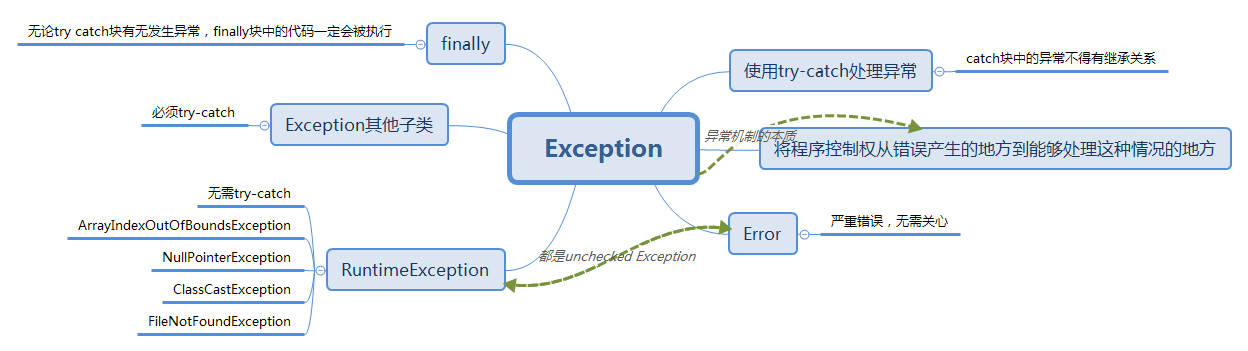
1. 本章学习总结
以你喜欢的方式(思维导图或其他)归纳总结异常相关内容。
2. 书面作业
本次PTA作业题集异常
1.常用异常
题目5-1
1.1 截图你的提交结果(出现学号)

1.2 自己以前编写的代码中经常出现什么异常、需要捕获吗(为什么)?应如何避免?
Answer:以前编写的代码出现过运行时间过长,数组越界等,不需要捕获。运行时间过长就需要优化代码;数组越界可以将数组开大一点。
1.3 什么样的异常要求用户一定要使用捕获处理?
Answer:除了Error与RuntimeException及其子类以外的异常都是Checked Exception,代码中必须try-catch(学习总结链接那有~)。
2.处理异常使你的程序更加健壮
题目5-2
2.1 截图你的提交结果(出现学号)

2.2 实验总结
Answer:一开始我是用for循环for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)然后如果是非整型字符串,这时候需要提示有异常,然后重新输入,在被抛出异常且被捕获后,在catch那里i--。
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int[] arr = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n-1;i++) {
String inputInt = sc.next();
try {
arr[i] = Integer.parseInt(inputInt);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
i--;
}
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}
还有就是可以直接在try里面异常后面的代码后面i++,如果异常了,try异常后面的代码就不执行了。
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int[] arr = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length;) {
String inputInt = sc.next();
try {
arr[i] = Integer.parseInt(inputInt);
i++;
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}
3.throw与throws
题目5-3
3.1 截图你的提交结果(出现学号)

3.2 阅读Integer.parsetInt源代码,结合3.1说说抛出异常时需要传递给调用者一些什么信息?
public static int parseInt(String s) throws NumberFormatException {
return parseInt(s,10);
}
Answer:Integer.parsetInt源代码可以看出,如果字符串不能转化成整数,则抛出NumberFormatException。类似的还有:如果数组越界,则抛出ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;如果指向了空指针,则抛出NullPointerException;如果强制转化类型失败,则抛出ClassCastException。
4.函数题
题目4-1(多种异常的捕获)
3.1 截图你的提交结果(出现学号)

3.2 一个try块中如果可能抛出多种异常,捕获时需要注意些什么?
Answer:try块后跟一个或多个catch块,每个catch块分别捕获不同类型的异常,注意!子类异常必须放在父类异常前面。
附上ppt哦!

5.为如下代码加上异常处理
byte[] content = null;
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("testfis.txt");
int bytesAvailabe = fis.available();//获得该文件可用的字节数
if(bytesAvailabe>0){
content = new byte[bytesAvailabe];//创建可容纳文件大小的数组
fis.read(content);//将文件内容读入数组
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(content));//打印数组内容
5.1 改正代码,让其可正常运行。注意:里面有多个方法均可能抛出异常
Answer:用throws的方法。
public static void main(String[] args)throws IOException{
byte[] content = null;
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("testfis.txt");
int bytesAvailabe = fis.available();//获得该文件可用的字节数
if(bytesAvailabe>0){
content = new byte[bytesAvailabe];//创建可容纳文件大小的数组
fis.read(content);//将文件内容读入数组
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(content));//打印数组内容
}
附上ppt:


5.2 如何使用Java7中的try-with-resources来改写上述代码实现自动关闭资源?
public class Main2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
byte[] content = null;
try(FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("testfis.txt");) {
int bytesAvailabe = fis.available();// 获得该文件可用的字节数
if (bytesAvailabe > 0) {
content = new byte[bytesAvailabe];// 创建可容纳文件大小的数组
fis.read(content);// 将文件内容读入数组
}
}
catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
System.out.println(e);
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(content));// 打印数组内容
}
}
重点考核:使用异常改进你的购物车系统(未提交,得分不超过6分)
举至少两个例子说明你是如何使用异常机制让你的程序变得更健壮。
说明要包含2个部分:1. 问题说明(哪里会碰到异常)。2.解决方案(关键代码)
- 在输入商品数量的时候,我们需要的是个整数,所以有可能会遇到NumberFormatException的异常;
String input=sc.next();
try{
number=Integer.parseInt(input);
}
catch(Exception e){
System.out.println(e);
}
- 可能我遇到的异常少了一点,然后问了下学霸说可以造就异常,就是先把所有的商品信息写进文件中然后再读入文件,在文件中有可能会找不到文件。
try{
openthefile;
}
catch(fileopenFailed)
选做:JavaFX入门
完成其中的作业3。内有代码,可在其上进行适当的改造。建议按照里面的教程,从头到尾自己搭建。
选做:课外阅读
JavaTutorial中Questions and Exercises
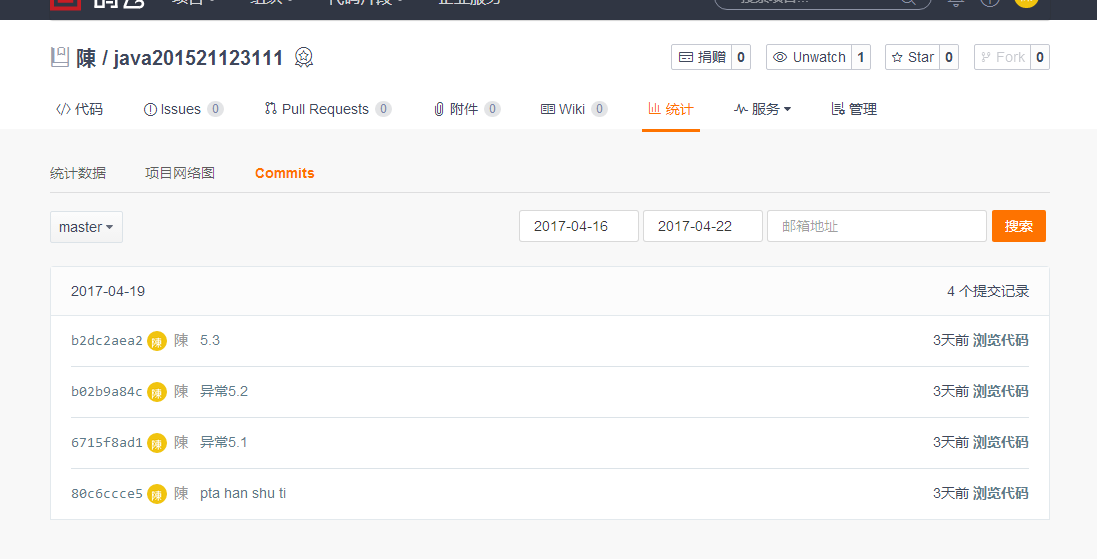
3码云上代码提交记录
题目集:异常
3.1. 码云代码提交记录
在码云的项目中,依次选择“统计-Commits历史-设置时间段”, 然后搜索并截图
4. 课外阅读
Best Practices for Exception Handling
Exception-Handling Antipatterns Blog
The exceptions debate