头文件 #include<stack>
stack<int> s;
stack<char> s;//定义一个名字为s 的存int char的stack
基本指令
s.pop() 栈顶出栈。。
s.push(x) x入栈(无返回值的函数)
s.top() 访问栈顶元素
s.empty() 判断栈是否为空 是的话返回true
s.size() 计算栈中含有的元素。。while(s.size()) s.pop();多用来清空栈中的元素 好了 了解了基本用法 看一道题目。。
hdu 1022
As the new term comes, the Ignatius Train Station is very busy nowadays. A lot of student want to get back to school by train(because the trains in the Ignatius Train Station is the fastest all over the world ^v^). But here comes a problem, there is only one railway where all the trains stop. So all the trains come in from one side and get out from the other side. For this problem, if train A gets into the railway first, and then train B gets into the railway before train A leaves, train A can't leave until train B leaves. The pictures below figure out the problem. Now the problem for you is, there are at most 9 trains in the station, all the trains has an ID(numbered from 1 to n), the trains get into the railway in an order O1, your task is to determine whether the trains can get out in an order O2.
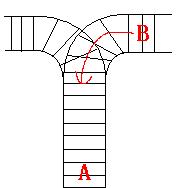
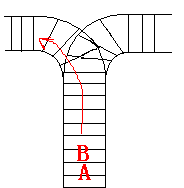
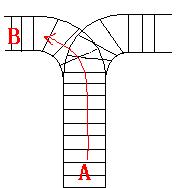



Input
The input contains several test cases. Each test case consists of an integer, the number of trains, and two strings, the order of the trains come in:O1, and the order of the trains leave:O2. The input is terminated by the end of file. More details in the Sample Input.
Output
The output contains a string "No." if you can't exchange O2 to O1, or you should output a line contains "Yes.", and then output your way in exchanging the order(you should output "in" for a train getting into the railway, and "out" for a train getting out of the railway). Print a line contains "FINISH" after each test case. More details in the Sample Output.
Sample Input
3 123 321
3 123 312
Sample Output
Yes.
in
in
in
out
out
out
FINISH
No.
FINISH
贴上代码#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
#include<string.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n,i,j;
int flag[100];
char in[100],out[100];
while(scanf("%d %s %s",&n,&in,&out)!=EOF)
{
memset(flag,0,sizeof(flag));
stack<char> s;
while(s.size()) s.pop();
i=j=0;
for(i;i<=n;)
{
if(s.empty()||(!s.empty()&&s.top()!=out[j]))
{
s.push(in[i]);
flag[i+j]++;
i++;
}
if(s.top()==out[j])
{
s.pop();
j++;
}
}
if(s.empty())
{
cout<<"Yes."<<endl;
for(i=0;i<n*2;i++)
{
if(flag[i]) cout<<"in"<<endl;
else cout<<"out"<<endl;
}
}
else cout<<"No."<<endl;
cout<<"FINISH"<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
#include<string.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n,i,j;
int flag[100];
char in[100],out[100];
while(scanf("%d %s %s",&n,&in,&out)!=EOF)
{
memset(flag,0,sizeof(flag));
stack<char> s;
while(s.size()) s.pop();
i=j=0;
for(i;i<=n;)
{
if(s.empty()||(!s.empty()&&s.top()!=out[j]))
{
s.push(in[i]);
flag[i+j]++;
i++;
}
if(s.top()==out[j])
{
s.pop();
j++;
}
}
if(s.empty())
{
cout<<"Yes."<<endl;
for(i=0;i<n*2;i++)
{
if(flag[i]) cout<<"in"<<endl;
else cout<<"out"<<endl;
}
}
else cout<<"No."<<endl;
cout<<"FINISH"<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
这是一道栈的入门题 要点有4个
1.如何判断入栈 出栈
当栈为空的时候 或者栈中的pop不是需要的元素的时候 入
当pop是需要的 出
2.如何设置循环的终止条件
一个只有n个数 所以入栈的次数只有n次 每次入栈 i++
3.标记的应用 人栈的标记值为1 由于每次入栈 出栈对应的i J都会++ 所以I+J就是需要标记的数
4.如何判断条件成立 s.empty()