1 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 2 """ 3 Created on Tue Sep 25 10:48:34 2018 4 5 @author: zhen 6 """ 7 8 import numpy as np 9 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 10 import sklearn.datasets as ds 11 import matplotlib.colors 12 from sklearn.cluster import DBSCAN 13 from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler 14 15 def expand(a, b): 16 d = (b - a) * 0.1 17 return a-d, b+d 18 19 if __name__ == "__main__": 20 N = 1000 21 centers = [[1, 2], [-1, -1], [1, -1], [-1, 1]] 22 data, y = ds.make_blobs(N, n_features=2, centers=centers, cluster_std=[0.5, 0.25, 0.7, 0.5], random_state=0) 23 # 归一化数据 24 data = StandardScaler().fit_transform(data) 25 # 数据的参数 26 params = ((0.2, 5), (0.2, 10), (0.2, 15), (0.3, 5), (0.3, 10), (0.3, 15)) 27 28 # 设置中文样式 29 matplotlib.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = [u'SimHei'] 30 matplotlib.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False 31 # 设置颜色 32 cm = matplotlib.colors.ListedColormap(list('rgbm')) 33 plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8), facecolor='w') 34 plt.suptitle(u'DBSCAN聚类', fontsize=20) 35 36 for i in range(6): 37 eps, min_samples = params[i] 38 # 创建密度聚类模型 39 model = DBSCAN(eps=eps, min_samples=min_samples) 40 # 训练模型 41 model.fit(data) 42 y_hat = model.labels_ 43 44 core_indices = np.zeros_like(y_hat, dtype=bool) 45 core_indices[model.core_sample_indices_] = True 46 47 y_unique = np.unique(y_hat) 48 n_clusters = y_unique.size - (1 if -1 in y_hat else 0) 49 # print(y_unique, '聚类簇的个数:', n_clusters) 50 51 plt.subplot(2, 3, i+1) 52 clrs = plt.cm.Spectral(np.linspace(0, 0.8, y_unique.size)) 53 # print(clrs) 54 55 x1_min, x2_min = np.min(data, axis=0) 56 x1_max, x2_max = np.max(data, axis=0) 57 x1_min, x1_max = expand(x1_min, x1_max) 58 x2_min, x2_max = expand(x2_min, x2_max) 59 60 for k, clr in zip(y_unique, clrs): 61 cur = (y_hat == k) 62 if k == -1: 63 plt.scatter(data[cur, 0], data[cur, 1], s=20, c='k') 64 # 设置散点图数据 65 plt.scatter(data[cur, 0], data[cur, 1], s=20, cmap=cm, edgecolors='k') 66 plt.scatter(data[cur & core_indices][:, 0], data[cur & core_indices][:, 1], 67 s=20, cmap=cm, marker='o', edgecolors='k') 68 # 设置x,y轴 69 plt.xlim((x1_min, x1_max)) 70 plt.ylim((x2_min, x2_max)) 71 plt.grid(True) 72 plt.title(u'epsilon = %.1f m = %d, 聚类数目:%d' % (eps, min_samples, n_clusters), fontsize=16) 73 plt.tight_layout() 74 plt.subplots_adjust(top=0.9) 75 plt.show() 76
结果:
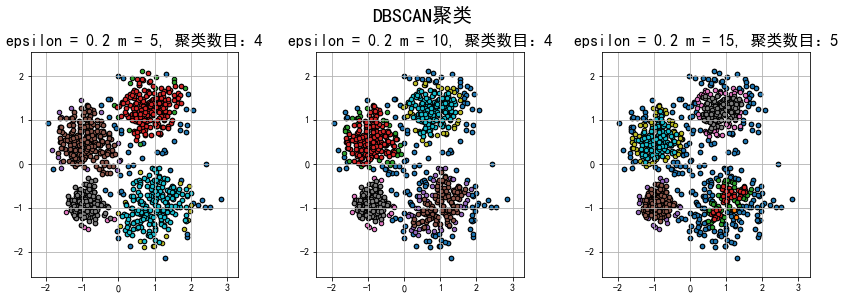
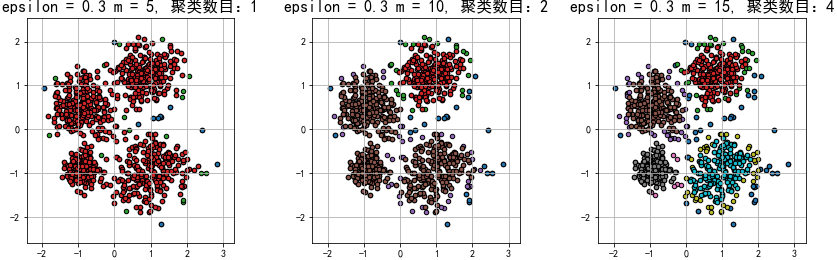
总结:
1.在epsilon(半径)相同的情况下,m(数量)越大,划分的聚类数目就可能越多,异常的数据就会划分的越多。在m(数量)相同的情况下,epsilon(半径)越大,划分的聚类数目就可能越少,异常的数据就会划分的越少。因此,epsilon和m是相互牵制的,合适的epsilon和m有利于更好的聚类,减少欠拟合或过拟合的情况。
2.和KMeans聚类相比,DBSCAN密度聚类更擅长聚不规则形状的数据,因此在数据不是接近圆形的方式分布的情况下,建议使用密度聚类!