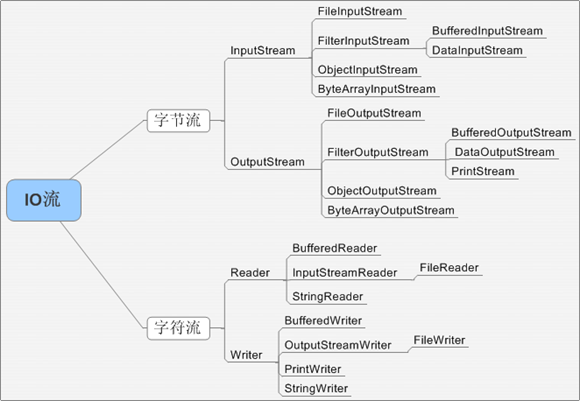
目录
- File
- InputStream
- OutputStream
- Writer
- Reader
- 流转换
- BufferedReader & BufferedWriter
- BufferedInputStream & BufferedOutputStream
- PrintStream
- ObjectStream
- ByteArrayStream
- DataStream
- StringStream
File类的使用
public static void main(String[] args) { //File.separator 表示分隔符 File file1 = new File("D:"+File.separator+"yyd"+File.separator+"cdut.txt"); //路径分隔符 // String s = File.pathSeparator; //文件是否存在 if(!file1.exists()){ try { //创建一个新文件 boolean b = file1.createNewFile(); System.out.println("创建文件:"+b); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } //删除文件 //System.out.println(file1.delete()); //得到文件的上一级路径 System.out.println(file1.getParent()); //判断一个路径是否是文件夹 System.out.println("是否是目录:"+file1.isDirectory()); ////判断一个路径是否是文件 System.out.println("是否是文件:"+file1.isFile()); File file2 = new File("d:\yydt"); //列出文件夹中的所有文件名 String[] fileName = file2.list(); for (String s : fileName) { System.out.println(s); } //列出文件夹中的所有文件,以File数组返回 File[] files = file2.listFiles(); for (File file : files) { System.out.println(file.getPath()+"---"+file.length()); } //创建文件夹 File file3 = new File("d:\zhangsan\lisi"); file3.mkdirs(); //重命名 File file4 = new File("d:\zhangsan\wangwu"); file3.renameTo(file4); }
IO
InputStream
/** * 字节输入流的读取方式三:每次读取指定大小的字节 */ public static void read3(){ try { File f = new File("d:\1.txt"); //构造一个字节输入流对象 InputStream in = new FileInputStream(f); //指定每次要读取的字节数组 byte[] bytes = new byte[10]; int len = -1;//每次读取的实际长度 StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); while((len = in.read(bytes))!=-1){ sb.append(new String(bytes,0,len)); } //关闭 in.close(); //输出 System.out.println(sb); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 字节输入流的读取方式二:一次性读取所有字节 */ public static void read2(){ try { File f = new File("d:\1.txt"); //构造一个字节输入流对象 InputStream in = new FileInputStream(f); //根据文件的大小构造字节数组 byte[] bytes = new byte[(int)f.length()]; int len = in.read(bytes); System.out.println(new String(bytes)); System.out.println("len="+len); //关闭 in.close(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 字节输入流的读取方式一:每次读取一个字节 */ public static void read1(){ try { //构造一个字节输入流对象 InputStream in = new FileInputStream("d:\1.txt"); int b = -1;//定义一个字节,-1表示没有数据 while((b=in.read())!=-1){ System.out.print((char)b); } //关闭 in.close(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { // read1(); // read2(); read3(); }
OutputStream
/** * 字节输出流的方式二:每次输出指定大小的字节 */ public static void write2() { try { // 创建一个文件字节输出流对象(参数true表示追加输出) OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("d:\1.txt", true); // String info = "hello,xiaobai"; String info = "one car come,one car go,two car pengpeng,one car die!"; byte[] bytes = info.getBytes(); out.write(bytes);// 输出一个字节数组 // out.write(bytes,0,5);//输出一个字节数组中的指定范围的字节 // 关闭流 out.close(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 字节输出流的方式一:每次输出一个字节 */ public static void write1() { try { // 创建一个文件字节输出流对象 OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("d:\1.txt"); String info = "hello,IO"; byte[] bytes = info.getBytes(); for (int i = 0; i < bytes.length; i++) { // 向文件中输出 out.write(bytes[i]); } // 关闭流 out.close(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { // write1(); write2(); System.out.println("success"); }
Writer
/** * 字符输出流方式一:以字符数组方式输出 */ public static void writer1(){ File f = new File("d:\2.txt"); try { //构造一个字符输出流对象(true表示追加输出) Writer out = new FileWriter(f,true); String info = "good good study,day day up!"; //向文件中输出 // out.write(info.toCharArray()); out.write(info); //关闭流 out.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { writer1(); }
Reader
/** * 字符输入流方式一:使用指定大小的字符数组输入 */ public static void reader1(){ File f = new File("d:\1.txt"); try { //构造一个字符输入流对象 Reader in = new FileReader(f); char[] cs = new char[20]; int len = -1; StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); while((len = in.read(cs))!=-1){ sb.append(new String(cs,0,len)); } //关闭流 in.close(); System.out.println(sb); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 使用字节流读取文本文件 */ public static void byteReader(){ File f = new File("d:\1.txt"); try { InputStream in = new FileInputStream(f); byte[] bytes = new byte[20]; int len = -1; StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); while((len = in.read(bytes))!=-1){ sb.append(new String(bytes,0,len)); } in.close(); System.out.println(sb); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { // byteReader(); reader1(); }
流转换
/** * 使用转换流,把字节流转换成字符流 */ public static void reader(){ try { //构造字节输入流 InputStream in = new FileInputStream("d:\1.txt"); //通过字节输入流构造一个字符输入流 Reader reader = new InputStreamReader(in); char[] cs = new char[50]; int len = -1; StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); while((len=reader.read(cs))!=-1){ sb.append(new String(cs,0,len)); } //关闭流 reader.close(); in.close(); System.out.println(sb); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 使用转换流,把字符流转换成字节流输出 * OutputStreamWriter */ public static void writer(){ try { //构造一个字节输出流 OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("d:\3.txt"); String info = "山不在高,有仙则名;学JAVA,没威哥不行"; //通过字节输出流构造一个字符输出流 Writer writer = new OutputStreamWriter(out); writer.write(info);//输出 //关闭流 writer.close(); out.close(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { // writer(); reader(); }
BufferedReader & BufferedWriter
/** * 使用缓冲流实现读取操作 */ public static void reader(){ try { Reader r = new FileReader("d:\5.txt"); //根据字符输入流构造一个字符缓中流 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(r); char[] cs = new char[512]; int len = -1; StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); while((len=br.read(cs))!=-1){ sb.append(new String(cs,0,len)); } br.close(); r.close(); System.out.println(sb); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 使用缓冲流实现写入操作 */ public static void write(){ try { Writer w = new FileWriter("d:\5.txt"); //根据字符输出流构造一个字符缓冲流 BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(w); bw.write("小白,怎么了,这是,被驴踢了吧"); bw.flush();//刷新 bw.close(); w.close(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { // write(); reader(); }
BufferedInputStream & BufferedOutputStream
public static void write(){ try { OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("d:\4.txt"); //根据字节输出流构造一个字节缓冲流 BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(out); String info = "good good study , day day up"; bos.write(info.getBytes()); bos.flush();//刷新缓冲区 bos.close(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 使用字节缓冲流进行读取操作 */ public static void input(){ try { InputStream in = new FileInputStream("d:\4.txt"); //根据字节输入流构造一个字节缓冲流 BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(in); Reader r = new InputStreamReader(bis); char[] cs = new char[512]; int len = -1; StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); while((len=r.read(cs))!=-1){ sb.append(new String(cs,0,len)); } r.close(); bis.close(); in.close(); System.out.println(sb); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { // input(); write(); }
PrintStream
/** * 使用PrintWriter打印流 */ public static void print2(){ try { BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("d:\2.txt")); PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(bw); pw.print(" ");//输出回车加换行符 pw.println(105); pw.println("张三李四王五"); pw.flush(); pw.close(); bw.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 使用PrintStream打印流 */ public static void print(){ try { OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("d:\1.txt"); BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(out); //构造字节打印流对象 PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(bos);// ps.println(3.14f); ps.println(188); ps.println(true); ps.println("好好学习,天天向上"); //关闭流 ps.flush(); out.close(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { // print(); print2(); }
ObjectStream
/** * 类通过实现 java.io.Serializable 接口以启用其序列化功能,标记接口,没有任何方法 */ public class Dog implements Serializable{ private String name; private transient int age; //使用transient关键字声明的属性将不会被序列化 public Dog() { super(); } public Dog(String name, int age) { super(); this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "Dog [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]"; } }
/** * 从文件中读取对象数组 */ public static void readerObject2(){ try { InputStream in = new FileInputStream("d:\obj.tmp"); //根据字节输入流构造一个对象流 ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(in); //读取一个对象 Dog[] dogs = (Dog[])ois.readObject(); //关闭 ois.close(); in.close(); for (Dog dog : dogs) { System.out.println(dog); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 把一组对象序列化到文件中 */ public static void writerObject2(){ try { OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("d:\obj.tmp"); //根据字节输出流构造一个对象流 ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(out); Dog[] dogs = {new Dog("小白",8),new Dog("小黑",2),new Dog("小红",4)}; // Dog dog1 = new Dog("小白",8); // Dog dog2 = new Dog("小黑",2); // Dog dog3 = new Dog("小红",4); oos.writeObject(dogs);//向文件写入对象 //关闭流 oos.close(); out.close(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 使用ObjectInputStream读取文件中的对象 */ public static void readerObject(){ try { InputStream in = new FileInputStream("d:\obj.tmp"); //根据字节输入流构造一个对象流 ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(in); //读取一个整数 int num = ois.readInt(); //读取一个对象 Dog dog = (Dog)ois.readObject(); //关闭 ois.close(); in.close(); System.out.println("num="+num); System.out.println(dog); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 使用ObjectOutputStream把对象写入文件中 */ public static void writerObject(){ try { OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("d:\obj.tmp"); //根据字节输出流构造一个对象流 ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(out); //输出数据 oos.writeInt(106); Dog dog = new Dog("小白",8); oos.writeObject(dog);//向文件写入对象 //关闭流 oos.close(); out.close(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { // writerObject(); // readerObject(); // writerObject2(); readerObject2(); }
ByteArrayStream
/** * 使用ByteArrayOutputStream写操作 */ public static void write(){ //创建一个字节数组输出流对象 ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); String info = "好好学习,天天向上!"; try { //往缓冲区中输出数据 baos.write(info.getBytes()); baos.write(10); // baos.toByteArray(); baos.close();//关闭无效 } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } //根据一个字节数组构造一个字节数组输入流 ByteArrayInputStream bais = new ByteArrayInputStream(baos.toByteArray()); byte[] bytes = new byte[512]; int len = -1; StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); try { while((len=bais.read(bytes))!=-1){ sb.append(new String(bytes,0,len)); } } catch (IOException e) { } System.out.println(sb); } public static void main(String[] args) { write(); }
DataStream
public static void reader(){ try { InputStream in = new FileInputStream("d:\3.txt"); //根据字节输入流构造一个数据输入流 DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(in); int flag = dis.readInt();//读取一个整数 String info = dis.readUTF();//读取一个UTF编码的字符串 //关闭流 dis.close(); in.close(); System.out.println("flag="+flag); System.out.println("info="+info); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void write(){ try { OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("d:\3.txt"); //根据字节输出流构造一个数据输出流 DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(out); dos.writeInt(1);//输出一个整数 dos.writeUTF("好好学习天天向上..."); dos.close(); out.close(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { // write(); reader(); }
StringStream
public static void writer(){ //写入操作 StringWriter sw = new StringWriter(); sw.write("好好学习。。天天向上 。。。"); //----------------------------------------- //读取操作,根据一个字符串去构造一个字符串输入流 StringReader sr = new StringReader(sw.toString()); char[] cs = new char[10]; int len = -1; try { while((len=sr.read(cs))!=-1){ System.out.print(new String(cs,0,len)); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { writer(); }
我是天王盖地虎的分割线