- String字符串的存储原理
1、String表示字符串类型,属于引用数据类型,不属于基本数据类型。创建出来的是字符串对象。
2、在JDK当中双引号括起来的字符串,例如:"abc"、"def"都是直接存储在“方法区”的“字符串常量池"当中的,是不可变的。因为字符串在实际的开发中使用太频繁,为了执行效事,所以把字符串放到了方法区的字符串常量池当中。
凡是双引号括起来的都在字符串常量池中有一份。
3、代码示例:
public class Demo{
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*这两行代码表示底层创建了3个字符串对象,
都在字符串常量池当中。*/
String s = "qwe";
String s1 = "qwe" + "asd";
}
}
4、内存图
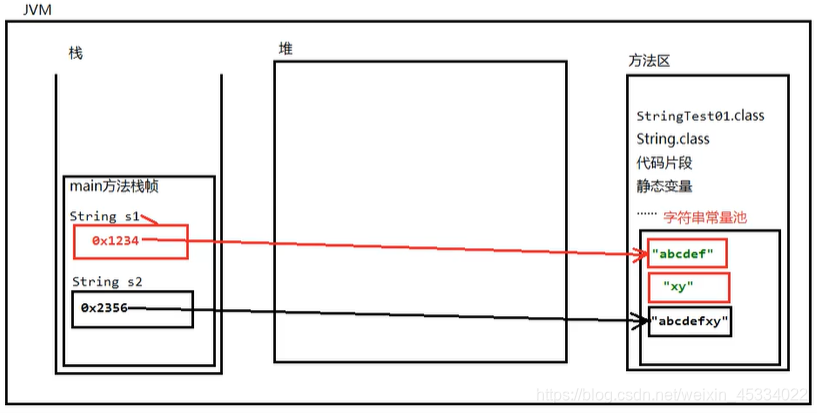
5、创建出来的是字符串对象。
/*一共3个对象:
方法区字符串常最池中有一个:"hello"
堆内存当中有两个String对象。一共3个。*/
String s1 = new String("hello");
String s2 = new String("hello");
- String类的构造方法
1、详见帮助文档
2、常见:
第一个:String s = new String("");
第二个:String s = "";最常用
第三个:String s = new String(char数组);
第四个:String s = new String(char数组,起始下标,长度);
第五个:String s = new String(byte数组);
第六个:String s = new String(byte数组,起始下标,长度); - String类的常见方法:
1、char charAt(int index)
代码示例:
public class Demo{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//string类当中常用方法。
// 1.char charAt(int index)
char c = "中国人".charAt(1);
/*"中国人”是一个字符串String对象。
只要是对象就能"点."*/
System.out.println(c); //国
}
}
2、compareTo方法
代码示例:
public class Demo{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = "ab".compareTo("bc");
System.out.println(a);//-1
int b = "as".compareTo("qw");
System.out.println(b);//-16
}
}
3、contains方法
代码示例:
public class Demo{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//判断前面的字符串中是否包含后面的子字符串。
System.out.println("qwerdf".contains("qwe"));
//true
System.out.println("qwerdf".contains("gb"));
//false
}
}
4、endsWith方法
代码示例:
public class Demo{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//判断当前字符串是否以某个字符串结尾。
System.out.println("qwerdf".endsWith("df"));
//true
System.out.println("qwerdf".endsWith("qwe"));
//false
}
}
5、equalsIgnoreCase方法
代码示例:
public class Demo{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//判断两个字符串是否相等,忽略大小写。
System.out.println("qwer".equalsIgnoreCase("QWer"));
//true
}
}
6、getBytes()方法
代码示例:
public class Demo{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//将字符串对象转换成字节数组
byte[] bytes = "abcd".getBytes();
for (int i = 0; i < bytes.length; i++) {
System.out.println(bytes[i]);
}
/*輸出:
* 97
* 98
* 99
* 100*/
}
}
7、indexOf()方法
代码示例:
public class Demo{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//判断某个子字符串在当前字符串中第一次出现处的索引。
System.out.println("javac++cpython".indexOf("java"));
/*输出:0*/
}
}
8、isEmpty()方法和length()方法
判断数组长度和判断字符串长度不一样。判断数组长度是length属性,判断字符串长度是length()方法。
代码示例:
public class Demo{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//判断某个子字符串是否为空。
String s = "";
System.out.println(s.isEmpty());
/*输出:true*/
String s1 = "abc";
System.out.println(s1.length());
/*输出:3*/
}
}
9、lastIndexOf()方法
代码示例:
public class Demo{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//判断某个子字符串在当前宇符串中最后一次出现的索引(下标)。
String s = "javapythongojavapythongo";
System.out.println(s.lastIndexOf("java"));
/*输出:12*/
}
}
10、replace方法
代码示例:
public class Demo{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//将当前字符串中的一段替换成新的字符串。
String s = "javapythongo";
System.out.println(s.replace("go","c++"));
/*输出:javapythonc++*/
String s1 = "javapythongojavapythongo";
System.out.println(s1.replace("go","c++"));
/*输出:javapythonc++javapythonc++*/
}
}
11、split方法
代码示例:
public class Demo{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//拆分字符串。
String[] s = "java&python&go&c++".split("&");
for (int i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
System.out.println(s[i]);
}
/*输出:
* java
* python
* go
* c++*/
}
}
12、substring方法
代码示例:
public class Demo{
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*截取字符串。参数是起始下标
或起始下标(包括)和结束下标(不包括)。*/
String s = "java&python&go&c++";
System.out.println(s.substring(5));
/*输出:python&go&c++*/
System.out.println(s.substring(5,11));
/*输出:python*/
/*上面的代码没有输出Python后面的&,
说明截取的时候没有截取到下标为11的&。
所以截取是左闭右开的*/
}
}
13、toCharArray方法
代码示例:
public class Demo{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//将字符串转换成char数组。
String s = "我是中国人";
char[] chars = s.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {
System.out.println(chars[i]);
}
/*输出:
我
是
中
国
人*/
}
}
14、toLowerCase()和toUpperCase()方法
代码示例:
public class Demo{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//将此String中的所有字符都转换为小写。
String s1 = "QWERdf".toLowerCase();
System.out.println(s1);
//输出:qwerdf
// 将此String中的所有字符都转换为大写。
String s2 = "qwerDF".toUpperCase();
System.out.println(s2);
//输出:QWERDF
}
}
15、trim()方法
代码示例:
public class Demo{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//去除字符串前后空格(中间的去不了)。
String s1 = " hello world ".trim();
System.out.println(s1);
//输出:hello world
}
}
16、valueOf方法
代码示例:
public class Demo{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//将“非字符串”转换成“字符串”。
String s1 = String.valueOf(true);
System.out.println(s1);
//输出:true
String s2 = String.valueOf(011);
System.out.println(s2);
/*输出:9
* 这里应该是将011默认为八进制,
* 输出时将八进制自动转换为十进制*/
String s3 = String.valueOf(11);
System.out.println(s3);
//输出:11
String s4 = String.valueOf(new User());
System.out.println(s4);
/*没有重写之前输出(内存地址):User@74a14482
* 重写toString方法后输出:VIP*/
}
}
class User {
@Override
public String toString() {
return "VIP";
}
}
PS:所以现在可以解释:println打印对象引用输出的是一个地址。
因为println调用了String.valueOf()方法,而valueOf又调用了toString方法。所以打印出来是一个地址。
因此println打印出来的都是字符串。