Service跟Activity也是出于统一级别的组件,且与Activity的最大区别之一主要是没有人机界面,主要是运行在程序的后台(我是这么理解的),帮助文档上说的是运行于进程的主线程中,但是服务并不是一个线程,这点是非常重要的。
一、 服务的启动
说明:服务的启动分为两种,一种是使用startService方法启动,另外一种是使用BindService方法,具体的来看看代码是如何实现的。
1、使用startService方法
@Override public void onClick(View arg0) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Intent intent = new Intent(); intent.setClass(MainActivity.this, Mp3Service.class); startService(intent); }
2、使用bingService方法
ServiceConnection conn = new ServiceConnection() { @Override public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } @Override public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub mp3binder binder = (mp3binder) service; binder.getData(); } }; @Override public void onClick(View arg0) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Intent intent = new Intent(); intent.setClass(MainActivity.this, Mp3Service.class); bindService(intent, conn, BIND_AUTO_CREATE); }
注意:使用这两种方式的区别在于:使用startService方法启动服务,无法获得返回值,或在是说没有返回值,使用bindService方法可以得到服务处理后的返回值
二、服务的实现
说明:服务的实现需要继承Service类,如果是使用startService方式的话,需要重写onStartCommand方法,如果是使用bindService方式的,需要重写onBind方法
三、服务的生命周期
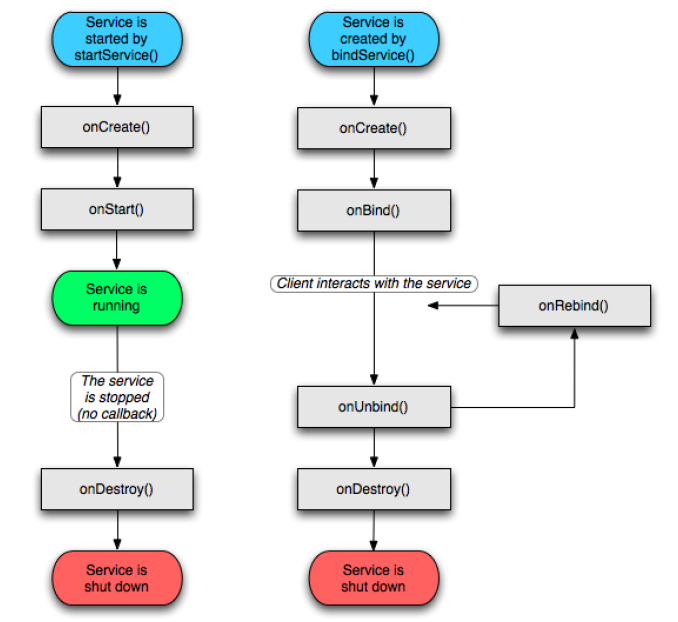
说明:
使用StartService运行服务的情景:使用这种方法启动服务,服务的onCreate()和onStart()这两个方法将被调用,服务会在后台运行直到退出,退出时将调用onDestroy()方法。
使用bindService运行服务的情景:使用这种方法启动服务,调用者(也就是服务的客户端)将获得和服务交互的类,通过其调用时服务的相关内容会处于活动状态。