前一篇我们已经讲过了Collectin是存放单值的最大接口,
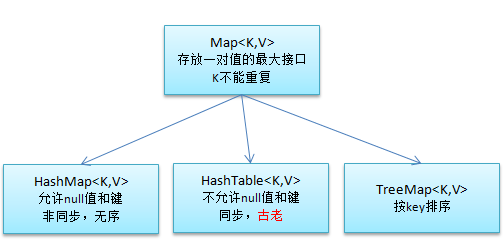
可以看到Map接口和其主要之类的关系图如下:
快速访问 HashMap HashTable TreeMap Map输出
那Map就是存放一对值的最大接口。此类的定义如下:
·public interface Map<K,V>
·K:此映射所维护的键的类型
·V:映射值的类型
Map<K,V>接口中提供的主要方法:
| No. | 方法 | 类型 | 说明 |
| 1 | public boolean containsKey(Object key) | 普通 | 判断是否含有指定键的元素 |
| 2 | public boolean containsValue(Object value) | 普通 | 判断是否含有指定值的元素 |
| 3 | public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() | 普通 | 返回此映射中包含的映射关系的集合 |
| 4 | public boolean equals(Object o) | 普通 | 判断是否和自指定元素相等 |
| 5 | public V get(Object key) | 普通 | 根据键值取得指定的值 |
| 6 | public Set<K> keySet() | 普通 | 取得全部键 |
| 7 | public V put(K key,V value) | 普通 | 向集合中加入指定键值 |
| 8 | public void putAll(Map<? extends K,? extends V> m) | 普通 | 向集合中加入指定的一组键值 |
| 9 | public V remove(Object key) | 普通 | 根据键删除指定键值 |
| 10 | public int size() | 普通 | 取得集合大小 |
| 11 | public Collection<V> values() | 普通 | 取得全部值 |
此类的定义如下:
public class HashMap<K,V>extends AbstractMap<K,V>implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable
此类里允许null的键和值,是非同步的,除此之外和HashTable基本上是相同的。并且是无序的。
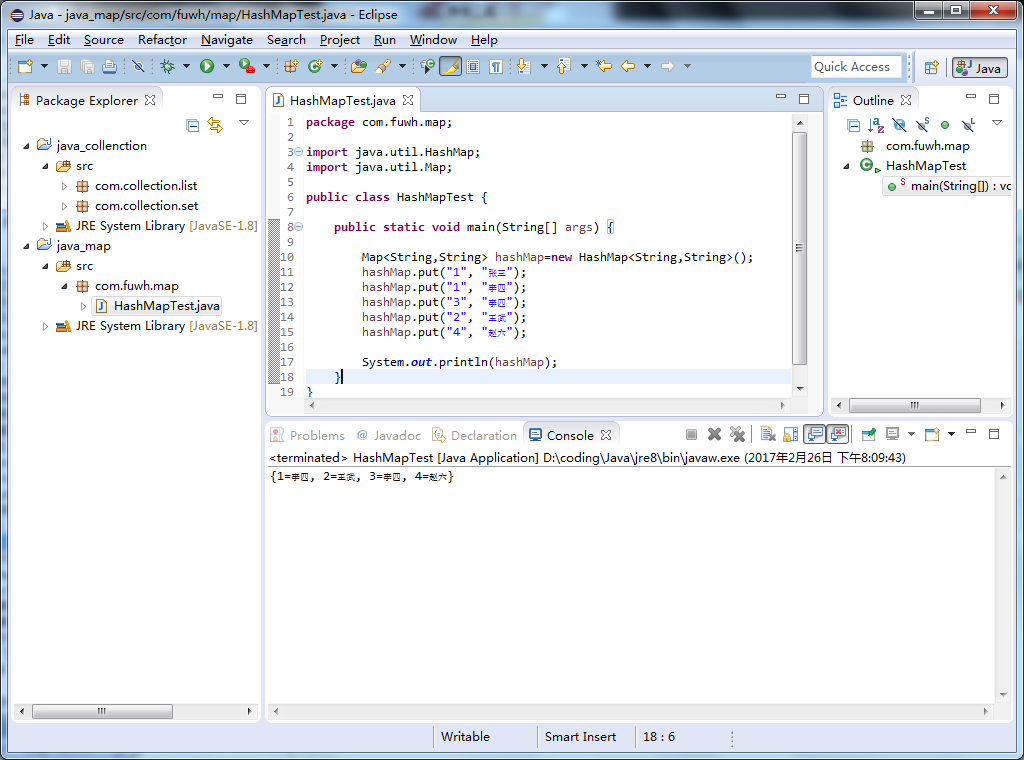
实例:

package com.fuwh.map; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; public class HashMapTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Map<String,String> hashMap=new HashMap<String,String>(); hashMap.put("1", "张三"); hashMap.put("1", "李四"); hashMap.put("3", "李四"); hashMap.put("2", "王武"); hashMap.put("4", "赵六"); System.out.println(hashMap); } }
这个类和Vector是同一时代的。
基本上使用也差不多。
实例:

package com.fuwh.map; import java.util.Hashtable; import java.util.Map; public class HashTableTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Map<String,String> hashTable=new Hashtable<String,String>(); hashTable.put("1", "张三"); hashTable.put("1", "李四"); hashTable.put("3", "李四"); hashTable.put("2", "王武"); hashTable.put("4", "赵六"); System.out.println(hashTable); } }

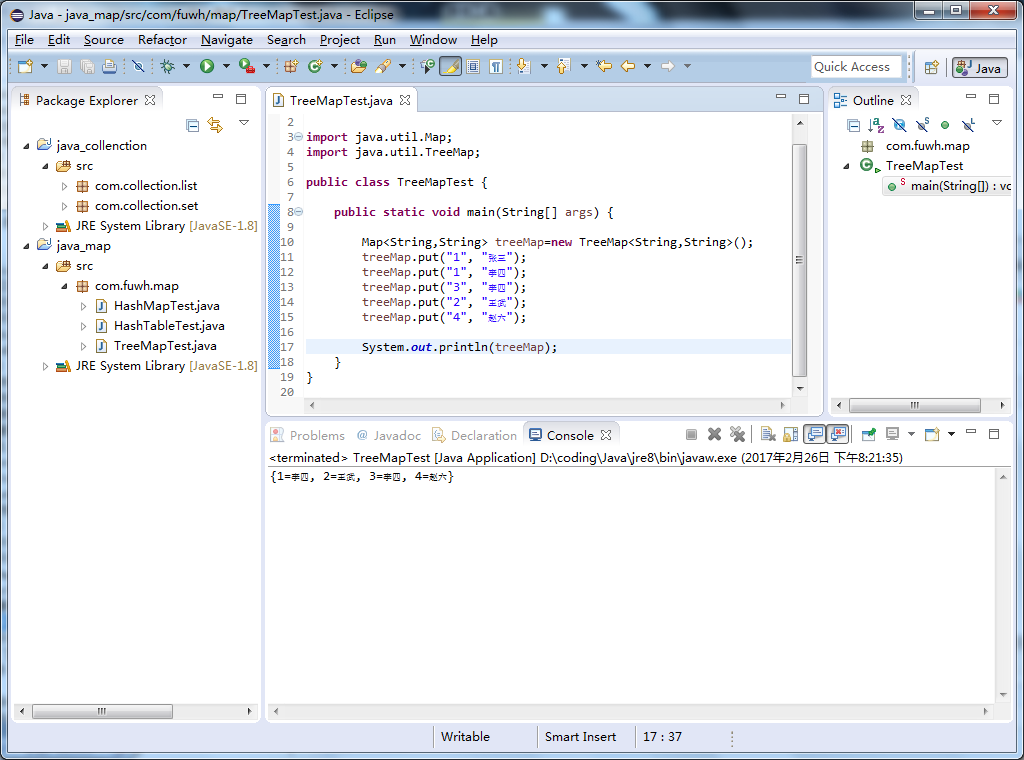
该类是基于红黑树的原理对其按照key的自然顺序排序。
实例:

package com.fuwh.map; import java.util.Map; import java.util.TreeMap; public class TreeMapTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Map<String,String> treeMap=new TreeMap<String,String>(); treeMap.put("1", "张三"); treeMap.put("1", "李四"); treeMap.put("3", "李四"); treeMap.put("2", "王武"); treeMap.put("4", "赵六"); System.out.println(treeMap); } }
虽然说集合都应该使用Iterator来输出。但是Map不能直接使用Iterator来输出。因为没有提供iterator()方法。
查看Map接口,可以发现,在此接口中有一个嵌套类,定义如下:
public static interface Map.Entry<K,V>
其实在Map中存放的虽然是键值对,实际上存放的是一个个的Map.Entry对象。
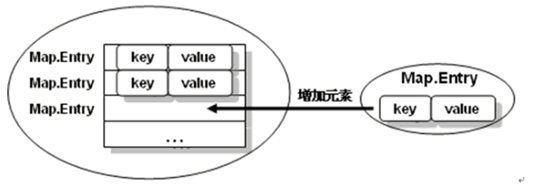
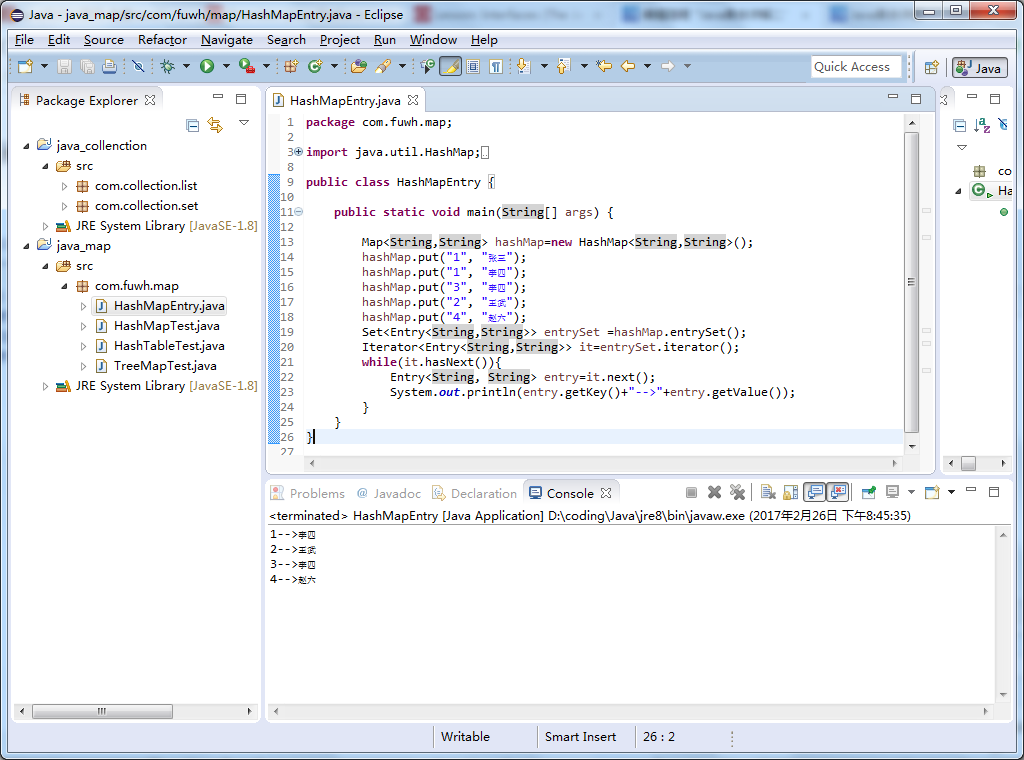
那么,就使用Map.Entry来对Map进行输出。
实例:

package com.fuwh.map; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Map.Entry; import java.util.Set; public class HashMapEntry { public static void main(String[] args) { Map<String,String> hashMap=new HashMap<String,String>(); hashMap.put("1", "张三"); hashMap.put("1", "李四"); hashMap.put("3", "李四"); hashMap.put("2", "王武"); hashMap.put("4", "赵六"); Set<Entry<String,String>> entrySet =hashMap.entrySet(); Iterator<Entry<String,String>> it=entrySet.iterator(); while(it.hasNext()){ Entry<String, String> entry=it.next(); System.out.println(entry.getKey()+"-->"+entry.getValue()); } } }
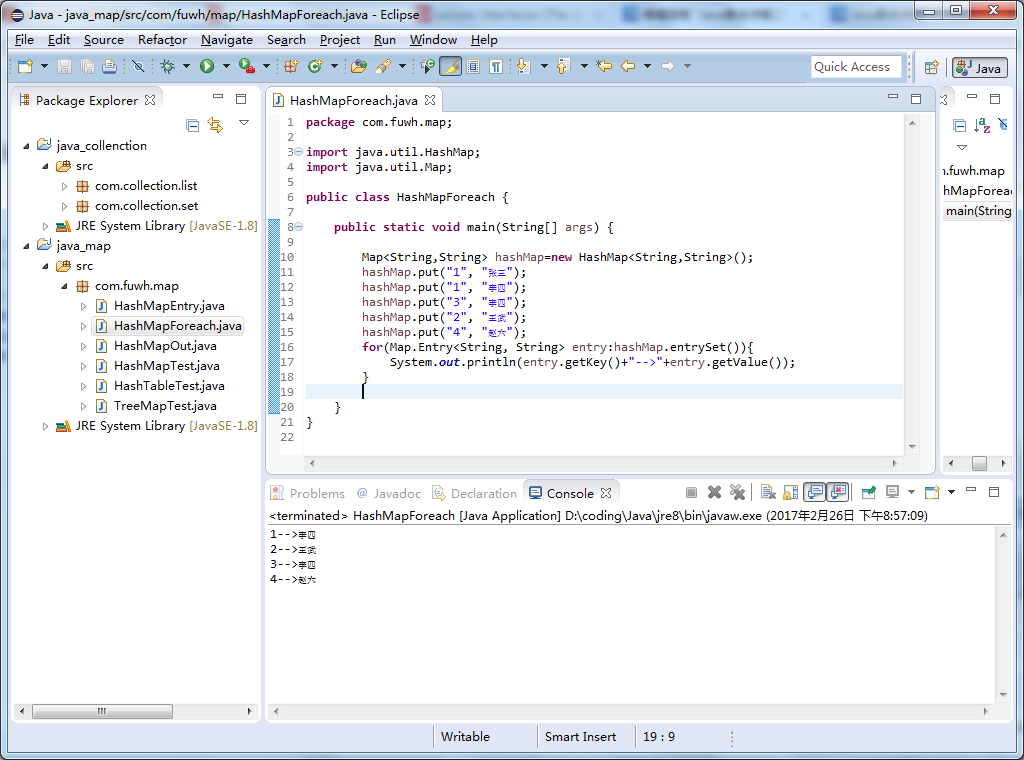
使用foreach输出:

package com.fuwh.map; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; public class HashMapForeach { public static void main(String[] args) { Map<String,String> hashMap=new HashMap<String,String>(); hashMap.put("1", "张三"); hashMap.put("1", "李四"); hashMap.put("3", "李四"); hashMap.put("2", "王武"); hashMap.put("4", "赵六"); for(Map.Entry<String, String> entry:hashMap.entrySet()){ System.out.println(entry.getKey()+"-->"+entry.getValue()); } } }
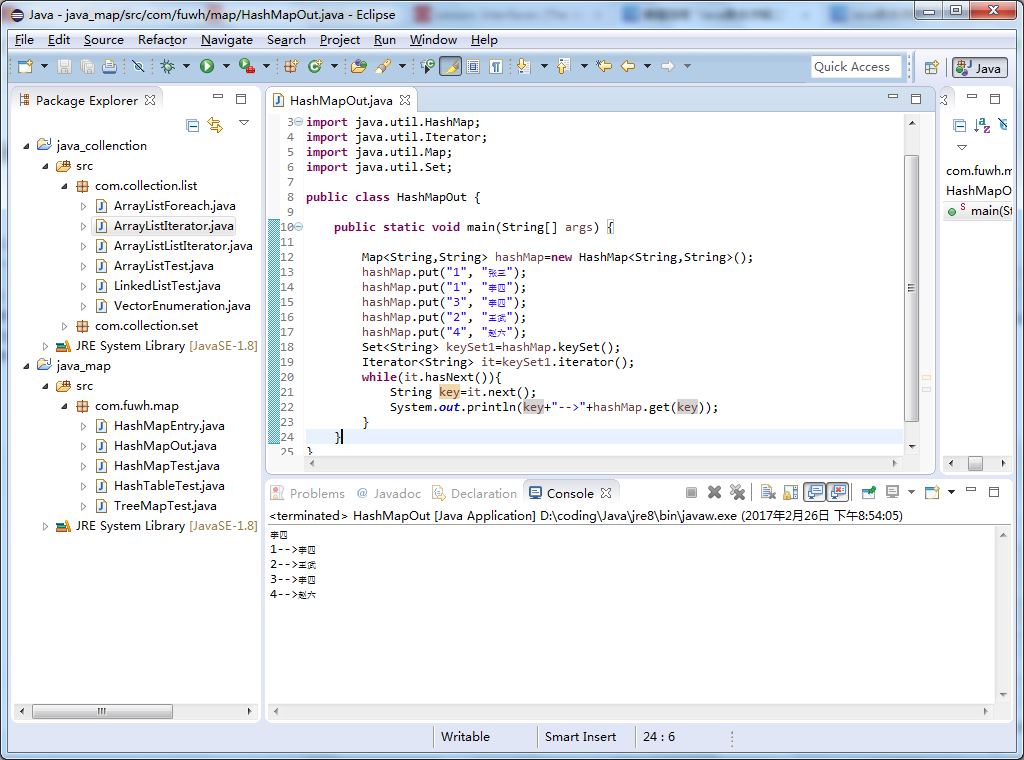
另一种输出方式:

package com.fuwh.map; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Set; public class HashMapOut { public static void main(String[] args) { Map<String,String> hashMap=new HashMap<String,String>(); hashMap.put("1", "张三"); hashMap.put("1", "李四"); hashMap.put("3", "李四"); hashMap.put("2", "王武"); hashMap.put("4", "赵六"); Set<String> keySet1=hashMap.keySet(); Iterator<String> it=keySet1.iterator(); while(it.hasNext()){ String key=it.next(); System.out.println(key+"-->"+hashMap.get(key)); } } }