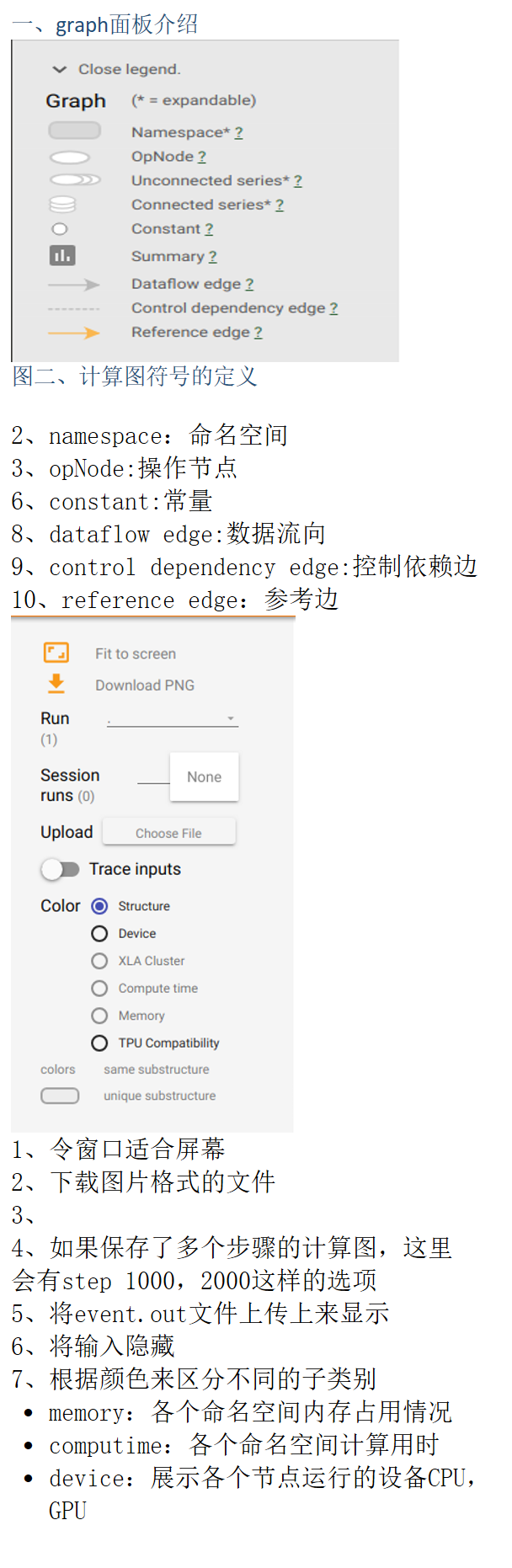
打开方式
打开tensorbaord
tensorboard --logdir=/home/q/deep/tensorboard_example
注意,空格双横线,等号两边没有空格文件的绝对路径名字要对,内部有下面的文件
在windows系统中,必须cd到所在盘中,比如说在F盘就不能打开G盘的tensorboard文件
记录数据
第一步 将网络进行命名空间的管理 # 参数概要 def variable_summaries(var): with tf.name_scope('summaries'): mean = tf.reduce_mean(var) # 平均值 tf.summary.scalar('mean', mean) with tf.name_scope('stddev'): stddev = tf.sqrt(tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(var - mean))) # 标准差 tf.summary.scalar('stddev', stddev) # 最大值 tf.summary.scalar('max', tf.reduce_max(var)) # 最小值 tf.summary.scalar('min', tf.reduce_min(var)) # 直方图 tf.summary.histogram('histogram', var) # 命名空间 with tf.name_scope('input'): # 定义两个placeholder x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,784],name='x-input') y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,10],name='y-input') with tf.name_scope('layer'): # 创建一个简单的神经网络 with tf.name_scope('wights'): W = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784,10]),name='W') variable_summaries(W) with tf.name_scope('biases'): b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]),name='b') variable_summaries(b) with tf.name_scope('wx_plus_b'): wx_plus_b = tf.matmul(x,W) + b with tf.name_scope('softmax'): prediction = tf.nn.softmax(wx_plus_b) with tf.name_scope('loss'): # 二次代价函数 loss = tf.losses.mean_squared_error(y, prediction) tf.summary.scalar('loss',loss) with tf.name_scope('train'): # 使用梯度下降法 train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.3).minimize(loss) # 初始化变量 init = tf.global_variables_initializer() with tf.name_scope('accuracy'): with tf.name_scope('correct_prediction'): # 结果存放在一个布尔型列表中 correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y,1),tf.argmax(prediction,1)) with tf.name_scope('accuracy'): # 求准确率 accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction,tf.float32)) tf.summary.scalar('accuracy',accuracy) 第二步 选择要记录的张量和记录的方式 举例 'stddev':这个就是在tensorboard里面展示的名字 stddev:这个就是要记录的张量 记录方式: scalar,线型图 histogram,直方图 等等还有好多 # 标准差 tf.summary.scalar('stddev', stddev) # 最大值 tf.summary.scalar('max', tf.reduce_max(var)) # 最小值 tf.summary.scalar('min', tf.reduce_min(var)) # 直方图 tf.summary.histogram('histogram', var) 第三步 执行保存 # merged = tf.summary.merge_all() tensorboard所有需要记录的张量都汇总在一起 #writer = tf.summary.FileWriter('logs/',sess.graph) 定义一个写法器,将这个会话中的图结构写进去,文件保存的位置是‘logs’文件夹,使用前最好是空文件夹 #summary,_ = sess.run([merged,train_step],feed_dict={x:batch_xs,y:batch_ys}) 获得每一次张量的具体数值 #writer.add_summary(summary,epoch) 将张量这次的数值写进该文件中。epoch就是观看的时候的时间变量,有用epoch的,有用batch的,不过最好使用batch # 合并所有的summary merged = tf.summary.merge_all() with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(init) writer = tf.summary.FileWriter('logs/',sess.graph) for epoch in range(51): for batch in range(n_batch): batch_xs,batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size) summary,_ = sess.run([merged,train_step],feed_dict={x:batch_xs,y:batch_ys}) writer.add_summary(summary,epoch) acc = sess.run(accuracy,feed_dict={x:mnist.test.images,y:mnist.test.labels}) print("Iter " + str(epoch) + ",Testing Accuracy " + str(acc))
保存文件格式
events.out.tfevents.1504159103.thinkjoy
events.out.tfevents.表示用于tensorboard的文件
后面的数字表示的是时间
thinkjoy是自己的电脑的名字,自己的就是qdw
面板介绍
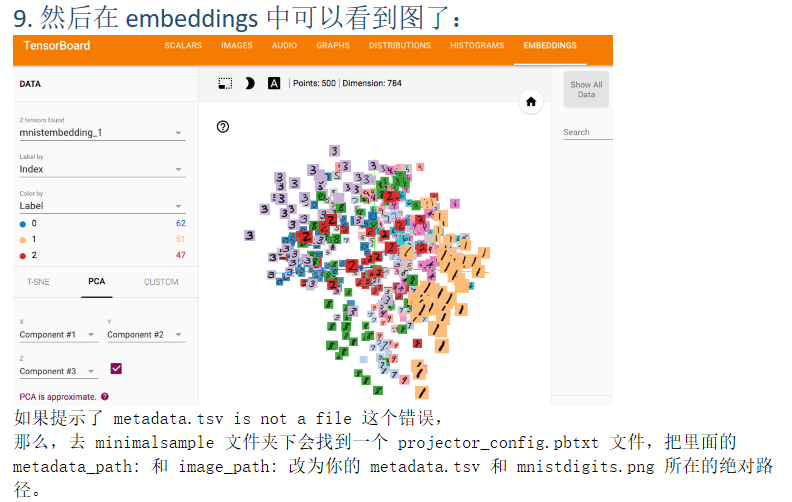
embeddings 高维可视化
来自 <https://blog.csdn.net/aliceyangxi1987/article/details/71079387> 第一步、指定一个2D的张量来储存嵌入 embedding_var = tf.Variable(…) 第二步、在LOG_DIR中保存模型 saver = tf.train.Saver() saver.save(session,os.path.join(LOG_DIR,'model_name.ckpt),step) 1. 引入 projector,data,定义 path: %matplotlib inline import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np import os from tensorflow.contrib.tensorboard.plugins import projector from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data LOG_DIR = 'minimalsample'#保存路径 NAME_TO_VISUALISE_VARIABLE = "mnistembedding"#需要可视化的变量 TO_EMBED_COUNT = 500 path_for_mnist_sprites = os.path.join(LOG_DIR,'mnistdigits.png') path_for_mnist_metadata = os.path.join(LOG_DIR,'metadata.tsv') mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/", one_hot=False) batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(TO_EMBED_COUNT) 2. 建立 embeddings, 也就是前面的第一步,最主要的就是你要知道想可视化查看的 variable 的名字 embedding_var = tf.Variable(batch_xs, name=NAME_TO_VISUALISE_VARIABLE) #这一步是制定了一个变量,并给他起了一个名字 summary_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(LOG_DIR)#创建一个writer 3. 建立 embedding projector 这一步很重要,要指定想要可视化的 variable,metadata 文件的位置 config = projector.ProjectorConfig() embedding = config.embeddings.add() embedding.tensor_name = embedding_var.name # 指定metadata的位置 embedding.metadata_path = path_for_mnist_metadata #'metadata.tsv' # 指定sprite位置 (we will create this later) embedding.sprite.image_path = path_for_mnist_sprites #'mnistdigits.png' embedding.sprite.single_image_dim.extend([28,28]) # Say that you want to visualise the embeddings projector.visualize_embeddings(summary_writer, config) 4. 保存,即上面第二步: Tensorboard 会从保存的图形中加载保存的变量,所以初始化 session 和变量,并将其保存在 logdir 中, sess = tf.InteractiveSession() sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) saver = tf.train.Saver() saver.save(sess, os.path.join(LOG_DIR, "model.ckpt"), 1) 5. 定义 helper functions: **create_sprite_image:** 将 sprits 整齐地对齐在方形画布上 **vector_to_matrix_mnist:** 将 MNIST 的 vector 数据形式转化为 images **invert_grayscale: **将黑背景变为白背景 def create_sprite_image(images): """Returns a sprite image consisting of images passed as argument. Images should be count x width x height""" if isinstance(images, list): images = np.array(images) img_h = images.shape[1] img_w = images.shape[2] n_plots = int(np.ceil(np.sqrt(images.shape[0]))) spriteimage = np.ones((img_h * n_plots ,img_w * n_plots )) for i in range(n_plots): for j in range(n_plots): this_filter = i * n_plots + j if this_filter < images.shape[0]: this_img = images[this_filter] spriteimage[i * img_h:(i + 1) * img_h, j * img_w:(j + 1) * img_w] = this_img return spriteimage def vector_to_matrix_mnist(mnist_digits): #返回的是矩阵形式 """Reshapes normal mnist digit (batch,28*28) to matrix (batch,28,28)""" return np.reshape(mnist_digits,(-1,28,28)) def invert_grayscale(mnist_digits): """ Makes black white, and white black """ return 1-mnist_digits 6. 保存 sprite image: 将 vector 转换为 images,反转灰度,并创建并保存 sprite image。 to_visualise = batch_xs to_visualise = vector_to_matrix_mnist(to_visualise) to_visualise = invert_grayscale(to_visualise) sprite_image = create_sprite_image(to_visualise) plt.imsave(path_for_mnist_sprites,sprite_image,cmap='gray') plt.imshow(sprite_image,cmap='gray') 7. 保存 metadata: 将数据写入 metadata,因为如果想在可视化时看到不同数字用不同颜色表示,需要知道每个 image 的标签,在这个 metadata 文件中有这样两列:”Index” , “Label” with open(path_for_mnist_metadata,'w') as f: f.write("Index Label ") for index,label in enumerate(batch_ys): f.write("%d %d " % (index,label)) 8. 执行: 我是用 jupyter notebook 写的,执行前面的代码后,会在当前 ipynb 所在文件夹下生成一个 minimalsample 文件夹, 要打开 tensorboard ,需要在终端执行: $ tensorboard --logdir=YOUR FOLDER/minimalsample --------------------- 作者:Alice熹爱学习 来源:CSDN 原文:https://blog.csdn.net/aliceyangxi1987/article/details/71079387 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请附上博文链接!
tensorboard记录的种类
