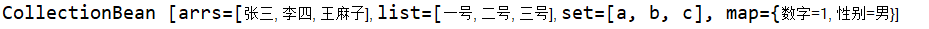1.掌握spring的属性注入的方法:
1.1构造方法注入普通值---------<constructor-arg>标签的使用
首先新建一个类

package spring.day1.demo3; public class car { private String name; private double price; public car(String name, Double price) { this.name = name; this.price = price; } @Override public String toString() { return "car [name=" + name + ", price=" + price + "]"; } }
在编写applicationContext2.xml

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!-- =======================引入spring的关于bean的约束 ========================= --> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- ================spring属性注入=============================== --> <!-- 构造方法注入 --> <bean id="car" class="spring.day1.demo3.car"> <constructor-arg name="name" value="宝马"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg name="price" value="500000"></constructor-arg> </bean> </beans>
在编写测试类SpringDemo3

package spring.day1.demo3; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class springDemo3 { @Test public void demo1() { ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext2.xml"); car bean = (car) applicationContext.getBean("car"); System.out.println(bean); } }
运行结果如下

1.2set方法注入普通值和对象属性(ref的使用)------<property>标签的使用
新建一个类car2

package spring.day1.demo3; public class car2 { private String name; private double price; public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public void setPrice(double price) { this.price = price; } @Override public String toString() { return "car2 [name=" + name + ", price=" + price + "]"; } }
新建一个Employee类

package spring.day1.demo3; public class employee { private String name; private car2 car; public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public void setCar(car2 car) { this.car = car; } @Override public String toString() { return "Employee [name=" + name + ", car=" + car + "]"; } }
在applicationContext2.xml中加入以下

<!-- set方法对car2注入普通值 --> <bean id="car2" class="spring.day1.demo3.car2"> <property name="name" value="奔驰"></property> <property name="price" value="600000"></property> </bean> <!-- set方法注入对象 --> <bean id="employee" class="spring.day1.demo3.employee"> <property name="name" value="张三"></property> <property name="car" ref="car2"></property> </bean>
在测试类SpringDemo3加入以下

@Test public void demo2() { ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext2.xml"); employee bean = (employee) applicationContext.getBean("employee"); System.out.println(bean); }
运行截图如下

1.3SPEL方式注入普通值和对象值(Spring3.0以后)
SpEL:Spring Expression Language,Spring的表达式语言。
语法格式:#{SPEL}

新建一个类carInfo

package spring.day1.demo3; public class carInfo { private String name; private double price; public String getName() { return "小三轮儿"; } public double getPrice() { return Math.random()*1000; } }
修改applicationContext2.xml为如下

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!-- =======================引入spring的关于bean的约束 ========================= --> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- ================spring属性注入=============================== --> <!-- 构造方法注入 --> <bean id="car" class="spring.day1.demo3.car"> <constructor-arg name="name" value="宝马"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg name="price" value="500000"></constructor-arg> </bean> <!-- set方法对car2注入普通值 --> <!-- <bean id="car2" class="spring.day1.demo3.car2"> <property name="name" value="奔驰"></property> <property name="price" value="600000"></property> </bean> --> <!-- set方法注入对象 --> <!-- <bean id="employee" class="spring.day1.demo3.employee"> <property name="name" value="张三"></property> <property name="car" ref="car2"></property> </bean> --> <!-- SPEL方式 --> <bean id="carInfo" class="spring.day1.demo3.carInfo"></bean> <bean id="car2" class="spring.day1.demo3.car2"> <property name="name" value="#{carInfo.name}"></property> <property name="price" value="#{carInfo.getPrice()}"></property> </bean> </beans>
在测试类SpringDemo3加入以下

@Test public void demo3() { ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext2.xml"); car2 bean = (car2) applicationContext.getBean("car2"); System.out.println(bean); }
运行截图如下

1.4P名称空间方式注入普通值和对象(Spring2.5以后)了解

2.集合属性注入(了解)
1.新建CollectionBean类
2.在applicationContext2.xml中加入如下代码
3.新建测试类测试

<!-- =======================spring集合属性的注入============================ --> <bean id="collectionBean" class="zcc.spring.demo5.CollectionBean"> <!-- 数组类型 --> <property name="arrs"> <list> <value>张三</value> <value>李四</value> <value>王麻子</value> </list> </property> <!-- List集合类型 --> <property name="list"> <list> <value>一号</value> <value>二号</value> <value>三号</value> </list> </property> <!-- Set集合类型 --> <property name="set"> <set> <value>a</value> <value>b</value> <value>c</value> </set> </property> <!-- Map集合类型 --> <property name="map"> <map> <entry key="数字" value="1"></entry> <entry key="性别" value="男"></entry> </map> </property> </bean>

package zcc.spring.demo5; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Set; /* * 集合属性的注入 */ public class CollectionBean { private String []arrs; private List<String> list; private Set<String> set; private Map<String,String> map; public void setArrs(String[] arrs) { this.arrs = arrs; } public void setList(List<String> list) { this.list = list; } public void setSet(Set<String> set) { this.set = set; } public void setMap(Map<String, String> map) { this.map = map; } @Override public String toString() { return "CollectionBean [arrs=" + Arrays.toString(arrs) + ", list=" + list + ", set=" + set + ", map=" + map + "]"; } }

package zcc.spring.demo5; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; /* * 集合类型的属性注入 */ public class SpringDemo5 { @Test public void demo1() { //创建spring的工厂来实例化xml中所有的bean对象 ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); CollectionBean bean = (CollectionBean) applicationContext.getBean("collectionBean"); System.out.println(bean); } }