HanLP(Han Language Processing)是由一系列模型与算法组成的Java工具包,目标是普及自然语言处理在生产环境中的应用。
HanLP具备功能完善、性能高效、架构清晰、语料时新、可自定义的特点。
环境搭建
1.创建java项目,导入HanLP必要的包

2.把对应的配置文件放置在src下
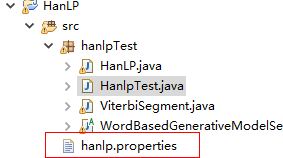
3.修改hanlp.properties配置文件,使其指向data(data中包含词典和模型)的上级路径,修改如下,
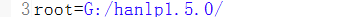
代码运行
1.第一个Demo
- System.out.println(HanLP.segment("你好,欢迎使用HanLP汉语处理包!"));
- //标准分词
- List<Term> standardList = StandardTokenizer.segment("商品和服务");
- System.out.println(standardList);
结果:

注意:HanLP.segment其实是对StandardTokenizer.segment的包装。
2.索引分词
- List<Term> indexList = IndexTokenizer.segment("主副食品");
- for (Term term : indexList)
- {
- System.out.println(term + " [" + term.offset + ":" + (term.offset + term.word.length()) + "]");
- }
结果:

注意:索引分词IndexTokenizer是面向搜索引擎的分词器,能够对长词全切分,另外通过term.offset可以获取单词在文本中的偏移量。
3.自然语言分词
- List<Term> nlpList = NLPTokenizer.segment("中国科学院计算技术研究所的宗成庆教授正在教授自然语言处理课程");
- System.out.println(nlpList);
结果:

注意:自然语言分词NLPTokenizer会执行全部命名实体识别和词性标注。
4.最短路径分词&N-最短路径分词
- String[] testCase = new String[]{
- "今天,刘志军案的关键人物,山西女商人丁书苗在市二中院出庭受审。",
- "刘喜杰石国祥会见吴亚琴先进事迹报告团成员",
- };
- //N-最短路径分词
- Segment nShortSegment = new NShortSegment().enableCustomDictionary(false).enablePlaceRecognize(true).enableOrganizationRecognize(true);
- for (String sentence : testCase)
- {
- System.out.println("N-最短分词:" + nShortSegment.seg(sentence));
- }
- //最短路径分词
- Segment shortestSegment = new DijkstraSegment().enableCustomDictionary(false).enablePlaceRecognize(true).enableOrganizationRecognize(true);
- for (String sentence : testCase)
- {
- System.out.println("最短路分词:" + shortestSegment.seg(sentence));
- }
结果:

注意:
-
N最短路分词器
NShortSegment比最短路分词器慢,但是效果稍微好一些,对命名实体识别能力更强。 -
一般场景下最短路分词的精度已经足够,而且速度比N最短路分词器快几倍,请酌情选择。
5.CRF(条件随机场算法)分词
- Segment segment = new CRFSegment();
- segment.enablePartOfSpeechTagging(true);
- List<Term> crfList = segment.seg("你看过环太平洋吗");
- System.out.println(crfList);
- for (Term term : crfList)
- {
- if (term.nature == null)
- {
- System.out.println("识别到新词:" + term.word);
- }
- }
结果:

注意:CRF对新词有很好的识别能力,但是无法利用自定义词典。
6.用户自定义词典
- // 动态增加
- CustomDictionary.add("攻城狮");
- // 强行插入
- CustomDictionary.insert("白富美", "nz 1024");
- // 删除词语(注释掉试试)
- //CustomDictionary.remove("攻城狮");
- System.out.println(CustomDictionary.add("单身狗", "nz 1024 n 1"));
- System.out.println("单身狗 : " + CustomDictionary.get("单身狗"));
- String text2 = "攻城狮逆袭单身狗,迎娶白富美,走上人生巅峰";
- String text23 = "王重阳和步惊云一起讨论盖聂的百步飞剑的诀窍! ";
- // AhoCorasickDoubleArrayTrie自动机分词
- final char[] charArray = text23.toCharArray();
- CustomDictionary.parseText(charArray, new AhoCorasickDoubleArrayTrie.IHit<CoreDictionary.Attribute>()
- {
- @Override
- public void hit(int begin, int end, CoreDictionary.Attribute value)
- {
- System.out.printf("[%d:%d]=%s %s ", begin, end, new String(charArray, begin, end - begin), value);
- }
- });
结果:

注意:
-
CustomDictionary是一份全局的用户自定义词典,可以随时增删,影响全部分词器。 -
另外可以在任何分词器中关闭它。通过代码动态增删不会保存到词典文件。
7.中国人名识别
- String[] testCase2 = new String[]{
- "签约仪式前,秦光荣、李纪恒、仇和等一同会见了参加签约的企业家。",
- "张浩和胡健康复员回家了",
- "编剧邵钧林和稽道青说",
- "这里有关天培的有关事迹",
- "龚学平等领导,邓颖超生前",
- };
- Segment segment2 = HanLP.newSegment().enableNameRecognize(true);
- for (String sentence : testCase2)
- {
- List<Term> termList = segment2.seg(sentence);
- System.out.println(termList);
- }
结果:

注意:目前分词器基本上都默认开启了中国人名识别,比如HanLP.segment()接口中使用的分词器等等,用户不必手动开启;
8.关键字提取
- String content = "程序员(英文Programmer)是从事程序开发、维护的专业人员。一般将程序员分为程序设计人员和程序编码人员,但两者的界限并不非常清楚,特别是在中国。软件从业人员分为初级程序员、高级程序员、系统分析员和项目经理四大类。";
- List<String> keywordList = HanLP.extractKeyword(content, 5);
- System.out.println(keywordList);
结果:
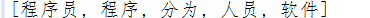
注意:其内部采用TextRankKeyword(类谷歌的PageRank)实现,用户可以直接调用TextRankKeyword.getKeywordList(document, size)。
9.简繁转换
- System.out.println(HanLP.convertToTraditionalChinese("用笔记本电脑写程序"));
- System.out.println(HanLP.convertToSimplifiedChinese("「以後等妳當上皇后,就能買士多啤梨慶祝了」"));
结果:

10.语义距离
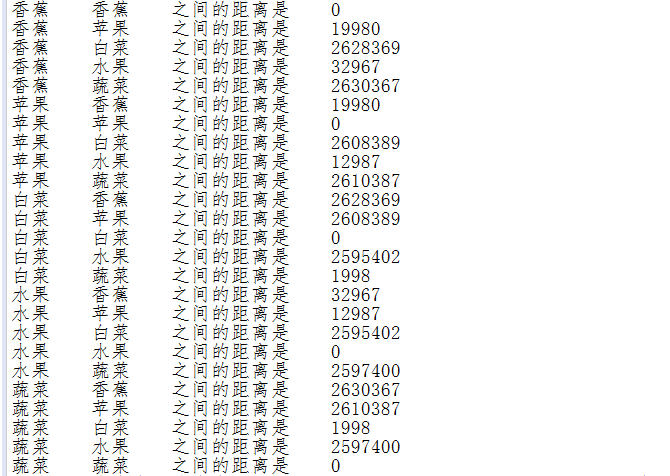
String[] wordArray2 = new String[]
{
"香蕉","苹果","白菜","水果","蔬菜"
};
for (String a : wordArray2){
for (String b : wordArray2)
{
System.out.println(a + " " + b + " 之间的距离是 " + CoreSynonymDictionary.distance(a, b));
}
}
结果:
注意:
-
说明
-
设想的应用场景是搜索引擎对词义的理解,词与词并不只存在“同义词”与“非同义词”的关系,就算是同义词,它们之间的意义也是有微妙的差别的。
-
算法
-
为每个词分配一个语义ID,词与词的距离通过语义ID的差得到。语义ID通过《同义词词林扩展版》计算而来。