树的相关术语
一个树结构包含一系列存在父子关系的节点。每个节点都有一个父节点(除了顶部的第一个节点)以及零个或多个子节点:

- 根节点:位于树顶部的节点叫作根节点(11)
- 内部节点:至少有一个子节点的节点称为内部节点(7、5、9、15、13 和 20)
- 外部节点:没有子元素的节点称为外部节点或叶节点(3、6、8、10、12、14、18 和 25)
- 子树:子树由节点和它的后代构成。例如,节点 13、12 和 14 构成了上图中树的一棵子树。
- 深度:节点的深度取决于它的祖先节点的数量。比如,节点 3 有 3 个祖先节点(5、7 和 11),它的深度为 3。
- 高度:树的高度取决于所有节点深度的最大值,上图中的树的高度为 3
深度广度优先遍历
首先创建一棵树

const tree = { val: 'a', children: [{ val: 'b', children: [ { val: 'd', children: [], }, { val: 'e', children: [], } ], }, { val: 'c', children: [ { val: 'f', children: [], }, { val: 'g', children: [], } ], } ] }
深度优先遍历(DFS)
深度优先遍历是从树中的根节点开始,沿着一条路一直走到底,然后从这条路尽头的节点回退到上一个节点,再从另一条路开始走到底...,不断重复此过程,直到所有的顶点都遍历完成。
- 访问根节点
- 对根节点的children挨个进行深度优先遍历

const dfs = (root) =>{
console.log(root.val);
root.children.forEach(dfs)
}
dfs(tree)
广度优先遍历(BFS)
- 广度优先遍历是从树的一个根的节点出发,先遍历这个节点的相邻节点,再依次遍历每个相邻节点的相邻节点。
- 新建一个队列,把根节点入队
- 把队头出队并访问
- 把队头的children挨个入队
- 重复上面两步,直到队列为空

const bfs = (root) =>{ const q = [root]; while(q.length>0){ const n = q.shift(); console.log(n.val); n.children.forEach(child =>{ q.push(child) }) } } bfs(tree)
二叉树(BT)和二叉搜索树(BST)
二叉树中的节点最多只能有两个子节点:一个是左侧子节点,另一个是右侧子节点。下面的例子就是一棵二叉树。
二叉搜索树(BST)是二叉树的一种,但是只允许你在左侧节点存储(比父节点)小的值,在右侧节点存储(比父节点)大的值

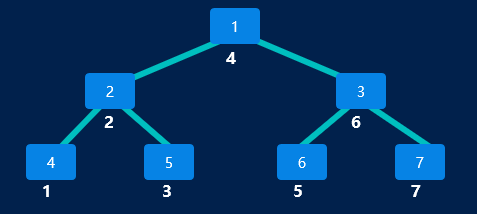
const bt={ val:1, left:{ val:2, left:{ val:4, left:null, right:null, }, right:{ val:5, left:null, right:null, } }, right:{ val:3, left:{ val:6, left:null, right:null, }, right:{ val:7, left:null, right:null, } } }
二叉树的先序遍历
先序遍历过程:根节点--左节点--右节点
实现步骤:
- 访问根节点
- 对根节点的左子树进行先序遍历
- 对根节点的右子树进行先序遍历


递归实现
const preorder = (root)=>{ if(!root){ return; } console.log(root.val); preorder(root.left); preorder(root.right); }; preorder(bt)
非递归实现
const preorder = (root) =>{ if(!root){ return; } const stack = [root]; while(stack.length){ const n = stack.pop(); console.log(n.val); if(n.right){ stack.push(n.right) } if(n.left){ stack.push(n.left) } } } preorder(bt)
二叉树的中序遍历
中序遍历过程:左节点--根节点--右节点
实现步骤:
- 对根节点的左子树进行中序遍历
- 访问根节点
- 对根节点的右子树进行中序遍历
递归实现
const inorder = (root)=>{ if(!root){ return; } inorder(root.left); console.log(root.val); inorder(root.right); }; inorder(bt);
非递归实现
const inorder = (root) =>{ if(!root){ return; } const stack = []; let p = root; while(stack.length || p){ while(p){ stack.push(p); p = p.left } const n = stack.pop(); console.log(n.val); p = n.right; } } inorder(bt)
二叉树的后序遍历
后序遍历过程:左节点--右节点--根节点
实现步骤:
- 对根节点的左子树进行后续遍历
- 对根节点的右子树进行后续遍历
- 访问根节点

递归实现
const postorder = (root)=>{ if(!root){ return; } postorder(root.left); postorder(root.right); console.log(root.val); }; postorder(bt)
非递归实现
const postorder = (root) =>{ if(!root){ return; } const stack = [root]; const outputStack = []; let p = root; while(stack.length){ const n = stack.pop(); outputStack.push(n); if(n.left){ stack.push(n.left); } if(n.right){ stack.push(n.right); } } while(outputStack.length){ const n = outputStack.pop(); console.log(n.val); } } postorder(bt)