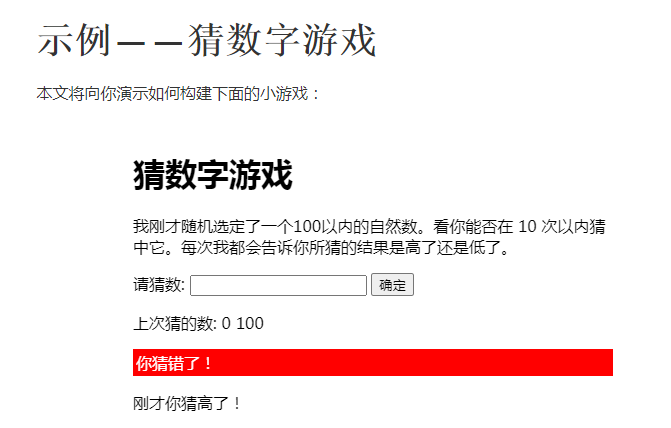
2020.7.1
JavaScript 初体验
数组


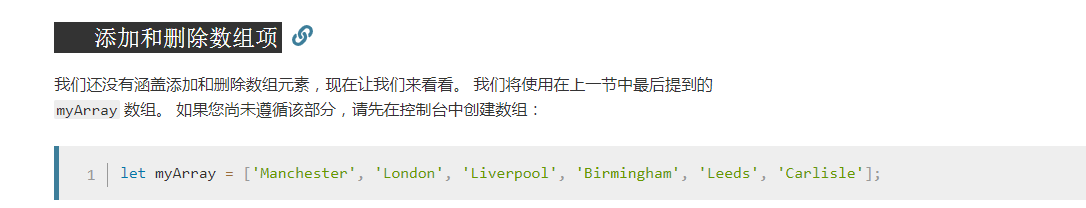


控制节点增删的实例:

1 var list = document.querySelector('.output ul'); 2 var searchInput = document.querySelector('.output input'); 3 var searchBtn = document.querySelector('.output button'); 4 5 list.innerHTML = ''; 6 7 var myHistory= []; 8 9 searchBtn.onclick = function() { 10 if(searchInput.value !== '') { 11 myHistory.unshift(searchInput.value); 12 13 list.innerHTML = ''; 14 15 for(var i = 0; i < myHistory.length; i++) { 16 var itemText = myHistory[i]; 17 var listItem = document.createElement('li'); 18 listItem.textContent = itemText; 19 list.appendChild(listItem); 20 } 21 22 if(myHistory.length >= 5) { 23 myHistory.pop(); 24 } 25 26 searchInput.value = ''; 27 searchInput.focus(); 28 } 29 }
笑话生成器
函数作用域和冲突
很形象的例子:

实例:

事件介绍
事件参考
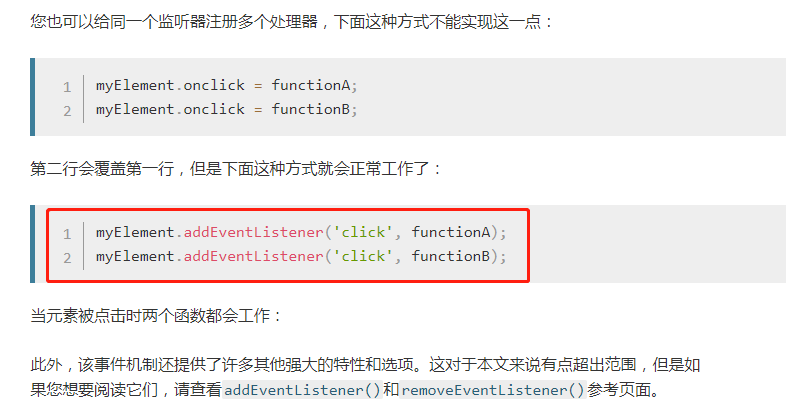
addEventListener()和removeEventListener()
对事件冒泡和捕捉的解释
事件委托
冒泡还允许我们利用事件委托——这个概念依赖于这样一个事实,如果你想要在大量子元素中单击任何一个都可以运行一段代码,您可以将事件监听器设置在其父节点上,并让子节点上发生的事件冒泡到父节点上,而不是每个子节点单独设置事件监听器。
JavaScript中matches(matchesSelector)的兼容写法
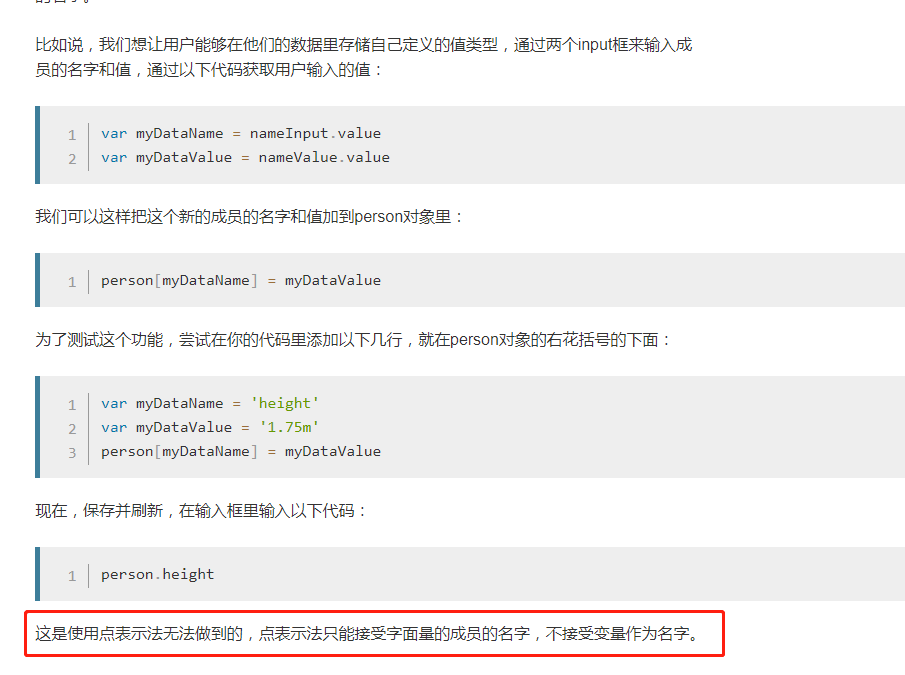
JavaScript 对象基础


"this"的含义

适合初学者的JavaScript面向对象
一个简单的例子
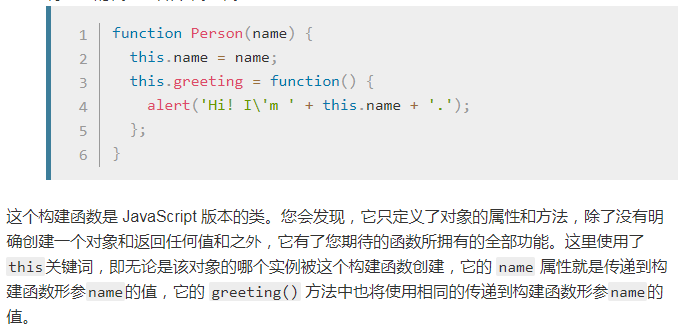
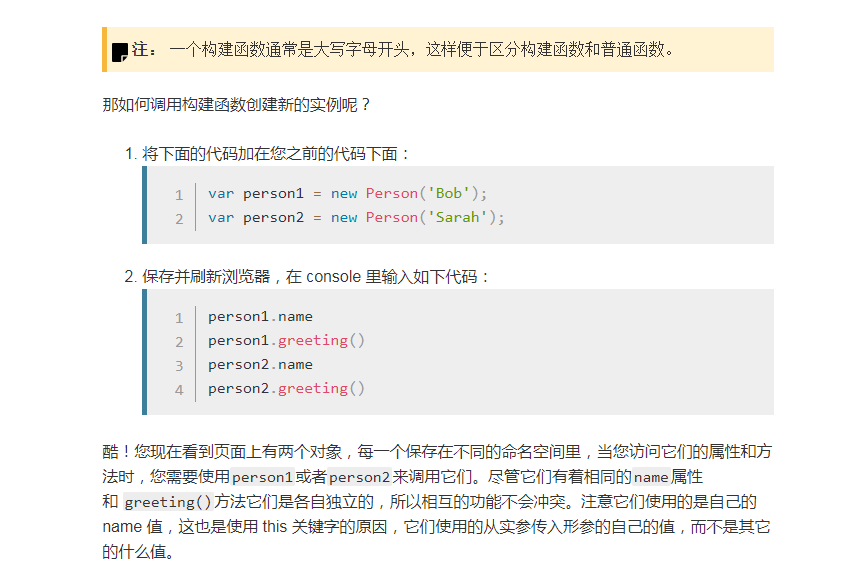
创建我们最终的构造函数




实践对象构造
画圆

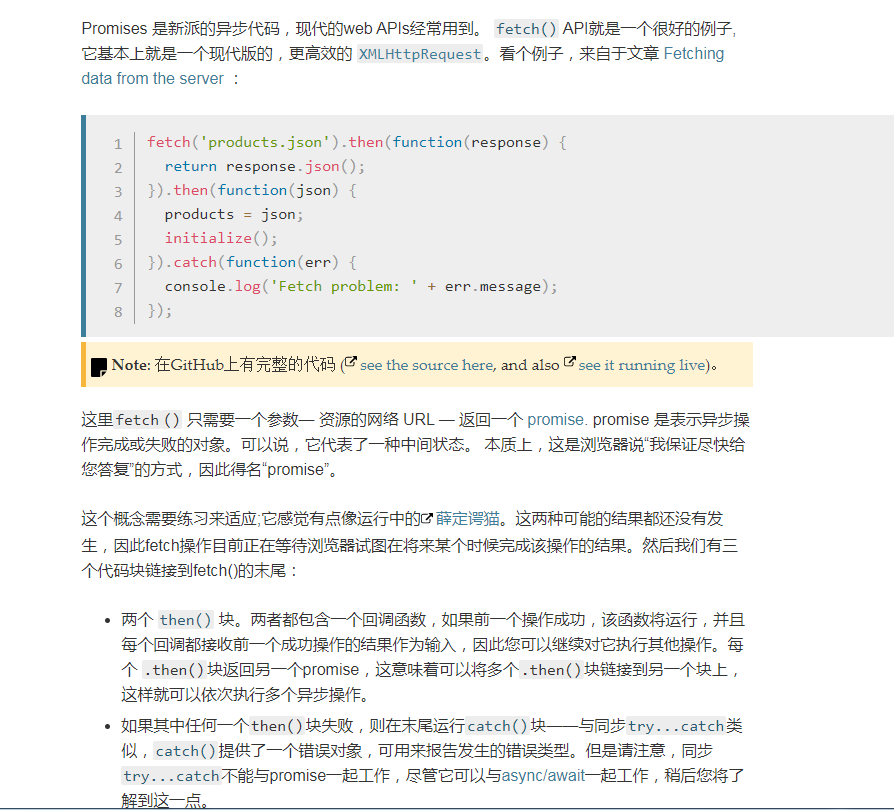
异步JavaScript
Promise
回调地狱
函数提升
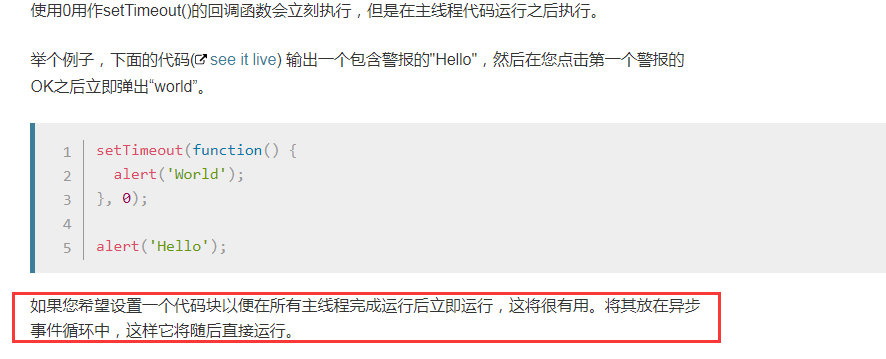
关于 setTimeout() 和 setInterval() 需要注意的几点

立即超时
一个更真实的例子
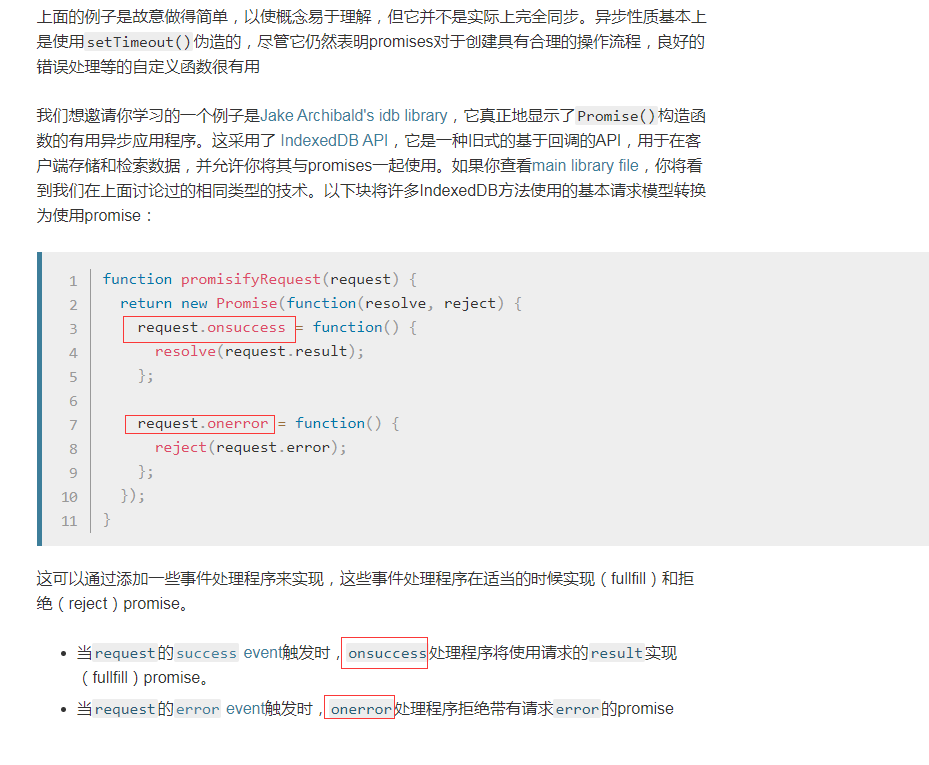

async和await:让异步编程更简单
async 关键字


等待Promise.all()

async/await的缺陷
不错的例子,将三个Promise对象存储在变量中,这样可以同时启动它们关联的进程(包含代码计时):

1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="utf-8"> 5 <title>Demonstration of fast async/await</title> 6 </head> 7 <body> 8 <script> 9 // Define custom promise function 10 11 function timeoutPromise(interval) { 12 return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { 13 setTimeout(function(){ 14 resolve("done"); 15 }, interval); 16 }); 17 }; 18 19 async function timeTest() { 20 const timeoutPromise1 = timeoutPromise(3000); 21 const timeoutPromise2 = timeoutPromise(3000); 22 const timeoutPromise3 = timeoutPromise(3000); 23 24 await timeoutPromise1; 25 await timeoutPromise2; 26 await timeoutPromise3; 27 } 28 29 let startTime = Date.now(); 30 timeTest().then(() => { 31 let finishTime = Date.now(); 32 let timeTaken = finishTime - startTime; 33 alert("Time taken in milliseconds: " + timeTaken); 34 }) 35 </script> 36 </body> 37 </html>

总结
选择正确的方法
BabelJS 库
Web API简介
实用代码,解析json:

1 var requestURL = 'https://mdn.github.io/learning-area/javascript/oojs/json/superheroes.json'; 2 var request = new XMLHttpRequest(); 3 request.open('GET', requestURL); 4 request.responseType = 'json'; 5 request.send(); 6 7 request.onload = function() { 8 var superHeroes = request.response; 9 populateHeader(superHeroes); 10 showHeroes(superHeroes); 11 }
跨域
浏览器的同源策略
HTTP访问控制(CORS)
Origin

基本的DOM 操作
Node的创建,增删

从Window对象中获取有用的信息
resize
·
操作文档
添加移除节点:

1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="utf-8"> 5 <title>Shopping list example</title> 6 <style> 7 li { 8 margin-bottom: 10px; 9 } 10 11 li button { 12 font-size: 8px; 13 margin-left: 20px; 14 color: #666; 15 } 16 </style> 17 </head> 18 <body> 19 20 <h1>My shopping list</h1> 21 22 <div> 23 <label for="item">Enter a new item:</label> 24 <input type="text" name="item" id="item"> 25 <button>Add item</button> 26 </div> 27 28 <ul> 29 30 </ul> 31 32 <script> 33 const list = document.querySelector('ul'); 34 const input = document.querySelector('input'); 35 const button = document.querySelector('button'); 36 37 button.onclick = function() { 38 let myItem = input.value; 39 input.value = ''; 40 41 const listItem = document.createElement('li'); 42 const listText = document.createElement('span'); 43 const listBtn = document.createElement('button'); 44 45 listItem.appendChild(listText); 46 listText.textContent = myItem; 47 listItem.appendChild(listBtn); 48 listBtn.textContent = 'Delete'; 49 list.appendChild(listItem); 50 51 listBtn.onclick = function(e) { 52 list.removeChild(listItem); 53 } 54 55 input.focus(); 56 } 57 </script> 58 </body> 59 </html>
从服务器获取数据
在现代网站和应用中另一个常见的任务是从服务端获取个别数据来更新部分网页而不用加载整个页面。 这看起来是小细节却对网站性能和行为产生巨大的影响。
ajax

1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="utf-8"> 5 <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge,chrome=1"> 6 <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width"> 7 8 <title>Ajax starting point</title> 9 10 <style> 11 html, pre { 12 font-family: sans-serif; 13 } 14 15 body { 16 width: 500px; 17 margin: 0 auto; 18 background-color: #ccc; 19 } 20 21 pre { 22 line-height: 1.5; 23 letter-spacing: 0.05rem; 24 padding: 1rem; 25 background-color: white; 26 } 27 28 label { 29 width: 200px; 30 margin-right: 33px; 31 } 32 33 select { 34 width: 350px; 35 padding: 5px; 36 } 37 38 </style> 39 <!--[if lt IE 9]> 40 <script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/html5shiv/3.7.3/html5shiv.js"></script> 41 <![endif]--> 42 </head> 43 44 <body> 45 <h1>Ajax starting point</h1> 46 47 <form> 48 <label for="verse-choose">Choose a verse</label> 49 <select id="verse-choose" name="verse-choose"> 50 <option>Verse 1</option> 51 <option>Verse 2</option> 52 <option>Verse 3</option> 53 <option>Verse 4</option> 54 </select> 55 </form> 56 57 <h2>The Conqueror Worm, <em>Edgar Allen Poe, 1843</em></h2> 58 59 <pre> 60 61 </pre> 62 63 <script> 64 const verseChoose=document.querySelector('select'); 65 const poemDisplay=document.querySelector('pre'); 66 let request=new XMLHttpRequest(); 67 68 verseChoose.onchange=function(){ 69 console.log("切换") 70 const verse=verseChoose.value; 71 console.log(verse); 72 updateDisplay(verse); 73 74 } 75 function updateDisplay(verse){ 76 console.log("进入更新") 77 verse=verse.replace(" ",""); 78 verse=verse.toLowerCase(); 79 console.log(verse) 80 let url=verse+'.txt'; 81 console.log(url) 82 83 request.open('GET',url); 84 request.responseType='text'; 85 request.send(); 86 console.log(request) 87 88 } 89 request.onload=function(){ 90 console.log("加载完成") 91 poemDisplay.textContent=request.response; 92 console.log(request.response); 93 } 94 updateDisplay('Verse 1'); 95 verseChoose.value='Verse 1' 96 // updateDisplay(); 97 98 99 </script> 100 </body> 101 </html>

1 // use fetch to retrieve the products and pass them to init 2 // report any errors that occur in the fetch operation 3 // once the products have been successfully loaded and formatted as a JSON object 4 // using response.json(), run the initialize() function 5 fetch('products.json').then(function(response) { 6 return response.json(); 7 }).then(function(json) { 8 let products = json; 9 initialize(products); 10 }).catch(function(err) { 11 console.log('Fetch problem: ' + err.message); 12 }); 13 14 // sets up the app logic, declares required variables, contains all the other functions 15 function initialize(products) { 16 // grab the UI elements that we need to manipulate 17 const category = document.querySelector('#category'); 18 const searchTerm = document.querySelector('#searchTerm'); 19 const searchBtn = document.querySelector('button'); 20 const main = document.querySelector('main'); 21 22 // keep a record of what the last category and search term entered were 23 let lastCategory = category.value; 24 // no search has been made yet 25 let lastSearch = ''; 26 27 // these contain the results of filtering by category, and search term 28 // finalGroup will contain the products that need to be displayed after 29 // the searching has been done. Each will be an array containing objects. 30 // Each object will represent a product 31 let categoryGroup; 32 let finalGroup; 33 34 // To start with, set finalGroup to equal the entire products database 35 // then run updateDisplay(), so ALL products are displayed initially. 36 finalGroup = products; 37 updateDisplay(); 38 39 // Set both to equal an empty array, in time for searches to be run 40 categoryGroup = []; 41 finalGroup = []; 42 43 // when the search button is clicked, invoke selectCategory() to start 44 // a search running to select the category of products we want to display 45 searchBtn.onclick = selectCategory; 46 47 function selectCategory(e) { 48 // Use preventDefault() to stop the form submitting — that would ruin 49 // the experience 50 e.preventDefault(); 51 52 // Set these back to empty arrays, to clear out the previous search 53 categoryGroup = []; 54 finalGroup = []; 55 56 // if the category and search term are the same as they were the last time a 57 // search was run, the results will be the same, so there is no point running 58 // it again — just return out of the function 59 if(category.value === lastCategory && searchTerm.value.trim() === lastSearch) { 60 return; 61 } else { 62 // update the record of last category and search term 63 lastCategory = category.value; 64 lastSearch = searchTerm.value.trim(); 65 // In this case we want to select all products, then filter them by the search 66 // term, so we just set categoryGroup to the entire JSON object, then run selectProducts() 67 if(category.value === 'All') { 68 categoryGroup = products; 69 selectProducts(); 70 // If a specific category is chosen, we need to filter out the products not in that 71 // category, then put the remaining products inside categoryGroup, before running 72 // selectProducts() 73 } else { 74 // the values in the <option> elements are uppercase, whereas the categories 75 // store in the JSON (under "type") are lowercase. We therefore need to convert 76 // to lower case before we do a comparison 77 let lowerCaseType = category.value.toLowerCase(); 78 for(let i = 0; i < products.length ; i++) { 79 // If a product's type property is the same as the chosen category, we want to 80 // display it, so we push it onto the categoryGroup array 81 if(products[i].type === lowerCaseType) { 82 categoryGroup.push(products[i]); 83 } 84 } 85 86 // Run selectProducts() after the filtering has been done 87 selectProducts(); 88 } 89 } 90 } 91 92 // selectProducts() Takes the group of products selected by selectCategory(), and further 93 // filters them by the tiered search term (if one has been entered) 94 function selectProducts() { 95 // If no search term has been entered, just make the finalGroup array equal to the categoryGroup 96 // array — we don't want to filter the products further — then run updateDisplay(). 97 if(searchTerm.value.trim() === '') { 98 finalGroup = categoryGroup; 99 updateDisplay(); 100 } else { 101 // Make sure the search term is converted to lower case before comparison. We've kept the 102 // product names all lower case to keep things simple 103 let lowerCaseSearchTerm = searchTerm.value.trim().toLowerCase(); 104 // For each product in categoryGroup, see if the search term is contained inside the product name 105 // (if the indexOf() result doesn't return -1, it means it is) — if it is, then push the product 106 // onto the finalGroup array 107 for(let i = 0; i < categoryGroup.length ; i++) { 108 if(categoryGroup[i].name.indexOf(lowerCaseSearchTerm) !== -1) { 109 finalGroup.push(categoryGroup[i]); 110 } 111 } 112 113 // run updateDisplay() after this second round of filtering has been done 114 updateDisplay(); 115 } 116 117 } 118 119 // start the process of updating the display with the new set of products 120 function updateDisplay() { 121 // remove the previous contents of the <main> element 122 while (main.firstChild) { 123 main.removeChild(main.firstChild); 124 } 125 126 // if no products match the search term, display a "No results to display" message 127 if(finalGroup.length === 0) { 128 const para = document.createElement('p'); 129 para.textContent = 'No results to display!'; 130 main.appendChild(para); 131 // for each product we want to display, pass its product object to fetchBlob() 132 } else { 133 for(let i = 0; i < finalGroup.length; i++) { 134 fetchBlob(finalGroup[i]); 135 } 136 } 137 } 138 139 // fetchBlob uses fetch to retrieve the image for that product, and then sends the 140 // resulting image display URL and product object on to showProduct() to finally 141 // display it 142 function fetchBlob(product) { 143 // construct the URL path to the image file from the product.image property 144 let url = 'images/' + product.image; 145 // Use fetch to fetch the image, and convert the resulting response to a blob 146 // Again, if any errors occur we report them in the console. 147 fetch(url).then(function(response) { 148 return response.blob(); 149 }).then(function(blob) { 150 // Convert the blob to an object URL — this is basically an temporary internal URL 151 // that points to an object stored inside the browser 152 let objectURL = URL.createObjectURL(blob); 153 // invoke showProduct 154 showProduct(objectURL, product); 155 }); 156 } 157 158 // Display a product inside the <main> element 159 function showProduct(objectURL, product) { 160 // create <section>, <h2>, <p>, and <img> elements 161 const section = document.createElement('section'); 162 const heading = document.createElement('h2'); 163 const para = document.createElement('p'); 164 const image = document.createElement('img'); 165 166 // give the <section> a classname equal to the product "type" property so it will display the correct icon 167 section.setAttribute('class', product.type); 168 169 // Give the <h2> textContent equal to the product "name" property, but with the first character 170 // replaced with the uppercase version of the first character 171 heading.textContent = product.name.replace(product.name.charAt(0), product.name.charAt(0).toUpperCase()); 172 173 // Give the <p> textContent equal to the product "price" property, with a $ sign in front 174 // toFixed(2) is used to fix the price at 2 decimal places, so for example 1.40 is displayed 175 // as 1.40, not 1.4. 176 para.textContent = '$' + product.price.toFixed(2); 177 178 // Set the src of the <img> element to the ObjectURL, and the alt to the product "name" property 179 image.src = objectURL; 180 image.alt = product.name; 181 182 // append the elements to the DOM as appropriate, to add the product to the UI 183 main.appendChild(section); 184 section.appendChild(heading); 185 section.appendChild(para); 186 section.appendChild(image); 187 } 188 }
第三方 API
google map
纽约时报例子 分页

YouTube
绘图
WebGL 教程
WebGL
由于 3D 绘图的复杂性,大多数人写代码时会使用第三方 JavaScript 库(比如 Three.js、PlayCanvas 或 Babylon.js)。大多数库的原理都基本类似,提供创建基本的、自定义性状的功能、视图定位摄影和光效、表面纹理覆盖,等等。库负责 与 WebGL 通信,你只需完成更高阶工作。
接触任何一个库都意味着要学一套全新的API(这里是第三方的版本),但与纯 WebGL 编程都大同小异。
- Canvas 教程:一个详尽的教程系列,更细致深入地讲解了 2D 画布所需的知识。必读。
- WebGL 教程:纯 WebGL 编程教程系列。
- 用 Three.js 创建一个简单的示例:Three.js 基础教程。我们还提供 PlayCanvas 和 Babylon.js 的基础教程。
- 游戏开发:MDN web 游戏开发目录页。提供与 2D、3D画布相关的实用教程和技术,可参考“技术”和“教程”菜单项。
我需要什么软件来构建一个网站
推荐了很多有用的工具
在互联网上做一件事要花费多少
一条龙服务,提供很多工具
如何设置一个本地测试服务器?
用python设置服务器

typeof与instanceof的区别,及Object.prototype.toString()方法
[] instanceof Array
Object.prototype.toString.call()