工作队列,用于多个消费者从队列中消费多个消息。
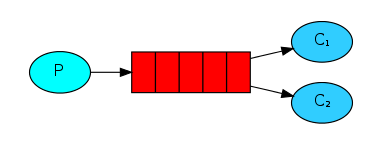
工作队列(又称:任务队列)背后的主要思想是避免立即执行资源密集型任务,并且必须等待它完成。相反,我们安排任务稍后完成。我们将任务封装 为消息并将其发送到队列。在后台运行的工作进程将弹出任务并最终执行作业。当您运行许多工作程序时,它们之间将共享任务。
这个概念在Web应用程序中特别有用,因为在短的HTTP请求窗口中无法处理复杂的任务。
工作队列程序
生产者发送消息:
/**
* @author Hayson
* @date 2018/11/23 13:39
* @description rabbitmq生产者发送多条消息
*/
public class Send {
final static String QUEUE = "helloWorld";
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
send();
}
public static void send() throws IOException, TimeoutException {
Connection connection = ConnectionUtils.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 没声明交换器,使用默认交换器
channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE, false, false, false, null);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
String message = "Hello World! " + i;
//发送消息,指定发送交换器(""则为自带默认交换器)
channel.basicPublish("", QUEUE, null, message.getBytes("UTF-8"));
System.out.println("发送消息:" + message);
}
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
}
消费者接收消息1:
/**
* @author Hayson
* @date 2018/11/23 13:41
* @description rabbitmq消费者接收消息1
*/
public class Receiver2 {
final static String QUEUE = "helloWorld";
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
recevier();
}
public static void recevier() throws IOException, TimeoutException {
Connection connection = ConnectionUtils.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE, false, false, false, null);
Consumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body)
throws IOException {
String message = new String(body, "UTF-8");
System.out.println("接收到消息:" + message);
}
};
channel.basicConsume(QUEUE, true, consumer);
//channel.close();
//connection.close();
}
}
消费者接收消息2:
/**
* @author Hayson
* @date 2018/11/23 13:41
* @description rabbitmq消费者接收消息2
*/
public class Receiver2 {
final static String QUEUE = "helloWorld";
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
recevier();
}
public static void recevier() throws IOException, TimeoutException {
Connection connection = ConnectionUtils.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE, false, false, false, null);
Consumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body)
throws IOException {
String message = new String(body, "UTF-8");
System.out.println("接收到消息:" + message);
}
};
channel.basicConsume(QUEUE, true, consumer);
//channel.close();
//connection.close();
}
}
先启动上面两个消费者客户端监听队列消息,后启动生产者发送消息,结果如下:
生产者:
发送消息:Hello World! 0
发送消息:Hello World! 1
发送消息:Hello World! 2
发送消息:Hello World! 3
发送消息:Hello World! 4
消费者1:
接收到消息:Hello World! 0
接收到消息:Hello World! 2
接收到消息:Hello World! 4
消费者2:
接收到消息:Hello World! 1
接收到消息:Hello World! 3
可以看到,RabbitMQ将按顺序将每条消息发送给下一个消费者。平均而言,每个消费者将获得相同数量的消息。这种分发消息的方式称为轮询法。上面还可以发送更多的消息和添加更多的消费者监听队列。