一、JSTL简介:
1.JSP标准标签库JSTL(JSP Standard Tag Library)是一个JSP标签集合,它封装了JSP应用的通用核心功能。
2.JSTL支持通用的、结构化的任务、比如迭代,条件判断,XML文档操作,国际化标签,SQL标签。除了这些,它还提供了一个框架来使用继承JSTL的自定义标签。
3.根据JSTL标签所提供的功能,可以将其分为5个类别,
1.核心标签
2.格式化标签
3.sql标签
4.XML标签
5.JSTL函数
下载地址:http://archive.apache.org/dist/jakarta/taglibs/standard/binaries/
安装步骤:
下载jakarta-taglibs-standard-1.1.2.zip ,拷贝其中的jar包到 web-info到lib目录下
在jsp头部包含<taglib>标签。
二、核心标签
1.引用核心标签库的语法如下:
<%@ taglib prefix = "c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
2.核心标签名称以及描述:
<c :out> 用于在jsp中显示数据,就像<%=...>
例子:
<ul>
<li> <c:out value="显示c:out标签"></c:out></li>
<li><c:out value="JSTLout的标签使用"></c:out></li>
</ul>
注意:下面这么写会只显示第一行,后面一行不显示。
<c:out value="显示c:out标签"></c:out>
<c:out value="JSTLout的标签使用"></c:out>
<c:set>用于保存数据
例子1:
<c:set value = "This is the first example of c:set" var = "first"></c:set>
<li><c:out value = "${first}"></c:out></li>
例子2:
<c:set var = "second">
This is the second example of c set
</c:set>
<li><c:out value = "${second}"></c:out></li>
<c:remove>用于移除一个变量,可以指定这个变量的作用域,若未指定,则默认为变量第一次出现的作用域,这个标签不是特别有用,不过可以用来保存JSP完成清理工作
例子:
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c" %>
<html>
<head>
<title><c:remove> Tag Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<c:set var="salary" scope="session" value="${2000*2}"/>
<p>Before Remove Value: <c:out value="${salary}"/></p>
<c:remove var="salary"/>
<p>After Remove Value: <c:out value="${salary}"/></p>
</body>
</html>
<c:catch>主要用于处理产生错误的异常状况,并且将错误信息存储起来
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"%>
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
<style>
body { font-size: 12px; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<c:catch var="e">
<c:set target="someBean" property="someProperty" value="Some Value"></c:set>
</c:catch>
<c:if test="e!=null">程序抛出了异常e!=null">程序抛出了异常{ e.class.name },原因: ${ e.message }
</c:if>
</body>
</html>
5.<c:if>
<c:if test="条件1" var="name" [scope="page|request|session|application"]></c:remove>
例子:
<body>
<c:set value="赵五" target="${person}" property="name"></c:set>
<c:set target="${person}" property="age">19</c:set>
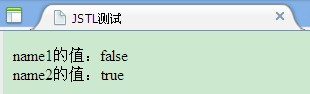
<c:if test="${person.name == '赵武'}" var="name1"></c:if>
<c:out value="name1的值:${name1}"></c:out><br/>
<c:if test="${person.name == '赵五'}" var="name2"></c:if>
<c:out value="name2的值:${name2}"></c:out>
</body>
效果:
6. <c:choose> <c:when> <c:otherwise> 三个标签通常嵌套使用,第一个标签在最外层,最后一个标签在嵌套中只能使用一次
例子:
<c:set var="score">85</c:set>
<c:choose>
<c:when test="${score>=90}">
你的成绩为优秀!
</c:when>
<c:when test="${score>=70&&score<90}">
您的成绩为良好!
</c:when>
<c:when test="${score>60&&score<70}">
您的成绩为及格
</c:when>
<c:otherwise>
对不起,您没有通过考试!
</c:otherwise>
</c:choose>
7.<c:forEach>
语法:<c:forEach var="name" items="Collection" varStatus="statusName" begin="begin" end="end" step="step"></c:forEach>
该标签根据循环条件遍历集合 Collection 中的元素。 var 用于存储从集合中取出的元素;items 指定要遍历的集合;varStatus 用于存放集合中元素的信息。varStatus 一共有4种状态属性,下面例子中说明:
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=GBK" %>
2 <%@page import="java.util.List"%>
3 <%@page import="java.util.ArrayList"%>
4 <%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
5 <html>
6 <head>
7 <title>JSTL: -- forEach标签实例</title>
8 </head>
9 <body>
10 <h4><c:out value="forEach实例"/></h4>
11 <hr>
12 <%
13 List a=new ArrayList();
14 a.add("贝贝");
15 a.add("晶晶");
16 a.add("欢欢");
17 a.add("莹莹");
18 a.add("妮妮");
19 request.setAttribute("a",a);
20 %>
21 <B><c:out value="不指定begin和end的迭代:" /></B><br>
22 <c:forEach var="fuwa" items="${a}">
23 <c:out value="${fuwa}"/><br>
24 </c:forEach>
25 <B><c:out value="指定begin和end的迭代:" /></B><br>
26 <c:forEach var="fuwa" items="${a}" begin="1" end="3" step="2">
27 <c:out value="${fuwa}" /><br>
28 </c:forEach>
29 <B><c:out value="输出整个迭代的信息:" /></B><br>
30 <c:forEach var="fuwa" items="${a}" begin="3" end="4" step="1" varStatus="s">
31 <c:out value="${fuwa}" />的四种属性:<br>
32 所在位置,即索引:<c:out value="${s.index}" /><br>
33 总共已迭代的次数:<c:out value="${s.count}" /><br>
34 是否为第一个位置:<c:out value="${s.first}" /><br>
35 是否为最后一个位置:<c:out value="${s.last}" /><br>
36 </c:forEach>
37 </body>
38 </html>

8.<c:forTokens> 用于浏览字符串,并根据指定的字符串截取字符串
语法:<c:forTokens items="stringOfTokens" delims="delimiters" [var="name" begin="begin" end="end" step="len" varStatus="statusName"]></c:forTokens>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=GBK"%>
2 <%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core"%>
3 <html>
4 <head>
5 <title>JSTL: -- forTokens标签实例</title>
6 </head>
7 <body>
8 <h4>
9 <c:out value="forToken实例" />
10 </h4>
11 <hr>
12 <c:forTokens items="北、京、欢、迎、您" delims="、" var="c1">
13 <c:out value="${c1}"></c:out>
14 </c:forTokens>
15 <br>
16 <c:forTokens items="123-4567-8854" delims="-" var="t">
17 <c:out value="${t}"></c:out>
18 </c:forTokens>
19 <br>
20 <c:forTokens items="1*2*3*4*5*6*7" delims="*" begin="1" end="3"
21 var="n" varStatus="s">
22 <c:out value="${n}" />的四种属性:<br>
23 所在位置,即索引:<c:out value="${s.index}" />
24 <br>
25 总共已迭代的次数:<c:out value="${s.count}" />
26 <br>
27 是否为第一个位置:<c:out value="${s.first}" />
28 <br>
29 是否为最后一个位置:<c:out value="${s.last}" />
30 <br>
31 </c:forTokens>
32 </body>
33 </html>

9.URL 操作标签
(1)<c:import> 把其他静态或动态文件包含到 JSP 页面。与<jsp:include>的区别是后者只能包含同一个web应用中的文件,前者可以包含其他web应用中的文件,甚至是网络上的资源。
语法:<c:import url="url" [context="context"] [value="value"] [scope="..."] [charEncoding="encoding"]></c:import>
<c:import url="url" varReader="name" [context="context"][charEncoding="encoding"]></c:import>
看个例子:
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=GBK"%>
2 <%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core"%>
3 <html>
4 <head>
5 <title>JSTL: -- import标签实例</title>
6 </head>
7 <body>
8 <h4>
9 <c:out value="import实例" />
10 </h4>
11 <hr>
12 <h4>
13 <c:out value="绝对路径引用的实例" />
14 </h4>
15 <c:catch var="error1">
16 <c:import url="http://www.baidu.com" />
17 </c:catch>
18 <c:out value="${error1}"></c:out>
19 <hr>
20 <h4>
21 <c:out value="相对路径引用的实例,引用本应用中的文件" />
22 </h4>
23 <c:catch>
24 <c:import url="a1.txt" charEncoding="gbk" />
25 </c:catch>
26 <hr>
27 <h4>
28 <c:out value="使用字符串输出、相对路径引用的实例,并保存在session范围内" />
29 </h4>
30 <c:catch var="error3">
31 <c:import var="myurl" url="a1.txt" scope="session" charEncoding="gbk"></c:import>
32 <c:out value="${myurl}"></c:out>
33 <c:out value="${myurl}" />
34 </c:catch>
35 <c:out value="${error3}"></c:out>
36 </body>
37 </html>
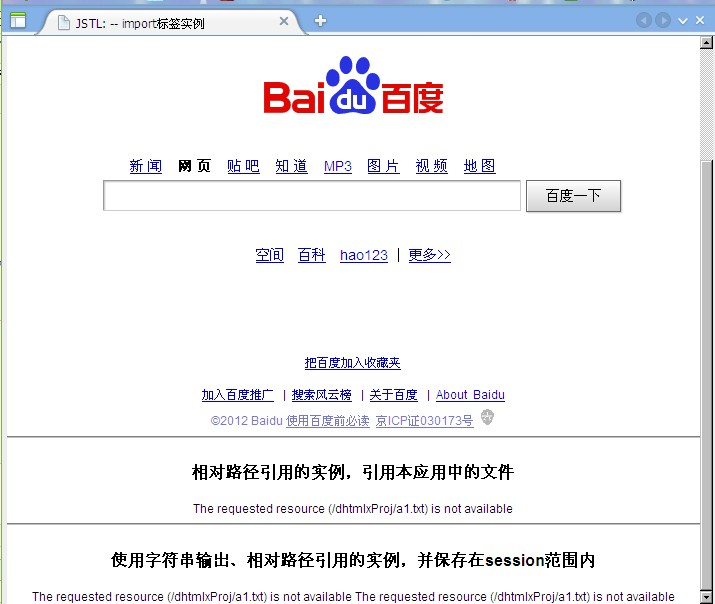
URL路径有个绝对路径和相对路径。相对路径:<c:import url="a.txt"/>那么,a.txt必须与当前文件放在同一个文件目录下。如果以"/"开头,表示存放在应用程序的根目录下,如Tomcat应用程序的根目录文件夹为 webapps。导入该文件夹下的 b.txt 的编写方式: <c:import url="/b.txt">。如果要访问webapps管理文件夹中的其他Web应用,就要用context属性。例如访问demoProj下的index.jsp,则:<c:import url="/index.jsp" context="/demoProj"/>.
(2)<c:redirect> 该标签用来实现请求的重定向。例如,对用户输入的用户名和密码进行验证,不成功则重定向到登录页面。或者实现Web应用不同模块之间的衔接
语法:<c:redirect url="url" [context="context"]/>
或:<c:redirect url="url" [context="context"]>
<c:param name="name1" value="value1">
</c:redirect>
看个例子:
1 <%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=GBK"%>
2 <%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core"%>
3 <c:redirect url="http://127.0.0.1:8080">
4 <c:param name="uname">lihui</c:param>
5 <c:param name="password">11111</c:param>
6 </c:redirect>
则运行后,页面跳转为:http://127.0.0.1:8080/?uname=lihui&password=11111
(3)<c:url> 用于动态生成一个 String 类型的URL,可以同上个标签共同使用,也可以使用HTML的<a>标签实验超链接。
语法:<c:url value="value" [var="name"] [scope="..."] [context="context"]>
<c:param name="name1" value="value1">
</c:url>
或:<c:url value="value" [var="name"] [scope="..."] [context="context"]/>
看个例子:
 View Code
View Code显示:
