TProtocol
TProtocol定义了消息怎么进行序列化和反序列化的。
TProtocol的类结构图如下:

TBinaryProtocol:二进制编码格式;
TCompactProtocol:高效率,密集的二进制编码格式,使用了zigzag压缩算法,使用了类似于ProtocolBuffer的Variable-Length Quantity (VLQ) 编码方式;
TTupleProtocol:继承于TCompactProtocol,C++中不支持,Java中支持;
TJSONProtocol:JSON格式;
TProtocolFactory接口:只有getProtocol一个方法,用于通过一个TTransport对象创建一个TProtocol对象;TProtocolFactory接口的实现类都在TProtocol子类中。
TProtocol
TProtocol是所有消息协议的父类,定义了公用的抽象方法。
public abstract class TProtocol { @SuppressWarnings("unused") private TProtocol() {} protected TTransport trans_;//Transport protected TProtocol(TTransport trans) { trans_ = trans; } public TTransport getTransport() { return trans_; } /** * Writing methods.写方法 */ //TMessage表示一个请求,发送请求时调用的方法 public abstract void writeMessageBegin(TMessage message) throws TException; public abstract void writeMessageEnd() throws TException; //TStruct表示一个对象,写对象时调用的方法 public abstract void writeStructBegin(TStruct struct) throws TException; public abstract void writeStructEnd() throws TException; //TField表示一个字段,写字段时调用的方法 public abstract void writeFieldBegin(TField field) throws TException; public abstract void writeFieldEnd() throws TException; //写字段结束标志调用的方法 public abstract void writeFieldStop() throws TException; //写TMap时调用的方法 public abstract void writeMapBegin(TMap map) throws TException; public abstract void writeMapEnd() throws TException; //写TList时调用的方法 public abstract void writeListBegin(TList list) throws TException; public abstract void writeListEnd() throws TException; //写TSet时调用的方法 public abstract void writeSetBegin(TSet set) throws TException; public abstract void writeSetEnd() throws TException; //String和基本数据类型的写 public abstract void writeBool(boolean b) throws TException; public abstract void writeByte(byte b) throws TException; public abstract void writeI16(short i16) throws TException; public abstract void writeI32(int i32) throws TException; public abstract void writeI64(long i64) throws TException; public abstract void writeDouble(double dub) throws TException; public abstract void writeString(String str) throws TException; //将buf中的数据写出 public abstract void writeBinary(ByteBuffer buf) throws TException; /** * Reading methods.读方法 */ public abstract TMessage readMessageBegin() throws TException; public abstract void readMessageEnd() throws TException; public abstract TStruct readStructBegin() throws TException; public abstract void readStructEnd() throws TException; public abstract TField readFieldBegin() throws TException; public abstract void readFieldEnd() throws TException; public abstract TMap readMapBegin() throws TException; public abstract void readMapEnd() throws TException; public abstract TList readListBegin() throws TException; public abstract void readListEnd() throws TException; public abstract TSet readSetBegin() throws TException; public abstract void readSetEnd() throws TException; public abstract boolean readBool() throws TException; public abstract byte readByte() throws TException; public abstract short readI16() throws TException; public abstract int readI32() throws TException; public abstract long readI64() throws TException; public abstract double readDouble() throws TException; public abstract String readString() throws TException; public abstract ByteBuffer readBinary() throws TException; public void reset() {} public Class<? extends IScheme> getScheme() { return StandardScheme.class; } }
TBinaryProtocol
TBinaryProtocol是二进制编码。
public class TBinaryProtocol extends TProtocol { private static final TStruct ANONYMOUS_STRUCT = new TStruct(); //版本号 protected static final int VERSION_MASK = 0xffff0000;//掩码 protected static final int VERSION_1 = 0x80010000;//版本号 protected boolean strictRead_ = false;//是否严格读 protected boolean strictWrite_ = true;//是否严格写 protected int readLength_; protected boolean checkReadLength_ = false; //工厂类 public static class Factory implements TProtocolFactory { protected boolean strictRead_ = false; protected boolean strictWrite_ = true; protected int readLength_; public Factory() { this(false, true); } public Factory(boolean strictRead, boolean strictWrite) { this(strictRead, strictWrite, 0); } public Factory(boolean strictRead, boolean strictWrite, int readLength) { strictRead_ = strictRead; strictWrite_ = strictWrite; readLength_ = readLength; } //通过TTransport实例获取一个TBinaryProtocol实例 public TProtocol getProtocol(TTransport trans) { TBinaryProtocol proto = new TBinaryProtocol(trans, strictRead_, strictWrite_); if (readLength_ != 0) { proto.setReadLength(readLength_); } return proto; } } public TBinaryProtocol(TTransport trans) { this(trans, false, true); } public TBinaryProtocol(TTransport trans, boolean strictRead, boolean strictWrite) { super(trans); strictRead_ = strictRead; strictWrite_ = strictWrite; } /** * 写方法 */ //发送一个请求,最终转换为对基本数据类型的写 public void writeMessageBegin(TMessage message) throws TException { if (strictWrite_) {// int version = VERSION_1 | message.type;//版本号和消息类型与运算 writeI32(version);//调用writeI32写版本号 writeString(message.name);//调用writeString写方法名 writeI32(message.seqid);//调用writeI32写序列号 } else { writeString(message.name); writeByte(message.type); writeI32(message.seqid); } } public void writeMessageEnd() {} public void writeStructBegin(TStruct struct) {} public void writeStructEnd() {} //写字段方法,最终转换为对基本数据类型的写 public void writeFieldBegin(TField field) throws TException { writeByte(field.type); writeI16(field.id); } public void writeFieldEnd() {} public void writeFieldStop() throws TException { writeByte(TType.STOP); } //写Map public void writeMapBegin(TMap map) throws TException { writeByte(map.keyType);//写Key类型 writeByte(map.valueType);//写value类型 writeI32(map.size);//写map大小 } public void writeMapEnd() {} //写List public void writeListBegin(TList list) throws TException { writeByte(list.elemType);//写元素类型 writeI32(list.size);//写list大小 } public void writeListEnd() {} //写Set public void writeSetBegin(TSet set) throws TException { writeByte(set.elemType);//写元素类型 writeI32(set.size);//写Set大小 } public void writeSetEnd() {} //写bool转换为写writeByte public void writeBool(boolean b) throws TException { writeByte(b ? (byte)1 : (byte)0); } private byte [] bout = new byte[1]; public void writeByte(byte b) throws TException { bout[0] = b; trans_.write(bout, 0, 1); } private byte[] i16out = new byte[2]; public void writeI16(short i16) throws TException { i16out[0] = (byte)(0xff & (i16 >> 8)); i16out[1] = (byte)(0xff & (i16)); trans_.write(i16out, 0, 2); } private byte[] i32out = new byte[4]; public void writeI32(int i32) throws TException { i32out[0] = (byte)(0xff & (i32 >> 24)); i32out[1] = (byte)(0xff & (i32 >> 16)); i32out[2] = (byte)(0xff & (i32 >> 8)); i32out[3] = (byte)(0xff & (i32)); trans_.write(i32out, 0, 4); } private byte[] i64out = new byte[8]; public void writeI64(long i64) throws TException { i64out[0] = (byte)(0xff & (i64 >> 56)); i64out[1] = (byte)(0xff & (i64 >> 48)); i64out[2] = (byte)(0xff & (i64 >> 40)); i64out[3] = (byte)(0xff & (i64 >> 32)); i64out[4] = (byte)(0xff & (i64 >> 24)); i64out[5] = (byte)(0xff & (i64 >> 16)); i64out[6] = (byte)(0xff & (i64 >> 8)); i64out[7] = (byte)(0xff & (i64)); trans_.write(i64out, 0, 8); } //写Double转换为writeI64 public void writeDouble(double dub) throws TException { writeI64(Double.doubleToLongBits(dub)); } //写String public void writeString(String str) throws TException { try { byte[] dat = str.getBytes("UTF-8");//转换为字节数组 writeI32(dat.length);//写数组长度 trans_.write(dat, 0, dat.length);//写数据 } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException uex) { throw new TException("JVM DOES NOT SUPPORT UTF-8"); } } //写ByteBuffer public void writeBinary(ByteBuffer bin) throws TException { int length = bin.limit() - bin.position(); writeI32(length); trans_.write(bin.array(), bin.position() + bin.arrayOffset(), length); } /** * Reading methods.读方法 */ //读一个请求,与写请求对应 public TMessage readMessageBegin() throws TException { int size = readI32();//读取消息的头部(4字节),可能是版本号和消息类型的组合,也可能直接是消息方法名 if (size < 0) { //如果小于0,就是二进制为第一位以1开头,说明是带有版本号的 //校验版本号是否正确 int version = size & VERSION_MASK; if (version != VERSION_1) { throw new TProtocolException(TProtocolException.BAD_VERSION, "Bad version in readMessageBegin"); } //三个参数依次为方法名、消息类型、消息序列号 return new TMessage(readString(), (byte)(size & 0x000000ff), readI32()); } else { if (strictRead_) { throw new TProtocolException(TProtocolException.BAD_VERSION, "Missing version in readMessageBegin, old client?"); } //readStringBody(size)为方法名,readByte()为消息类型,readI32()为消息序列号 return new TMessage(readStringBody(size), readByte(), readI32()); } } public void readMessageEnd() {} public TStruct readStructBegin() { return ANONYMOUS_STRUCT; } public void readStructEnd() {} public TField readFieldBegin() throws TException { byte type = readByte(); short id = type == TType.STOP ? 0 : readI16(); return new TField("", type, id); } public void readFieldEnd() {} public TMap readMapBegin() throws TException { return new TMap(readByte(), readByte(), readI32()); } public void readMapEnd() {} public TList readListBegin() throws TException { return new TList(readByte(), readI32()); } public void readListEnd() {} public TSet readSetBegin() throws TException { return new TSet(readByte(), readI32()); } public void readSetEnd() {} public boolean readBool() throws TException { return (readByte() == 1); } private byte[] bin = new byte[1]; public byte readByte() throws TException { if (trans_.getBytesRemainingInBuffer() >= 1) { byte b = trans_.getBuffer()[trans_.getBufferPosition()]; trans_.consumeBuffer(1); return b; } readAll(bin, 0, 1); return bin[0]; } private byte[] i16rd = new byte[2]; public short readI16() throws TException { byte[] buf = i16rd; int off = 0; if (trans_.getBytesRemainingInBuffer() >= 2) { buf = trans_.getBuffer(); off = trans_.getBufferPosition(); trans_.consumeBuffer(2); } else { readAll(i16rd, 0, 2); } return (short) (((buf[off] & 0xff) << 8) | ((buf[off+1] & 0xff))); } private byte[] i32rd = new byte[4]; public int readI32() throws TException { byte[] buf = i32rd; int off = 0; if (trans_.getBytesRemainingInBuffer() >= 4) { buf = trans_.getBuffer(); off = trans_.getBufferPosition(); trans_.consumeBuffer(4); } else { readAll(i32rd, 0, 4); } return ((buf[off] & 0xff) << 24) | ((buf[off+1] & 0xff) << 16) | ((buf[off+2] & 0xff) << 8) | ((buf[off+3] & 0xff)); } private byte[] i64rd = new byte[8]; public long readI64() throws TException { byte[] buf = i64rd; int off = 0; if (trans_.getBytesRemainingInBuffer() >= 8) { buf = trans_.getBuffer(); off = trans_.getBufferPosition(); trans_.consumeBuffer(8); } else { readAll(i64rd, 0, 8); } return ((long)(buf[off] & 0xff) << 56) | ((long)(buf[off+1] & 0xff) << 48) | ((long)(buf[off+2] & 0xff) << 40) | ((long)(buf[off+3] & 0xff) << 32) | ((long)(buf[off+4] & 0xff) << 24) | ((long)(buf[off+5] & 0xff) << 16) | ((long)(buf[off+6] & 0xff) << 8) | ((long)(buf[off+7] & 0xff)); } public double readDouble() throws TException { return Double.longBitsToDouble(readI64()); } public String readString() throws TException { int size = readI32(); if (trans_.getBytesRemainingInBuffer() >= size) { try { String s = new String(trans_.getBuffer(), trans_.getBufferPosition(), size, "UTF-8"); trans_.consumeBuffer(size); return s; } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) { throw new TException("JVM DOES NOT SUPPORT UTF-8"); } } return readStringBody(size); } public String readStringBody(int size) throws TException { try { checkReadLength(size); byte[] buf = new byte[size]; trans_.readAll(buf, 0, size); return new String(buf, "UTF-8"); } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException uex) { throw new TException("JVM DOES NOT SUPPORT UTF-8"); } } public ByteBuffer readBinary() throws TException { int size = readI32(); checkReadLength(size); if (trans_.getBytesRemainingInBuffer() >= size) { ByteBuffer bb = ByteBuffer.wrap(trans_.getBuffer(), trans_.getBufferPosition(), size); trans_.consumeBuffer(size); return bb; } byte[] buf = new byte[size]; trans_.readAll(buf, 0, size); return ByteBuffer.wrap(buf); } private int readAll(byte[] buf, int off, int len) throws TException { checkReadLength(len); return trans_.readAll(buf, off, len); } public void setReadLength(int readLength) { readLength_ = readLength; checkReadLength_ = true; } protected void checkReadLength(int length) throws TException { if (length < 0) { throw new TException("Negative length: " + length); } if (checkReadLength_) { readLength_ -= length; if (readLength_ < 0) { throw new TException("Message length exceeded: " + length); } } } }
其中TMessage表示一个请求,看一下TMessage的结构。
public final class TMessage { public TMessage() { this("", TType.STOP, 0); } public TMessage(String n, byte t, int s) { name = n; type = t; seqid = s; } public final String name;//方法名 public final byte type;//消息类型 public final int seqid;//消息序列号 @Override public String toString() { return "<TMessage name:'" + name + "' type: " + type + " seqid:" + seqid + ">"; } @Override public boolean equals(Object other) { if (other instanceof TMessage) { return equals((TMessage) other); } return false; } public boolean equals(TMessage other) { return name.equals(other.name) && type == other.type && seqid == other.seqid; } }
消息类型定义如下:
public final class TMessageType { public static final byte CALL = 1;//客户端请求 public static final byte REPLY = 2;//服务端响应 public static final byte EXCEPTION = 3;//服务端返回异常 public static final byte ONEWAY = 4;//单向RPC,客户端请求不要求服务端响应 }
TField表示一个字段,TField结构如下:
public class TField { public TField() { this("", TType.STOP, (short)0); } public TField(String n, byte t, short i) { name = n; type = t; id = i; } public final String name;//字段名 public final byte type;//字段类型 public final short id;//该字段在对象中的序号,与Thrift文件中的序号一致 public String toString() { return "<TField name:'" + name + "' type:" + type + " field-id:" + id + ">"; } public boolean equals(TField otherField) { return type == otherField.type && id == otherField.id; } }
Thrift定义的数据类型
public final class TType { public static final byte STOP = 0; public static final byte VOID = 1; public static final byte BOOL = 2; public static final byte BYTE = 3; public static final byte DOUBLE = 4; public static final byte I16 = 6; public static final byte I32 = 8; public static final byte I64 = 10; public static final byte STRING = 11; public static final byte STRUCT = 12; public static final byte MAP = 13; public static final byte SET = 14; public static final byte LIST = 15; public static final byte ENUM = 16; }
TProcessor
TProcessor是服务端Thrift框架转入用户逻辑的关键。先看一下类结构图。TProcessor对TServer中一次请求的InputProtocol和OutputTProtocol进行操作,也就是从InputProtocol中读出Client的请求数据,向OutputProtcol中写入用户逻辑的返回值。
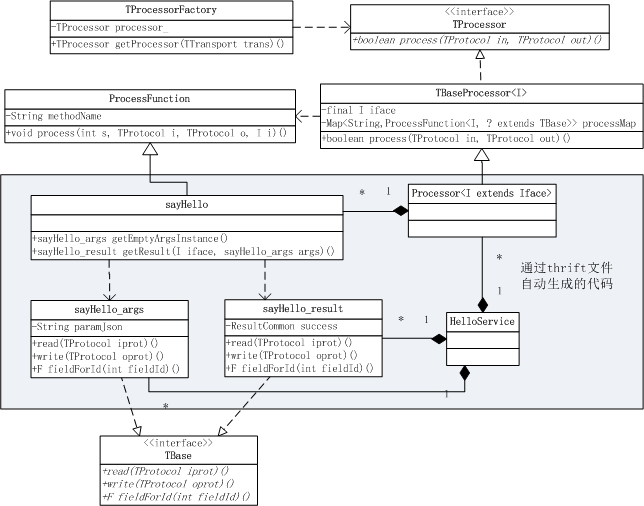
TProcessor接口:只有一个抽象方法process();
TBaseProcessor类:实现了TProcessor接口,给出了process()方法的具体实现;
Processor类:通过thrift文件自动生成的代码,继承了TBaseProcessor类,在Processor类内部为每一个方法生成了一个类,如sayHello类;
TProcessorFactory类:一个工厂类,返回一个TProcessor单例;
ProcessFunction类:处理函数抽象类。
HelloService类:由thrift文件自动生成的类,包含内部类Processor类、参数类、返回结果类等等。
TProcessor
public interface TProcessor { public boolean process(TProtocol in, TProtocol out) throws TException; }
TBaseProcessor
public abstract class TBaseProcessor<I> implements TProcessor { private final I iface;//业务逻辑实现的接口,接口中的方法即thrift文件中定义的方法 private final Map<String,ProcessFunction<I, ? extends TBase>> processMap;//处理方法Map,key为方法名,Value为方法对象 protected TBaseProcessor(I iface, Map<String, ProcessFunction<I, ? extends TBase>> processFunctionMap) { this.iface = iface; this.processMap = processFunctionMap; } @Override public boolean process(TProtocol in, TProtocol out) throws TException { TMessage msg = in.readMessageBegin();//读出客户端发的请求 ProcessFunction fn = processMap.get(msg.name);//根据方法名从processMap中找到处理方法 if (fn == null) { //如果找不到该方法,返回异常 TProtocolUtil.skip(in, TType.STRUCT); in.readMessageEnd(); TApplicationException x = new TApplicationException(TApplicationException.UNKNOWN_METHOD, "Invalid method name: '"+msg.name+"'"); out.writeMessageBegin(new TMessage(msg.name, TMessageType.EXCEPTION, msg.seqid)); x.write(out); out.writeMessageEnd(); out.getTransport().flush(); return true; } fn.process(msg.seqid, in, out, iface);//处理请求 return true; } }
ProcessFunction
Thrift将方法抽象为ProcessFunction类,每一个方法都会生成一个ProcessFunction类的子类。
public abstract class ProcessFunction<I, T extends TBase> { private final String methodName;//方法名 public ProcessFunction(String methodName) { this.methodName = methodName; } //处理请求 public final void process(int seqid, TProtocol iprot, TProtocol oprot, I iface) throws TException { T args = getEmptyArgsInstance();//获取一个参数实例(TBase子类的参数实例),由子类实现 try { args.read(iprot);//从iprot中读取参数,具体实现由thrift文件自动生成(见sayHello_args类) } catch (TProtocolException e) { //读取参数异常,返回异常 iprot.readMessageEnd(); TApplicationException x = new TApplicationException(TApplicationException.PROTOCOL_ERROR, e.getMessage()); oprot.writeMessageBegin(new TMessage(getMethodName(), TMessageType.EXCEPTION, seqid)); x.write(oprot); oprot.writeMessageEnd(); oprot.getTransport().flush(); return; } iprot.readMessageEnd(); TBase result = getResult(iface, args);//获取处理结果,此时调用业务逻辑,具体实现由thrift文件自动生成(见sayHello类) oprot.writeMessageBegin(new TMessage(getMethodName(), TMessageType.REPLY, seqid)); result.write(oprot);//将result写到oprot,具体实现由thrift文件自动生成(见sayHello_result类) oprot.writeMessageEnd(); oprot.getTransport().flush(); } //获取处理结果,调用业务逻辑,由子类实现 protected abstract TBase getResult(I iface, T args) throws TException; //获取一个参数实例,由子类实现 protected abstract T getEmptyArgsInstance(); public String getMethodName() { return methodName; } }
Processor
public static class Processor<I extends Iface> extends org.apache.thrift.TBaseProcessor<I> implements org.apache.thrift.TProcessor { private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Processor.class.getName()); public Processor(I iface) { super(iface, getProcessMap(new HashMap<String, org.apache.thrift.ProcessFunction<I, ? extends org.apache.thrift.TBase>>())); } protected Processor(I iface, Map<String, org.apache.thrift.ProcessFunction<I, ? extends org.apache.thrift.TBase>> processMap) { super(iface, getProcessMap(processMap)); } //初始化processMap,在Processor初始化时会调用该方法 private static <I extends Iface> Map<String, org.apache.thrift.ProcessFunction<I, ? extends org.apache.thrift.TBase>> getProcessMap(Map<String, org.apache.thrift.ProcessFunction<I, ? extends org.apache.thrift.TBase>> processMap) { processMap.put("sayHello", new sayHello()); return processMap; } //每个方法生成一个类 private static class sayHello<I extends Iface> extends org.apache.thrift.ProcessFunction<I, sayHello_args> { public sayHello() { super("sayHello"); } //获取空参数实例 protected sayHello_args getEmptyArgsInstance() { return new sayHello_args(); } //获取返回结果 protected sayHello_result getResult(I iface, sayHello_args args) throws org.apache.thrift.TException { sayHello_result result = new sayHello_result(); result.success = iface.sayHello(args.paramJson);//调用业务逻辑接口的sayHello方法, return result; } } }
最后总结一下TProcessor的处理流程:
1)TServer接收到请求后,调用TProcessor的process(TProtocol in, TProtocol out)方法进行处理;
2)TProcessor通过in.readMessageBegin()获取客户端请求,并根据请求方法名找到对应的ProcessFunction实例;
3)调用ProcessFunction的process方法;
首先从inTProtocol中读取参数,
然后通过调用getResult(iface, args)方法调用业务逻辑,获取到返回结果,
最后将返回结果写入到outTProtocol。