重点整理面积并的思想 以及PushUp的及时更新 还有就是cover的实现 以及建树每个节点存的信息(每个节点存的是一个线段的信息)
http://www.tuicool.com/articles/6Zf6J3 大致思想
再就是 得注意线段树维护的信息是什么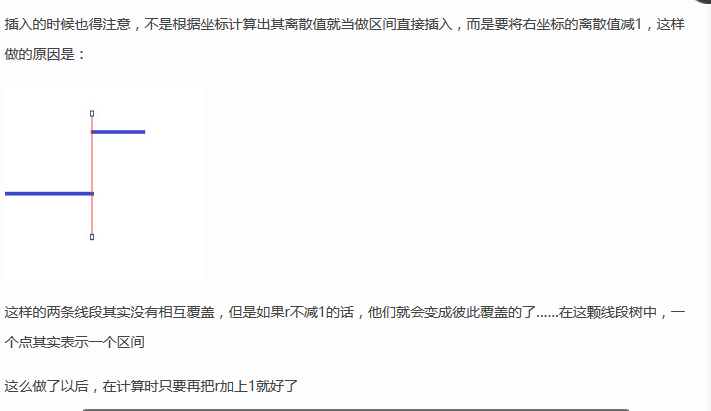
如图所示 一个点维护的是一段线段的长度
然后在对浮点数建树的时候 得用上离散化的思想
#include<cstdio> #include<string.h> #include<iostream> #define maxn 10005 #define lson l,m,rt<<1 #define rson m+1,r,rt<<1|1 #include<algorithm> using namespace std; struct node//区分线段树节点的值 以及线段树需要维护的值 { double x1,x2,y; int c; node(double x1=0,double x2=0,double y=0,int c=0):x1(x1),x2(x2),y(y),c(c){}//自定义函数 用来初始化赋值 bool friend operator<(node a,node b) { return a.y<b.y; } }; double sum2[maxn<<2],sum1[maxn<<2]; int cover[maxn<<2];//用来表示该段完全覆盖的次数 double x[maxn<<1]; void Pushup(int rt,int l,int r)//cover表示的是一个区间完全覆盖的次数 注意 是完全覆盖! { if(cover[rt]>=2) sum2[rt]=x[r]-x[l-1],sum1[rt]=x[r]-x[l-1];//当覆盖超过两次的时候 满足条件 直接计算 else { if(cover[rt]==1) { sum1[rt]=x[r]-x[l-1]; if(l==r) sum2[rt]=0; else sum2[rt]=sum1[rt<<1]+sum1[rt<<1|1];// 在确定这段已经完全覆盖的一次的时候 要看子段是否有覆盖一次的 有的话 加起来就是两次了 } else if(l==r) sum2[rt]=0,sum1[rt]=0; else sum1[rt]=sum1[rt<<1]+sum1[rt<<1|1],sum2[rt]=sum2[rt<<1]+sum2[rt<<1|1];// 这段确定一次都没有完全覆盖的时候 看子段是否有覆盖的情况 } } void build(int l,int r,int rt) { cover[rt]=0; if(l==r) { sum1[rt]=0; sum2[rt]=0; return; } int m=(l+r)/2; build(lson); build(rson); Pushup(rt,l,r); } void updata(int l,int r,int rt,int L,int R,int c) { if(L<=l&&r<=R) { cover[rt]+=c; Pushup(rt,l,r); return; } int m=(l+r)/2; if(L<=m) updata(lson,L,R,c); if(R>m) updata(rson,L,R,c); Pushup(rt,l,r); } int main() { int n,Case=1,t; node stu[maxn<<1]; cin>>t; while(t--) { scanf("%d",&n); for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { double x1,y1,x2,y2; scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf",&x1,&y1,&x2,&y2); stu[i*2]=node(x1,x2,y1,1);//底边为1 //扫描的时候 用来更改cover的值 stu[i*2+1]=node(x1,x2,y2,-1);//顶边为-1 x[i*2]=x1,x[i*2+1]=x2; } sort(x,x+2*n);/离散化第一步 排序 int nn=unique(x,x+2*n)-x;//第二步 去重 build(1,nn,1); sort(stu,stu+2*n);//按高度递增排序 double ans=0;
for(int i=0;i<2*n-1;i++) { int l=lower_bound(x,x+nn,stu[i].x1)-x+1;//二分是要在去重之后的长度进行的 int r=lower_bound(x,x+nn,stu[i].x2)-x; updata(1,nn,1,l,r,stu[i].c); ans+=(stu[i+1].y-stu[i].y)*sum2[1]; //当 stu[i+1].y-stu[i].y 的值不为0的时候 说明一层统计结束 sum【1】表示这层总线段长度
} printf("%.2lf ",ans); } return 0; }