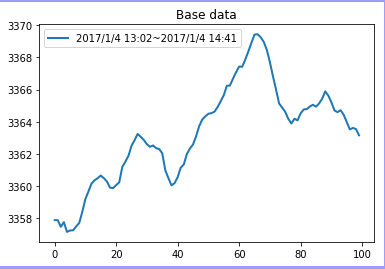
1 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 2 """ 3 Created on Mon Dec 2 14:49:59 2018 4 5 @author: zhen 6 """ 7 8 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 9 import numpy as np 10 import pandas as pd 11 from datetime import datetime 12 13 def normal(a): #最大值最小值归一化 14 return (a - np.min(a)) / (np.max(a) - np.min(a)+0.000001) 15 16 def normalization(x): # np.std:计算矩阵的标准差(方差的算术平方根) 17 return (x - np.mean(x)) / np.std(x) 18 19 def corrcoef(a,b): 20 corrc = np.corrcoef(a,b) # 计算皮尔逊相关系数,用于度量两个变量之间的相关性,其值介于-1到1之间 21 corrc = corrc[0,1] 22 return (16 * ((1 - corrc) / (1 + corrc)) ** 1) # ** 表示乘方 23 24 startTimeStamp = datetime.now() # 获取当前时间 25 # 加载数据 26 filename = 'C:/Users/zhen/.spyder-py3/sh000300_2017.csv' 27 # 获取第一,二列的数据 28 all_date = pd.read_csv(filename,usecols=[0, 1, 3], dtype = 'str') 29 all_date = np.array(all_date) 30 data = all_date[:, 0] 31 times = all_date[:, 1] 32 33 data_points = pd.read_csv(filename,usecols=[3]) 34 data_points = np.array(data_points) 35 data_points = data_points[:,0] #数据 36 37 topk = 10 #只显示top-10 38 baselen = 100 39 basebegin = 361 40 basedata = data[basebegin]+' '+times[basebegin]+'~'+data[basebegin+baselen-1]+' '+times[basebegin+baselen-1] 41 base = data_points[basebegin:basebegin+baselen]#一天的数据是240个点 42 length = len(data_points) #数据长度 43 44 # 分割片段 45 subseries = [] 46 dateseries = [] 47 for j in range(0,length): 48 if (j < (basebegin - baselen) or j > (basebegin + baselen - 1)) and j <length - baselen: 49 subseries.append(data_points[j:j+baselen]) 50 dateseries.append(j) #开始位置 51 52 # 片段搜索 53 listdistance = [] 54 for i in range(0, len(subseries)): 55 tt = np.array(subseries[i]) 56 distance = corrcoef(base, tt) 57 listdistance.append(distance) 58 59 # 排序 60 index = np.argsort(listdistance,kind='quicksort') #排序,返回排序后的索引序列 61 62 # 显示,要匹配的数据 63 plt.figure(0) 64 plt.plot((base),label = basedata, linewidth='2') 65 plt.legend(loc='upper left') 66 plt.title('Base data') 67 68 # 原始数据 69 plt.figure(1) 70 num = index[0] 71 length = len(subseries[num]) 72 begin = data[dateseries[num]]+' '+times[dateseries[num]] 73 end = data[dateseries[num]+length-1]+' '+times[dateseries[num]+length-1] 74 label = begin+'~'+end 75 plt.plot((subseries[num]), label=label, linewidth='2') 76 plt.legend(loc='upper left') 77 plt.title('Similarity data') 78 79 # 结果集对比 80 plt.figure(2) 81 plt.plot(normalization(base),label= basedata,linewidth='2') 82 length = len(subseries[num]) 83 begin = data[dateseries[num]] + ' ' + times[dateseries[num]] 84 end = data[dateseries[num] + length - 1] + ' ' + times[dateseries[num] + length - 1] 85 label = begin + '~' + end 86 plt.plot(normalization(subseries[num]), label=label, linewidth='3') 87 plt.legend(loc='lower right') 88 plt.title('normal similarity search') 89 plt.show() 90 91 endTimeStamp=datetime.now() 92 print('run time', (endTimeStamp-startTimeStamp).seconds, "s")
结果: