) { Node<K,V> e; return (e = removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true)) == null ? null : e.value; }
removeNode函数
/** * Implements Map.remove and related methods * * @param hash hash for key * @param key the key * @param value the value to match if matchValue, else ignored * @param matchValue if true only remove if value is equal * @param movable if false do not move other nodes while removing * @return the node, or null if none */ final HashMap.Node<K,V> removeNode(int hash, Object key, Object value, boolean matchValue, boolean movable) { HashMap.Node<K,V>[] tab; HashMap.Node<K,V> p; int n, index; //判断table表是否为空 if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && (p = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) { HashMap.Node<K,V> node = null, e; K k; V v; if (p.hash == hash && ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) //得到要移除的元素是桶中的第一个元素(位于数组中) node = p; else if ((e = p.next) != null) { if (p instanceof HashMap.TreeNode) //要移除的元素位于红黑树中 node = ((HashMap.TreeNode<K,V>)p).getTreeNode(hash, key); else { //要移除的元素位于链表中 do { if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) { //链表中匹配到了要移除的元素 node = e; break; } //p存储链表中要移除节点的前一个节点 p = e; } while ((e = e.next) != null); } } //至此,要移除的元素node已经找到,;判断是根据key移除还是根据key和value移除 if (node != null && (!matchValue || (v = node.value) == value || (value != null && value.equals(v)))) { if (node instanceof HashMap.TreeNode) //node节点为红黑树节点,调用treeNode的方法移除 ((HashMap.TreeNode<K,V>)node).removeTreeNode(this, tab, movable); else if (node == p) //node节点是桶中的第一个元素,将node.next变成桶中的第一个元素 tab[index] = node.next; else //node节点在链表中,p存储的是要移除节点的前一个节点,将其的next由指向node转为指向node的next p.next = node.next; //结构性修改加一 ++modCount; //元素个数减一 --size; //删除后回调 afterNodeRemoval(node); return node; } } return null; }
说明:hashMap中并没有直接提供removeNode接口给用户使用,而是通过remove(Object key)函数和remove(Object key,Object value)函数,再调用removeNode来获取元素的。removeNode函数主要完成两方面的事情。一、找到要remove的元素(桶中第一个元素、红黑树中、链表中)。二、根据一中元素所在的位置做相应的移除操作。
举例:
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Map map = new HashMap(); map.put("zs1", "zhangsan1"); map.put("zs2", "zhangsan2"); map.put("zs3", "zhangsan3"); map.put("zs4", "zhangsan4"); map.put("zs5", "zhangsan5"); System.out.println("remove之前:=========" + map); Object value = map.remove("zs1"); System.out.println("所移除元素的value:==========" + value); System.out.println("remove之后:=========" + map); } }
结果:
remove之前:========={zs2=zhangsan2, zs1=zhangsan1, zs4=zhangsan4, zs3=zhangsan3, zs5=zhangsan5}
所移除元素的value:==========zhangsan1
remove之后:========={zs2=zhangsan2, zs4=zhangsan4, zs3=zhangsan3, zs5=zhangsan5}
图示说明remove前后元素在链表中位置:remove zs1(桶中的第一个元素)和remove zs4(链表中的元素)

4.3 改:putVal函数----修改元素
详见4.1,与添加元素是同一个操作
4.4 查:get和getNode函数----获取元素
/** * Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped, * or {@code null} if this map contains no mapping for the key. * * <p>More formally, if this map contains a mapping from a key * {@code k} to a value {@code v} such that {@code (key==null ? k==null : * key.equals(k))}, then this method returns {@code v}; otherwise * it returns {@code null}. (There can be at most one such mapping.) * * <p>A return value of {@code null} does not <i>necessarily</i> * indicate that the map contains no mapping for the key; it's also * possible that the map explicitly maps the key to {@code null}. * The {@link #containsKey containsKey} operation may be used to * distinguish these two cases. * * @see #put(Object, Object) */ public V get(Object key) { Node<K,V> e; return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value; }
getNode函数
/** * Implements Map.get and related methods * * @param hash hash for key * @param key the key * @return the node, or null if none */ final HashMap.Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) { HashMap.Node<K,V>[] tab; HashMap.Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k; //判断table是否为空 if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && (first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) { //table不为空并将桶中的第一个元素(位于数组中)赋值给first if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node ((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) //根据hash值和key判断是桶中的第一个元素(位于table数组中) return first; //不是桶中的第一个元素 if ((e = first.next) != null) { if (first instanceof HashMap.TreeNode) //要找的Node节点位于红黑树中 return ((HashMap.TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key); //位于链表中,将e.next赋值给e,循环获取和key匹配的Node节点 do { if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) return e; } while ((e = e.next) != null); } } //table为空,返回null return null; }
说明:hashMap中并没有直接提供getNode接口给用户使用,而是通过get函数,再通过get函数调用getNode来获取元素的。
4.5 扩容:reSize函数----hashMap的扩容
/** * Initializes or doubles table size. If null, allocates in * accord with initial capacity target held in field threshold. * Otherwise, because we are using power-of-two expansion, the * elements from each bin must either stay at same index, or move * with a power of two offset in the new table. * * @return the table */ final HashMap.Node<K,V>[] resize() { //保存原table HashMap.Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table; //获取原table的容量 int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length; //获取原table的阈值 int oldThr = threshold; //定义新table的容量和阈值 int newCap, newThr = 0; //原table容量大于0 if (oldCap > 0) { if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) { //原table的容量已经达到最大值,不再进行扩容,直接返回原table threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE; return oldTab; } //原table的容量未达最大值 else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY) //容量翻倍,使用左移,效率更高 newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold 阈值翻倍 } //原table的容量 == 0,再进行原阈值方面的判断 else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold //原阈值大于0,新table的容量 == 原阈值 newCap = oldThr; else { // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults //原table的容量 == 0,原阈值 == 0,那么新table的容量和阈值使用默认的容量(16)和阈值(12) newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY; newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY); } if (newThr == 0) { //原table的阈值大于0且新table的阈值等于0,定义新table的阈值 //举例:public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor)构造hashMap时,适用此种情况 float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor; newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ? (int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE); } //至此,新table的容量和阈值都已经取值完成。 //将新table的阈值赋值给hashMap的属性threshold threshold = newThr; @SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"}) //初始化table Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap]; table = newTab; //判断原table是否为空 if (oldTab != null) { for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) { Node<K,V> e; if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) { oldTab[j] = null; if (e.next == null)//说明桶中只有一个元素(位于数组中) newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e;//重新将原数组的值放入新数组中 else if (e instanceof TreeNode)//该桶中的node节点类型是treeNode,红黑树,打乱重新分配 ((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap); else { // preserve order //桶中的元素是链表结构,重新rehash链表,即将链表拆分成两条 Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null; Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null; Node<K,V> next; do { next = e.next; //以e.hash & oldCap是否为零来拆分该链表中的元素 if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) { if (loTail == null) loHead = e; else loTail.next = e;//重新指向该node节点中的next节点 loTail = e; } else { if (hiTail == null) hiHead = e; else hiTail.next = e;//重新指向该node节点中的next节点 hiTail = e; } } while ((e = next) != null); if (loTail != null) { //将rehash后的原链表的最后一个元素loTail的next属性置为null loTail.next = null; //原链表在table数组中的索引位置没有改变 newTab[j] = loHead; } if (hiTail != null) { //将rehash后的新生成的链表的最后一个元素hiTail的next属性置为null hiTail.next = null; //将hiHead置于newTab中,形成新的链表结构 newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead; } } } } } //返回扩容后的newTab return newTab; }
说明:进行扩容,会伴随着一次重新hash分配,并且会遍历hash表中所有的元素,是非常耗时的。在编写程序中,要尽量避免resize。hashMap的扩容函数主要完成两方面的事情。一、生成新table的容量和阈值。二、将原table中的元素置于新生成的table中。
图示说明扩容前后元素的分布,假如链表中555,888,112的hash&oldCap == 0,其余都不等于0
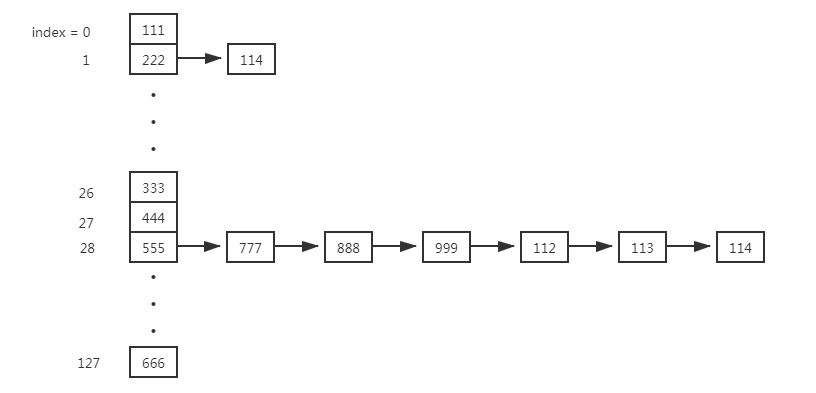
扩容后

关于扩容时红黑树的切分,以这篇文章中红黑树的插入与删除map的size = 128,index = 26中的红黑树为例进行拆分
测试代码
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException { Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<String, String>(); for (int i = 0; i < 65; i++) { map.put("sdf"+ String.valueOf(i),"s" + String.valueOf(i)); if(getHashCodeIndex("sdf"+ String.valueOf(i)) == 26){ System.out.println("index=======26时的key:" + "sdf"+ String.valueOf(i)); } } map.put("caocao","11"); map.put("sevennnn","22"); map.put("hate","33"); map.put("happyy","44"); map.put("hapqw","55"); map.put("mg","66"); map.put("vqv","77"); map.put("vaf","88"); for (int i = 0; i < 23; i++) { map.put("qwe"+ String.valueOf(i),"q" + String.valueOf(i)); if(getHashCodeIndex("qwe"+ String.valueOf(i)) == 26){ System.out.println("index=======26时的key:" + "qwe"+ String.valueOf(i)); } } //进行扩容 map.put("qwe23","q23"); } /** * @Description table大小为128,添加元素时在数组中的下标index * @Param [key] * @return int * @date 2020/8/28 14:32 * @auther Administrator */ public static int getHashCodeIndex(String key){ int h; h = key.hashCode(); int hash = h ^ (h >>> 16); return 127 & hash; } }
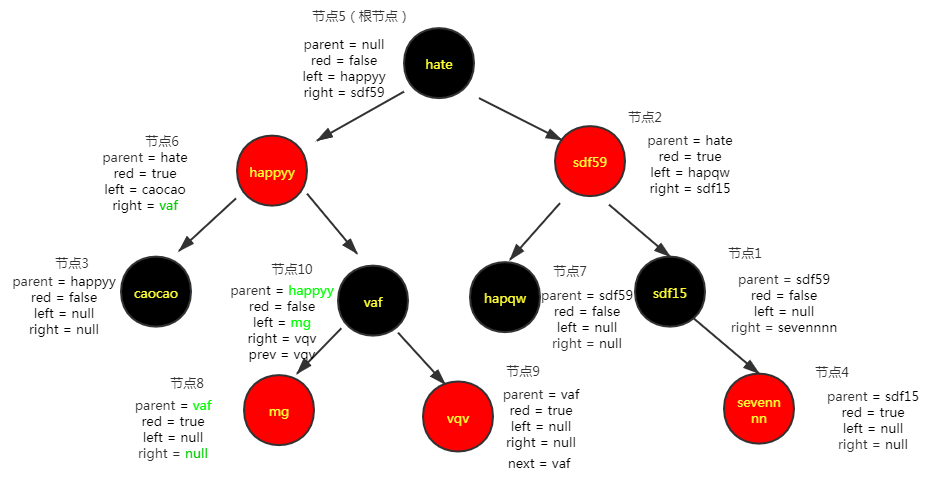
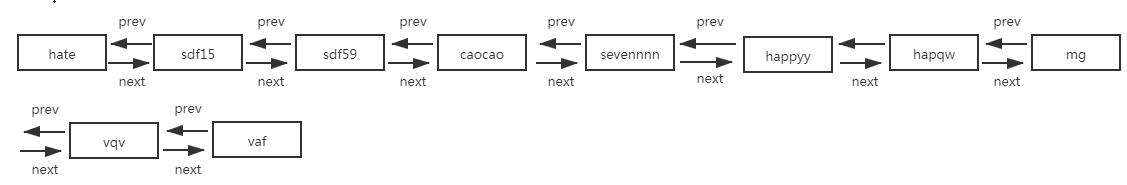
链表转化成红黑树时,原链表的顺序仍被保留(红黑树的根节点会被移动到链表的第一位),此外,红黑树中还维护了节点间的prev属性。
各节点之间的双向链表如下,这样的结构为红黑树的切分以及红黑树转成链表做好了铺垫
当添加地97个元素的时候进行扩容,红黑树切分代码如下
/** * Splits nodes in a tree bin into lower and upper tree bins, * or untreeifies if now too small. Called only from resize; * see above discussion about split bits and indices. * * @param map the map * @param tab the table for recording bin heads * @param index the index of the table being split * @param bit the bit of hash to split on */ final void split(HashMap<K,V> map, Node<K,V>[] tab, int index, int bit) { TreeNode<K,V> b = this; // Relink into lo and hi lists, preserving order TreeNode<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null; TreeNode<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null; int lc = 0, hc = 0; for (TreeNode<K,V> e = b, next; e != null; e = next) { next = (TreeNode<K,V>)e.next; e.next = null; if ((e.hash & bit) == 0) {//重新分配红黑树在数组中的位置,切分成两棵树 if ((e.prev = loTail) == null) loHead = e; else loTail.next = e; loTail = e; ++lc; } else { if ((e.prev = hiTail) == null) hiHead = e; else hiTail.next = e; hiTail = e; ++hc; } } if (loHead != null) {//切分后树的节点数<=6时,将红黑树转为链表 if (lc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) tab[index] = loHead.untreeify(map); else { tab[index] = loHead; if (hiHead != null) // (else is already treeified) loHead.treeify(tab);//因为原红黑树已经切分成两个红黑树,需要维护红黑树的平衡 } } if (hiHead != null) { if (hc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) tab[index + bit] = hiHead.untreeify(map); else { tab[index + bit] = hiHead; if (loHead != null) hiHead.treeify(tab); } } }
切分之后
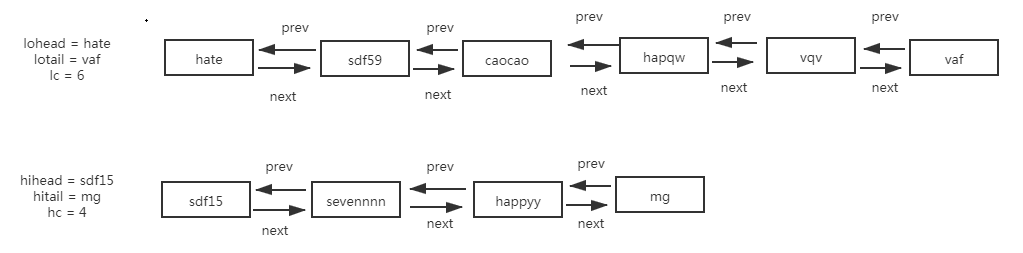
切分后树中节点数<=6,红黑树将转成链表。
五、总结
5.1再谈HashCode的重要性
前面讲到了,HashMap中对Key的HashCode要做一次rehash,防止一些糟糕的Hash算法生成的糟糕的HashCode,那么为什么要防止糟糕的HashCode?糟糕的HashCode意味着的是Hash冲突,即多个不同的Key可能得到的是同一个HashCode,糟糕的Hash算法意味着的就是Hash冲突的概率增大,这意味着HashMap的性能将下降,表现在两方面:
1、有10个Key,可能6个Key的HashCode都相同,另外四个Key所在的Entry均匀分布在table的位置上,而某一个位置上却连接了6个Entry。这就失去了HashMap的意义,HashMap这种数据结构性高性能的前提是,Entry均匀地分布在table位置上,但现在确是1 1 1 1 6的分布。所以,我们要求HashCode有很强的随机性,这样就尽可能地可以保证了Entry分布的随机性,提升了HashMap的效率。
2、HashMap在一个某个table位置上遍历链表的时候的代码:
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k)))
看到,由于采用了"&&"运算符,因此先比较HashCode,HashCode都不相同就直接pass了,不会再进行equals比较了。HashCode因为是int值,比较速度非常快,而equals方法往往会对比一系列的内容,速度会慢一些。Hash冲突的概率大,意味着equals比较的次数势必增多,必然降低了HashMap的效率了。参考:HashCode的作用。
5.2 hashMap和hashTable的区别
1、Hashtable是线程安全的,Hashtable所有对外提供的方法都使用了synchronized,也就是同步,而HashMap则是线程非安全的。
2、Hashtable不允许空的value,空的value将导致空指针异常,而HashMap则无所谓,没有这方面的限制。
hashTable的put源码:
public synchronized V put(K key, V value) { // Make sure the value is not null if (value == null) { throw new NullPointerException(); } ................. ................. }
参考资料: