Definition
Arthur Samuel: Machine Learing is the field of study that gives the computer the ablility to learn with out being explicitly programmed.
Tom Mitchell: a computer program is said to learn from experience E with respect to some class of tasks T and performance measure P, if its performance at task in T, as measured by P, improves with experience E.
Taxonomy
- Supervised Learning
- Unsupervised Learning
- Reinforcement Learning
Supervised Learning
- eg: Housing Price Prediction
- Given: a dataset that contains n samples(x1, y1),...,(xn, yn), x is for square feet, y is for price
- Task: if a residence has x square feet, predict its price?
- Given: a dataset that contains n samples(x1, y1),...,(xn, yn), x is for square feet, y is for price
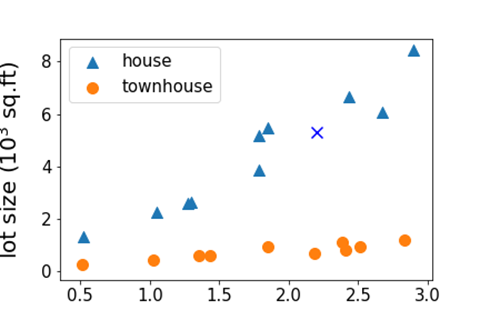
- Regression vs Classification
- regression: if y ∈ R is a continuous variable, e.g., price prediction
- classification: the label is a discrete variable,e.g., the task of predicting the types of residence
- Supervised Learning in Computer Vision
- Image Classification, x = raw pixels of the image, y = the main object
- Object localization and detection, x = raw pixel of the image, y = the bounding boxes
- Supervised Learning in Natural Language Processing
- Machine translation
Unsupervised Learning
- Dataset contains no labels: x1,...,xn
- Goal(vaguely-posed): to find interesting structures in the data
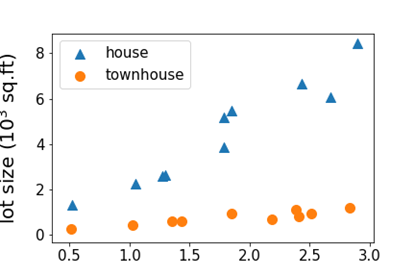
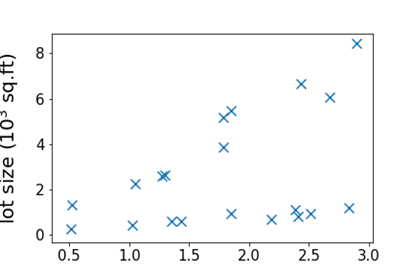
- Clustering
Reinforcement Learning
- The algorithm can collect data interactively
Other Tools/Toptics In This Course
- Deep learning basics
- Introduction to learning theory
- Bias偏差 variance方差 tradeoff
- Feature selection
- ML advice
- Broader aspects of ML
- Robustness/fairness