1, contains()方法底层依赖的是equals()方法,而定义的类中没有equal()方法,所以它会使用父类Object中的equals()方法,而Object的equals()方法比较的是地址值。 而new的对象,地址值不同。
2,泛型类型必须是引用类型
obj.setObj(new Integer(27));
(String)obj.getObj()//汇报类型转换错误
3,反省通配符(?)
4,treeSet:自然排序,唯一(TreeSet底層就是treeMap)
真正的比较依赖于元素的CompareTo()方法,而这个方法是定义在Comparable里面的,
所以要想重写该方法,就必须先实现COmparable接口,这个接口表示的就是自然排序
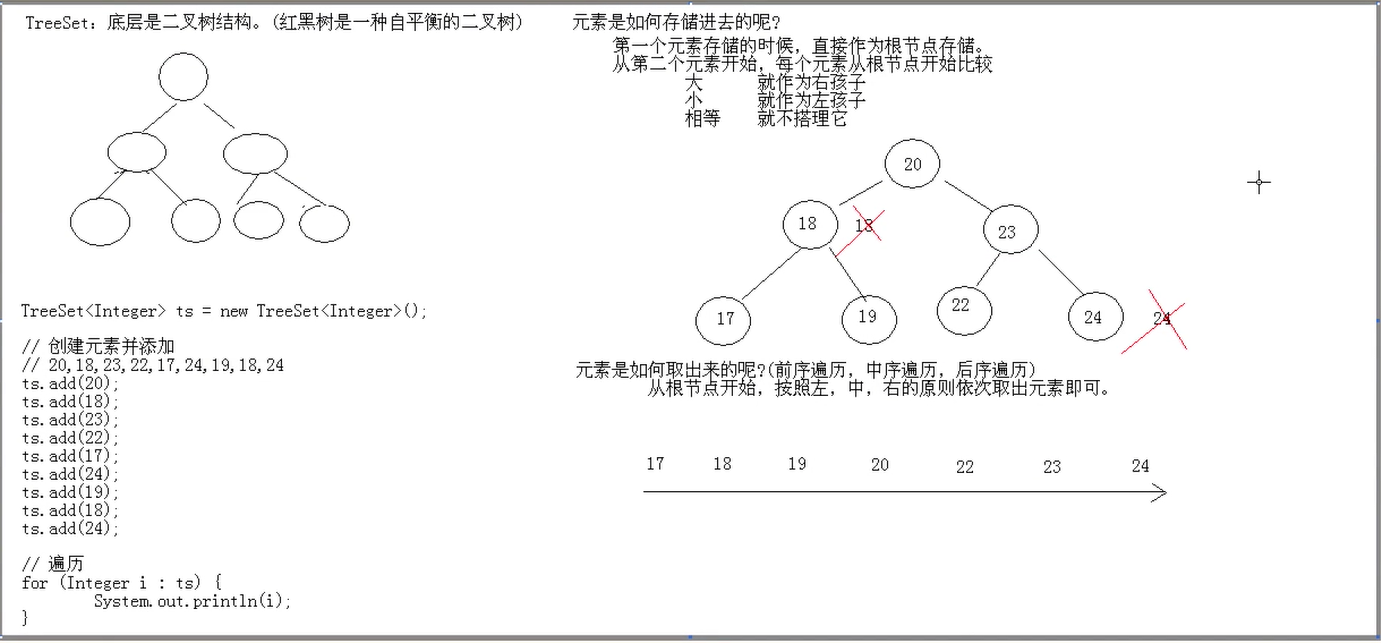
底层是二叉树结构(红黑树是一种自平衡的二叉树)。
二叉树三种遍历:
中序遍历:先左子树,后根节点,再右子树
前序遍历:先根节点,后左子树,再右子树
后序遍历:先左子树,后右子树,再根节点
源码:①TreeSet<String> set = new TreeSet<String>();
②set.add("d");
public boolean add(E e) {
return m.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
}
private transient NavigableMap<E,Object> m;
API:
ANavigableSetimplementation based on aTreeMap.
TreeMap的put();
public V put(K key, V value) {
Entry<K,V> t = root;
if (t == null) {
compare(key, key); // type (and possibly null) check
root = new Entry<>(key, value, null);
size = 1;
modCount++;
return null;
}
int cmp;
Entry<K,V> parent;
// split comparator and comparable paths
Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
if (cpr != null) {
do {
parent = t;
cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key);//key-t.key
if (cmp < 0) // key小放左边
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0) // key大放右边
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value); //相等,不放,但是变更value(?)
} while (t != null);
}
else {
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
do {
parent = t;
cmp = k.compareTo(t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<>(key, value, parent);
if (cmp < 0)
parent.left = e;
else
parent.right = e;
fixAfterInsertion(e);
size++;
modCount++;
return null;
}
总结:TreeSet集合保证元素排序和唯一性的原理
唯一性:根据比较的返回值是否为0来决定的
排序:
A:自然排序(元素具备比较性)
让元素所属的类实现自然排序接口Comparable
B:比较器排序(集合具备比较性)
让集合的构造方法接收一个比较器接口的子类对象Comparator