1.如何实现多线程
1.1实现Runnable接口,实现run()方法。
public class Main4 implements Runnable { public static void main(String[] args) { Main4 m = new Main4(); new Thread(m).start(); } @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { System.out.println(i); } } }
1.2继承Thread接口,重写run()方法。
public class Main4 extends Thread { public static void main(String[] args) { new Main4().start(); } @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { System.out.println(i); } } }
1.3实现Callable接口,实现call()方法。
public class Main4 implements Callable { public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { Callable c = new Main4(); FutureTask<Integer> ft = new FutureTask<>(c); new Thread(ft).start(); System.out.println(ft.get()); } @Override public Integer call() throws Exception { int i = 0; for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) {} return i; } }
2.Runnable、Thread、Callable三种方式实现多线程的区别
2.1Runnable
@FunctionalInterface public interface Runnable { public abstract void run(); }
Runnable接口很简单,里面只有一个抽象方法run()。run()方法里面的是这个线程要执行的内容。
2.2Thread
public class Thread implements Runnable { public Thread() { init(null, null, "Thread-" + nextThreadNum(), 0); } public Thread(Runnable target) { init(null, target, "Thread-" + nextThreadNum(), 0); } Thread(Runnable target, AccessControlContext acc) { init(null, target, "Thread-" + nextThreadNum(), 0, acc); } public Thread(ThreadGroup group, Runnable target) { init(group, target, "Thread-" + nextThreadNum(), 0); } public Thread(String name) { init(null, null, name, 0); } public Thread(ThreadGroup group, String name) { init(group, null, name, 0); } public Thread(ThreadGroup group, String name) { init(group, null, name, 0); } public Thread(Runnable target, String name) { init(null, target, name, 0); } public Thread(ThreadGroup group, Runnable target, String name) { init(group, target, name, 0); } public Thread(ThreadGroup group, Runnable target, String name, long stackSize) { init(group, target, name, stackSize); } }
Thread类实现了Runnable接口,因此我们继承Thread,实际上也是间接的实现了Runnable接口。
Thread中一共有9个构造函数,但是里面实际调用的分别是:
init(ThreadGroup g, Runnable target, String name, long stackSize)
init(ThreadGroup g, Runnable target, String name, long stackSize, AccessControlContext acc)
我们查看了第一个init()方法源码,在内部其实是调用了第二个init方法,将最后一个参数置空。因此我们只要详细看5个参数的init()方法即可。
private void init(ThreadGroup g, Runnable target, String name, long stackSize) { init(g, target, name, stackSize, null); //内部其实调用了另一个init方法 } private void init(ThreadGroup g, Runnable target, String name, long stackSize, AccessControlContext acc) { if (name == null) {throw new NullPointerException("name cannot be null"); } this.name = name; //指定线程名称 Thread parent = currentThread(); //获取当前线程 SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager(); if (g == null) { /* Determine if it's an applet or not */ /* If there is a security manager, ask the security manager what to do. */ if (security != null) { g = security.getThreadGroup(); //使用安全管理器要求的线程组 } /* If the security doesn't have a strong opinion of the matter use the parent thread group. */ if (g == null) { g = parent.getThreadGroup(); //安全性没有明确的要求,可以使用父类线程组。 } } /* checkAccess regardless of whether or not threadgroup is explicitly passed in. */ g.checkAccess(); /* * Do we have the required permissions? */ if (security != null) { if (isCCLOverridden(getClass())) { security.checkPermission(SUBCLASS_IMPLEMENTATION_PERMISSION); } } g.addUnstarted(); this.group = g; //线程组 this.daemon = parent.isDaemon(); //是否守护线程 this.priority = parent.getPriority(); //优先级 if (security == null || isCCLOverridden(parent.getClass())) //上下文类加载器 this.contextClassLoader = parent.getContextClassLoader(); else this.contextClassLoader = parent.contextClassLoader; this.inheritedAccessControlContext = acc != null ? acc : AccessController.getContext(); this.target = target; //将被执行的目标线程 setPriority(priority); //设置优先级(1-10),不在范围内则抛出异常。由于线程组的最大优先级可以设置,参数大于线程组的最大优先级,取线程组最大优先级。 if (parent.inheritableThreadLocals != null) this.inheritableThreadLocals = ThreadLocal.createInheritedMap(parent.inheritableThreadLocals); /* Stash the specified stack size in case the VM cares */ this.stackSize = stackSize; /* Set thread ID */ tid = nextThreadID(); //线程的唯一id }
2.3Callable
@FunctionalInterface public interface Callable<V> { V call() throws Exception; }
Callable接口也很简单,里面只有一个方法call()。
使用Callable时,需要使用FutureTask类进行调用。
查看FutureTask类的继承关系,可知其最上面也是实现了Runnable接口。
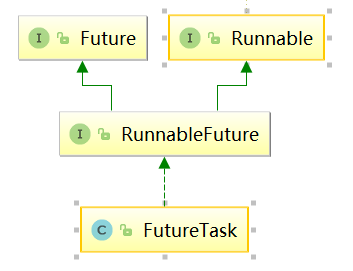
查看FutureTask的构造函数,一共有两个。
FutureTask(Callable<V> callable):futureTask内部有一个私有变量Callable,令其等于传入的callable。
FutureTask(Runnable runnable, V result):调用Executors的静态方法,创建内部一个实现了callable接口的内部类,call()方法执行Runnable的run(),执行成功后返回result。
源码如下:
public FutureTask(Callable<V> callable) { if (callable == null) throw new NullPointerException(); this.callable = callable; this.state = NEW; // ensure visibility of callable } public FutureTask(Runnable runnable, V result) { this.callable = Executors.callable(runnable, result); //见下方 this.state = NEW; // ensure visibility of callable }
public static <T> Callable<T> callable(Runnable task, T result) { if (task == null) throw new NullPointerException(); return new RunnableAdapter<T>(task, result); } static final class RunnableAdapter<T> implements Callable<T> { final Runnable task; final T result; RunnableAdapter(Runnable task, T result) { this.task = task; this.result = result; } public T call() { task.run(); return result; } }
在FutureTask中定义了运行状态一共有7种(注意它们各自的数值,会经常使用>=、<=等方式来处理逻辑走向):
/* * NEW -> COMPLETING -> NORMAL 新建->执行->完成 * NEW -> COMPLETING -> EXCEPTIONAL 新建->执行->异常 * NEW -> CANCELLED 新建->取消 * NEW -> INTERRUPTING -> INTERRUPTED 新建->中断运行->中断状态 */ private volatile int state; private static final int NEW = 0; private static final int COMPLETING = 1; private static final int NORMAL = 2; private static final int EXCEPTIONAL = 3; private static final int CANCELLED = 4; private static final int INTERRUPTING = 5; private static final int INTERRUPTED = 6;
FutureTask的run()方法,内部核心代码是调用了callable.call()。如果顺利执行,会执行set(result)方法,将结果保存到成员变量private Object outcome中。
public void run() { if (state != NEW || !UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, runnerOffset, null, Thread.currentThread())) return; try { Callable<V> c = callable; if (c != null && state == NEW) { V result; boolean ran; try { result = c.call(); ran = true; } catch (Throwable ex) { result = null; ran = false; setException(ex); } if (ran) set(result); } } finally { // runner must be non-null until state is settled to // prevent concurrent calls to run() runner = null; // state must be re-read after nulling runner to prevent // leaked interrupts int s = state; if (s >= INTERRUPTING) handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(s); } }
FutureTask的get()方法,在线程t1中调用线程t2的get()方法,可见如果t2的run()仍未执行完成,则会一直等待执行完成后,获取返回值,才会继续往下执行t1。
public V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { int s = state; if (s <= COMPLETING) s = awaitDone(false, 0L); //如果线程刚被新建,或正在运行,等待执行完成。 return report(s); //返回run()方法中保存的outcome } private int awaitDone(boolean timed, long nanos) throws InterruptedException { final long deadline = timed ? System.nanoTime() + nanos : 0L; //在线程类中,0通常用来代表不限制时间 WaitNode q = null; boolean queued = false; for (;;) { if (Thread.interrupted()) { removeWaiter(q); throw new InterruptedException(); } int s = state; if (s > COMPLETING) { if (q != null) q.thread = null; return s; } else if (s == COMPLETING) // cannot time out yet Thread.yield(); //仍在执行中,令当前线程让出cpu资源。因为通常是在一个线程t1里调用另一个线程t2的get()方法,即令t1让出cpu,t2可以参与竞争 else if (q == null) q = new WaitNode(); else if (!queued) queued = UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, waitersOffset, q.next = waiters, q); else if (timed) { nanos = deadline - System.nanoTime(); if (nanos <= 0L) { removeWaiter(q); return state; } LockSupport.parkNanos(this, nanos); } else LockSupport.park(this); } }
3总结
实际上不论是使用哪一种方式实现,最后调用时都是需要使用Thread类的start()方法进行调用。因此,线程的主要类,我们研究Thread类即可。
线程的状态state,在Thread类中以内部枚举的形式存在
public enum State { NEW, //新建状态,尚未执行start方法 RUNNABLE, //可运行状态,已经执行start方法,竞争cpu资源 BLOCKED, //阻塞状态,等待获取锁进入代码块 WAITING, //等待状态,线程进入此状态只有三种方法:wait()、join()、park(),注意这些方法都没有参数,即不会由于超时问题而重新变为可运行或执行状态 TIMED_WAITING, //定时等待状态,进入此方法的方式与waiting类似,但是该方法有时间限制,当达到指定时间后会重新变为Runnable,如sleep、wait(long)等 TERMINATED; //终止状态,线程已经执行完毕 }
几种常用方法介绍:
yield():当前线程暂停执行,让出cpu,重新竞争。有可能仍然是该线程竞争到cpu。
sleep(long):当前线程暂停执行(不释放锁),休眠指定毫秒数,其他线程竞争cpu,当指定时间过去,当前线程继续执行。
interrupt():中断当前线程,通常用来让内部是while(!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupt())的run()方法中断运行。
wait():令当前线程进入等待状态(释放锁),只能使用在synchronized块中。因此,当线程执行wait方法的时候一定是取得了锁。可以通过notify()或notifyAll()方法重新唤醒
join():通常是在一个线程t1里面调用另一个线程t2的join方法,当t1执行到这里的时候,会获取t2的锁并执行t2,直到t2执行完毕,再继续执行t1下面的步骤。
join(long):与join()类似,不同处在于t1最多只会等待long秒,当时间到达后,如果t2仍没有执行完毕,那么t1也会继续执行下面的步骤。
join()方法例子:
public class Main4 extends Thread { public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { Main4 m1 = new Main4(); Main4 m2 = new Main4(); m1.start(); m1.join(); System.out.println("---------------main---------------"); m2.start(); } @Override public void run() { int i = 0; for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "[i="+i+"]"); try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
如上程序,控制台会先打印m1线程的0-9,然后再打印"---main---",最后打印m2线程的0-9.
如果我们将m1.join()改为m1.join(1000),那么会先打印m1的0,这时达到参数1000ms,main线程会继续并行往下执行,打印"---main---",然后启动m2线程,m1与m2争夺cpu竞相打印。
需要注意的是,join(0)不是等待0ms,而是等价于join()方法。源码中join()内部只有一行代码:join(0)。
_