--------安装
pip install pymysql
-----连接数据库
1.数据库中查询出的数据
SELECT book_id,book_name FROM t_book WHERE market_rule=1
2.连接数据库
import pymysql import types #连接数据库 connect=pymysql.connect(host="192.168.6.41",user="lrtsaudio",password="2&Ty3DW75i!(vgo.l3Odp1fgWgEG",port=3306,db="audiobook") #创建一个游标对象:有两种创建方法 cursor=connect.cursor()
#或:cursor=pymysql.cursors.Cursor(connect) #使用游标的execute()方法执行sql语句 cursor.execute("SELECT book_id,book_name FROM t_book WHERE market_rule=1") #使用fetchall()获取全部数据 r1=cursor.fetchall() print(r1) print(type(r1)) #关闭游标连接 cursor.close() #关闭数据库连接 connect.close()
结果如下:(返回结果为元组)

也可以通过字典来传递参数:效果是一样的
dbinfo={"host":"192.168.6.41",
"user":"lrtsaudio",
"password":"2&Ty3DW75i!(vgo.l3Odp1fgWgEG",
"db":"audiobook"
}
sql="SELECT * FROM t_book WHERE market_rule=1"
connect1=pymysql.connect(**dbinfo)
cursor1=connect1.cursor()
cursor1.execute(sql)
r2=cursor1.fetchall()
print(r2)
cursor1.close()
connect1.close
-------connect()各个参数代表的意思
host=None, # 要连接的主机地址 user=None, # 用于登录的数据库用户 password='', # 密码 database=None, # 要连接的数据库 port=0, # 端口,一般为 3306 unix_socket=None, # 选择是否要用unix_socket而不是TCP/IP charset='', # 字符编码 sql_mode=None, # Default SQL_MODE to use. read_default_file=None, # 从默认配置文件(my.ini或my.cnf)中读取参数 conv=None, # 转换字典 use_unicode=None, # 是否使用 unicode 编码 client_flag=0, # Custom flags to send to MySQL. Find potential values in constants.CLIENT. cursorclass=<class 'pymysql.cursors.Cursor'>, # 选择 Cursor 类型 init_command=None, # 连接建立时运行的初始语句 connect_timeout=10, # 连接超时时间,(default: 10, min: 1, max: 31536000) ssl=None, # A dict of arguments similar to mysql_ssl_set()'s parameters.For now the capath and cipher arguments are not supported. read_default_group=None, # Group to read from in the configuration file. compress=None, # 不支持 named_pipe=None, # 不支持 no_delay=None, # autocommit=False, # 是否自动提交事务 db=None, # 同 database,为了兼容 MySQLdb passwd=None, # 同 password,为了兼容 MySQLdb local_infile=False, # 是否允许载入本地文件 max_allowed_packet=16777216, # 限制 `LOCAL DATA INFILE` 大小 defer_connect=False, # Don't explicitly connect on contruction - wait for connect call. auth_plugin_map={}, # read_timeout=None, # write_timeout=None, bind_address=None # 当客户有多个网络接口,指定一个连接到主机
-------查询数据
import pymysql dbinfo={"host":"192.168.6.41", "user":"lrtsaudio", "password":"2&Ty3DW75i!(vgo.l3Odp1fgWgEG", "db":"audiobook" } sql1="SELECT book_id,book_name FROM t_book WHERE market_rule=1" sql2="SELECT * FROM audiobook.w_activity_ticket_3 WHERE user_id=234739503" connect1=pymysql.connect(**dbinfo) cursor1=connect1.cursor() cursor1.execute(sql1) #返回值为受影响的行数,如下: """ num=cursor1.execute(sql1) print(num) #结果:num=8 """ r_all=cursor1.fetchall()#取出全部查询结果 r_one=cursor1.fetchone()#取出一行查询结果。从第一行开始取 r_many=cursor1.fetchmany(size=2)#取出其中几行查询结果 print(r_all) print(r_one) print(r_many) cursor1.close() connect1.close()

注释掉fetchall的代码后结果:
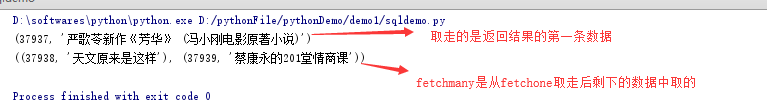
!!!也就是说:
如fetchall(),fetchmany(),fetchone()同时作用于同一个查询时,每个方法执行开头是上一个方法执行的结尾
----可以通过scroll()来重置游标位置,从我们需要的位置获取我们想要的数据
cursor.scroll(sele,value,mode="")
# value: 偏移量 大于0向后移动; 小于0向前移动 # mode: relative:表示从当前所在的行开始移动; absolute:表示从第一行开始移动 (默认relative)
.....
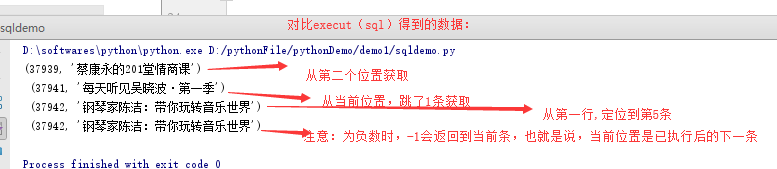
cursor1.execute(sql1) cursor1.scroll(2) #mode不填时,默认为“relative” r1=cursor1.fetchone() cursor1.scroll(1,mode="relative") r2=cursor1.fetchone() cursor1.scroll(5,mode="absolute") r3=cursor1.fetchone() cursor1.scroll(-1) r4=cursor1.fetchone() print(r1," ",r2," ",r3," ",r4)
.....
结果:
----游标类型:可控制返回数据类型
上面的实例中,使用的均是普通游标,返回结果为元组:查看起来不太方便,我们可以通过游标类型来控制数据返回类型

----游标类型:
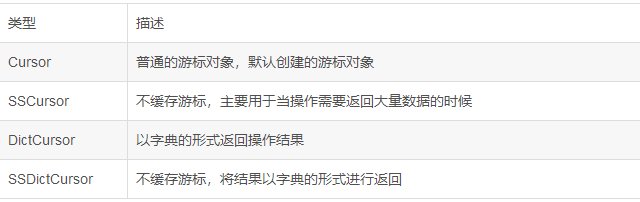
--有两种方法定义游标类型:(只需其中一种即可)
#1.在connect()中通过 “cursorclass=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor” 来定义 connect=pymysql.connect(host="192.168.6.41",user="lrtsaudio",password="2&Ty3DW75i!(vgo.l3Odp1fgWgEG",port=3306,db="audiobook",cursorclass=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) #2.在创建游标时定义(两种创建游标的方法使用方式如下:)
cursor=connect.cursor(pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) cursor=pymysql.cursors.Dictcursor(connect)
结果:返回字典类型的list

--不缓存游标的用法:
