官网下载:
http://nginx.org/en/docs/windows.html
官方说明:
nginx的Windows版本使用原生Win32 API(非Cygwin模拟层)。当前nginx/Windows只使用select作为通知方法,所以不要期待它有很高的性能和扩展性。鉴于这点和一些已知问题,nginx/Windows目前还处于beta阶段。nginx/Windows和Unix版本相比,功能几乎已经齐全,除了XSLT过滤器、图像过滤器、GeoIP模块和嵌入Perl语言支持以外。
安装nginx/Windows,需要下载最新的1.7.4开发版本,因为开发分支上包含了所有已知的问题修复,尤其是针对Windows版本的问题修复。解压缩下载得到的zip文件,进入nginx-1.7.4目录,运行nginx。下面给出一个在C盘根目录下安装的例子:
cd c: unzip nginx-1.7.4.zip cd nginx-1.7.4 start nginx
可以在命令行运行tasklist命令来查看nginx进程:
C: ginx-1.7.4>tasklist /fi "imagename eq nginx.exe" Image Name PID Session Name Session# Mem Usage =============== ======== ============== ========== ============ nginx.exe 652 Console 0 2 780 K nginx.exe 1332 Console 0 3 112 K
其中一个是主进程,另一个是工作进程。如果nginx没有启动,请查看logserror.log文件以寻找失败原因。如果日志文件不存在,那失败原因会记录在Windows事件日志中。如果某次请求没有展示预想的页面,而是展示了错误页面,也请查看logserror.log文件。
我报的错误:
2014/08/29 11:23:58 [emerg] 3844#5628: bind() to 0.0.0.0:80 failed (10013: An attempt was made to access a socket in a way forbidden by its access permissions)
输入:netstat -aon | findstr :80
D:
ginx-1.7.4>netstat -aon | findstr :80
TCP 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING 1564
TCP 192.168.52.134:1033 180.149.156.143:80 CLOSE_WAIT 3120
TCP 192.168.52.134:1455 220.181.150.32:80 ESTABLISHED 4008
TCP 192.168.52.134:3402 218.30.116.11:80 ESTABLISHED 4008
TCP 192.168.52.134:5108 218.30.103.235:80 CLOSE_WAIT 3692
TCP 192.168.52.134:5177 218.30.103.235:80 CLOSE_WAIT 4564
TCP 192.168.52.134:5252 218.30.103.235:80 CLOSE_WAIT 3156
TCP 192.168.52.134:5254 218.30.103.235:80 CLOSE_WAIT 3668
TCP 192.168.52.134:5266 218.30.103.235:80 CLOSE_WAIT 3608
80端口被占用。
1、打开注册表:regedit
2、找到:HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetservicesHTTP
3、找到一个REG_DWORD类型的项Start,将其改为0
4、重启系统,System进程不会占用80端口
重启之后,start nginx.exe 。在浏览器中,输入127.0.01,即可看到亲爱的“Welcome to nginx!” 了。
或者:
这是80端口被占用的缘故,修改下端口即可。
文件conf/nginx.conf
server {
listen 8888;
server_name localhost;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
在浏览器中输入127.0.0.1:8888看到下面页面即说明成功。
Welcome to nginx!
If you see this page, the nginx web server is successfully installed and working. Further configuration is required.
For online documentation and support please refer tonginx.org.
Commercial support is available atnginx.com.
Thank you for using nginx.
nginx/Windows使用工作目录作为前缀将配置文件中设置的相对目录补齐。就上面安装的例子而言,工作目录应该是C:
ginx-1.7.4(工作目录基本上与运行文件所在的目录相同)。配置文件中的目录请使用“/”,而不是“”做目录分隔:
access_log logs/site.log; root C:/web/html;
nginx/Windows作为标准控制台应用运行,而不是系统服务。可以用下面的命令控制:
nginx -s stop 快速退出 nginx -s quit 优雅退出 nginx -s reload 更换配置,启动新的工作进程,优雅的关闭以往的工作进程 nginx -s reopen 重新打开日志文件
已知问题
- 虽然可以启动若干工作进程运行,实际上只有一个进程在处理请求所有请求。
- 一个工作进程只能处理不超过1024个并发连接。
- 缓存和其他需要共享内存支持的模块在Windows Vista及后续版本的操作系统中无法工作,因为在这些操作系统中,地址空间的布局是随机的。
日后可能加强的功能
- 作为系统服务运行。
- 使用“I/O完成端口”作为事件模型。
- 使用单工作进程多线程的模型。
http://www.cnblogs.com/happyday56/p/3829409.html
http://www.cnblogs.com/mecity/archive/2011/06/20/2085529.html
linux安装后和apache80端口相同,修改端口:
root用户安装:
sudo apt-get install nginx
whereis nginx
/usr/sbin/nginx
linux源代码编译安装:
tar -zxvf nginx-1.7.0.tar.gz
安装向导:http://nginx.org/en/docs/configure.html
部分选项:
-
--prefix=— defines a directory that will keep server files. This same directory will also be used for all relative paths set bypathconfigure(except for paths to libraries sources) and in thenginx.confconfiguration file. It is set to the/usr/local/nginxdirectory by default. -
--sbin-path=— sets the name of an nginx executable file. This name is used only during installation. By default the file is namedpathprefix/sbin/nginx -
--conf-path=— sets the name of anpathnginx.confconfiguration file. If needs be, nginx can always be started with a different configuration file, by specifying it in the command-line parameter-c. By default the file is namedfileprefix/conf/nginx.conf
-
--with-http_ssl_module— enables building a module that adds the HTTPS protocol support to an HTTP server. This module is not built by default. The OpenSSL library is required to build and run this module.
-
--with-select_module--without-select_module— enables or disables building a module that allows the server to work with theselect()method. This module is built automatically if the platform does not appear to support more appropriate methods such as kqueue, epoll, rtsig, or /dev/poll. -
--with-poll_module--without-poll_module— enables or disables building a module that allows the server to work with thepoll()method. This module is built automatically if the platform does not appear to support more appropriate methods such as kqueue, epoll, rtsig, or /dev/poll.
-
--with-pcre-jit— builds the PCRE library with “just-in-time compilation” support (1.1.12, the pcre_jit directive). -
--with-zlib=— sets the path to the sources of the zlib library. The library distribution (version 1.1.3 — 1.2.7) needs to be downloaded from the zlib site and extracted. The rest is done by nginx’spath./configureandmake. The library is required for the ngx_http_gzip_modulemodule.
--with-http_gzip_static_module 开启gzip
–with-pcre:为了支持rewrite重写功能,必须制定pcre
我的编译选项;
–with-http_stub_status_module:支持nginx状态查询
–with-http_ssl_module:支持https
–with-pcre:为了支持rewrite重写功能,必须制定pcre
nginx依赖以下一些软件库,在安装之前请确保安装了这些软件库,它们包括:gcc,openssl,zlib,pcre(可通过rpm -q命令查询是否已安装),其中前三个库可通过系统盘进行安装,这里仅简单说说pcre的安装:
下载pcre至/home目录下,这里选择的版本是pcre-8.10,下载完后执行以下操作
- 1.[root@localhost home]# tar zxvf pcre-8.10.tar.gz //解压缩
- 2.[root@localhost home]# cd pcre-8.10 //切换到该目录下
- 3.[root@localhost pcre-8.10]#./configure //配置
- 4.[root@localhost pcre-8.10]#make
- 5.[root@localhost pcre-8.10]#make install //安装
- 怎样在Debian/Ubuntu Linux下安装pcre-devel呢?
Perl-compatible regular expression library. PCRE has its own native API, but a set of “wrapper” functions that are based on the POSIX API are also supplied in the library libpcreposix. Note that this just provides a POSIX calling interface to PCRE: the regular expressions themselves still follow Perl syntax and semantics. The header file for the POSIX-style functions is called pcreposix.h. To install PCRE, type thy following command:
Perl兼容正则表达式库(PCRE)有自己原生API,但是这一系列封装函是基于POSIX API,而POSIX API也支持libpcreposix库。这样只要提供一个POSIX的调用接口给PCRE后,正则表达式本身仍遵循Perl的语法和语义。POSIX-style的头文件是pcreposix.h,所以,安装PCRE,需要运行以下命令。
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install libpcre3 libpcre3-dev
你可能还需要安装
sudo apt-get install openssl libssl-dev
配置时使用"with-http_stub_status_module"参数来启用 Nginx 的 NginxStatus 功能,以监控 Nginx 的当前状态
./configure --prefix=/opt/nginx --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-zlib --with-pcre=pcre路径
configure遇到错误:
./configure: error: the HTTP rewrite module requires the PCRE library.
You can either disable the module by using --without-http_rewrite_module
option, or install the PCRE library into the system, or build the PCRE library
statically from the source with nginx by using --with-pcre=<path> option.
用--with-pcre指定的是源代码路径。
下载pcre:
如果通过FTP的方式,下载地址为:ftp://ftp.csx.cam.ac.uk/pub/software/programming/pcre/
如果通过http的方式,下载地址为:http://sourceforge.net/projects/pcre/files/pcre/
启动:
执行sbin目录下的nginx,可以启动nginx了
root@iZ2 vwZ:/opt/nginx/sbin# ./nginx
nginx: [emerg] bind() to 0.0.0.0:80 failed (98: Address already in use)
nginx: [emerg] bind() to 0.0.0.0:80 failed (98: Address already in use)
说明80端口已经占用,改成8080
nginx管理脚本:
官方提供的
https://www.nginx.com/resources/wiki/start/topics/examples/redhatnginxinit/
将以上脚本保存到/etc/init.d/nginx文件,并修改两个地方:
- nginx=”/usr/sbin/nginx” 修改成nginx执行程序的路径。
- NGINX_CONF_FILE=”/etc/nginx/nginx.conf” 修改成配置文件的路径。
开机启动
chkconfig nginx on
ubuntu上面的管理脚本:http://github.com/JasonGiedymin/nginx-init-ubuntu
centos开放80端口
iptables -A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 80 -j ACCEPT
/etc/rc.d/init.d/iptables save
/etc/rc.d/init.d/iptables restart一定要重启
参考:
http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2013-06/85330.htm
配置:
#设定查看Nginx状态的地址
location /NginxStatus {
stub_status on;
access_log on;
auth_basic "NginxStatus";
auth_basic_user_file conf/htpasswd;
}
}
}
备注:conf/htpasswd 文档的内容用 apache 提供的 htpasswd 工具来产生即可!
查看 Nginx 运行状态 输入地址http://www.rekfan.com/NginxStatus/ 。输入验证帐号密码,即可看到类似如下内容:
Active connections: 328
server accepts handled requests
9309 8982 28890
Reading: 1 Writing: 3 Waiting: 324
nginx location配置:
43 location / {
44 root html;
45 index index.html index.htm;
46 }
47
48 #error_page 404 /404.html;
49
50 # redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
51 #
52 error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
53 location = /50x.html {
54 root html;
55 }
一篇文章:
语法规则: location [=|~|~*|^~] /uri/ { … }
= 开头表示精确匹配
^~ 开头表示uri以某个常规字符串开头,理解为匹配 url路径即可。nginx不对url做编码,因此请求为/static/20%/aa,可以被规则^~ /static/ /aa匹配到(注意是空格)。
~ 开头表示区分大小写的正则匹配
~* 开头表示不区分大小写的正则匹配
!~和!~*分别为区分大小写不匹配及不区分大小写不匹配 的正则
/ 通用匹配,任何请求都会匹配到。
多个location配置的情况下匹配顺序为(参考资料而来,还未实际验证,试试就知道了,不必拘泥,仅供参考):
首先匹配 =,其次匹配^~, 其次是按文件中顺序的正则匹配,最后是交给 / 通用匹配。当有匹配成功时候,停止匹配,按当前匹配规则处理请求。
例子,有如下匹配规则:
location = / {
#规则A
}
location = /login {
#规则B
}
location ^~ /static/ { #匹配url路径
#规则C
}
location ~ .(gif|jpg|png|js|css)$ {
#规则D
}
location ~* .png$ {
#规则E
}
location !~ .xhtml$ {
#规则F
}
location !~* .xhtml$ {
#规则G
}
location / {
#规则H
}
那么产生的效果如下:
访问根目录/, 比如http://localhost/ 将匹配规则A
访问 http://localhost/login 将匹配规则B,http://localhost/register 则匹配规则H
访问 http://localhost/static/a.html 将匹配规则C
访问 http://localhost/a.gif, http://localhost/b.jpg 将匹配规则D和规则E,但是规则D顺序优先,规则E不起作用,而 http://localhost/static/c.png 则优先匹配到规则C
访问 http://localhost/a.PNG 则匹配规则E,而不会匹配规则D,因为规则E不区分大小写。
访问 http://localhost/a.xhtml 不会匹配规则F和规则G,http://localhost/a.XHTML不会匹配规则G,因为不区分大小写。规则F,规则G属于排除法,符合匹配规则但是不会匹配到,所以想想看实际应用中哪里会用到。
访问 http://localhost/category/id/1111 则最终匹配到规则H,因为以上规则都不匹配,这个时候应该是nginx转发请求给后端应用服务器,比如FastCGI(php),tomcat(jsp),nginx作为方向代理服务器存在。
所以实际使用中,个人觉得至少有三个匹配规则定义,如下:
#直接匹配网站根,通过域名访问网站首页比较频繁,使用这个会加速处理,官网如是说。
#这里是直接转发给后端应用服务器了,也可以是一个静态首页
# 第一个必选规则
location = / {
proxy_pass http://tomcat:8080/index
}
# 第二个必选规则是处理静态文件请求,这是nginx作为http服务器的强项
# 有两种配置模式,目录匹配或后缀匹配,任选其一或搭配使用
location ^~ /static/ {
root /webroot/static/;
}
location ~* .(gif|jpg|jpeg|png|css|js|ico)$ {
root /webroot/res/;
}
#第三个规则就是通用规则,用来转发动态请求到后端应用服务器
#非静态文件请求就默认是动态请求,自己根据实际把握
#毕竟目前的一些框架的流行,带.php,.jsp后缀的情况很少了
location / {
proxy_pass http://tomcat:8080/
}
三、ReWrite语法
last – 基本上都用这个Flag。
break – 中止Rewirte,不在继续匹配
redirect – 返回临时重定向的HTTP状态302
permanent – 返回永久重定向的HTTP状态301
1、下面是可以用来判断的表达式:
-f和!-f用来判断是否存在文件
-d和!-d用来判断是否存在目录
-e和!-e用来判断是否存在文件或目录
-x和!-x用来判断文件是否可执行
2、下面是可以用作判断的全局变量
例:http://localhost:88/test1/test2/test.php
$host:localhost
$server_port:88
$request_uri:http://localhost:88/test1/test2/test.php
$document_uri:/test1/test2/test.php
$document_root:D:
ginx/html
$request_filename:D:
ginx/html/test1/test2/test.php
四、Redirect语法
server {
listen 80;
server_name start.igrow.cn;
index index.html index.php;
root html;
if ($http_host !~ “^star.igrow.cn$" {
rewrite ^(.*) http://star.igrow.cn$1 redirect;
}
}
五、防盗链
location ~* .(gif|jpg|swf)$ {
valid_referers none blocked start.igrow.cn sta.igrow.cn;
if ($invalid_referer) {
rewrite ^/ http://$host/logo.png;
}
}
六、根据文件类型设置过期时间
location ~* .(js|css|jpg|jpeg|gif|png|swf)$ {
if (-f $request_filename) {
expires 1h;
break;
}
}
七、禁止访问某个目录
location ~* .(txt|doc)${
root /data/www/wwwroot/linuxtone/test;
deny all;
}
一些可用的全局变量:
$args
$content_length
$content_type
$document_root
$document_uri
$host
$http_user_agent
$http_cookie
$limit_rate
$request_body_file
$request_method
$remote_addr
$remote_port
$remote_user
$request_filename
$request_uri
$query_string
$scheme
$server_protocol
$server_addr
$server_name
$server_port
$uri
----------------
更多:
http://blog.rekfan.com/articles/196.html
匹配规则:
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000002797606
某次配置:
下载phpredisAdmin后,把phpredisAdmin文件夹名改成redis,放在/www/下。
location ^~ /redis/ { #静态文件
root /www/redis;
}
location ~ ^/redis/.*.php$ {
index index.php ;
root /www/redis;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /www/redis$fastcgi_script_name ;
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
include fastcgi_params;
}
访问exmaple.com/redis/a.php会报错:
"/www/redis/redis/a.php
查了下,$fastcgi_script_name:
$fastcgi_script_name
这个变量等于一个以斜线结尾的请求URI加上fastcgi_index给定的参数。可以用这个变量代替SCRIPT_FILENAME 和PATH_TRANSLATED,以确定php脚本的名称。
如下例,请求"/info/":
fastcgi_index index.php; fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /home/www/scripts/php$fastcgi_script_name;
SCRIPT_FILENAME等于"/home/www/scripts/php/info/index.php"。
关于一些对location认识的误区
1、 location 的匹配顺序是“先匹配正则,再匹配普通”。
矫正: location 的匹配顺序其实是“先匹配普通,再匹配正则”。我这么说,大家一定会反驳我,因为按“先匹配普通,再匹配正则”解释不了大家平时习惯的按“先匹配正则,再匹配普通”的实践经验。这里我只能暂时解释下,造成这种误解的原因是:正则匹配会覆盖普通匹配(实际的规则,比这复杂,后面会详细解释)。
2、 location 的执行逻辑跟 location 的编辑顺序无关。
矫正:这句话不全对,“普通 location ”的匹配规则是“最大前缀”,因此“普通 location ”的确与 location 编辑顺序无关;但是“正则 location ”的匹配规则是“顺序匹配,且只要匹配到第一个就停止后面的匹配”;“普通location ”与“正则 location ”之间的匹配顺序是?先匹配普通 location ,再“考虑”匹配正则 location 。注意这里的“考虑”是“可能”的意思,也就是说匹配完“普通 location ”后,有的时候需要继续匹配“正则 location ”,有的时候则不需要继续匹配“正则 location ”。两种情况下,不需要继续匹配正则 location :( 1 )当普通 location 前面指定了“ ^~ ”,特别告诉 Nginx 本条普通 location 一旦匹配上,则不需要继续正则匹配;( 2 )当普通location 恰好严格匹配上,不是最大前缀匹配,则不再继续匹配正则。
总结一句话: “正则 location 匹配让步普通 location 的严格精确匹配结果;但覆盖普通 location 的最大前缀匹配结果”。
斯蒂芬
官方文档解释
REFER: http://wiki.nginx.org/NginxHttpCoreModule#location
location
syntax: location [=|~|~*|^~|@] /uri/ { … }
default: no
context: server
This directive allows different configurations depending on the URI.
(译者注:1 、different configurations depending on the URI 说的就是语法格式:location [=|~|~*|^~|@] /uri/ { … } ,依据不同的前缀“= ”,“^~ ”,“~ ”,“~* ”和不带任何前缀的(因为[A] 表示可选,可以不要的),表达不同的含义, 简单的说尽管location 的/uri/ 配置一样,但前缀不一样,表达的是不同的指令含义。2 、查询字符串不在URI范围内。例如:/films.htm?fid=123 的URI 是/films.htm 。)
It can be configured using both literal strings and regular expressions. To use regular expressions, you must use a prefix:
- “~” for case sensitive matching
- “~*” for case insensitive matching
译文:上文讲到location /uri/ 可通过使用不同的前缀,表达不同的含义。对这些不同前缀,分下类,就2 大类:正则location ,英文说法是location using regular expressions 和普通location ,英文说法是location using literal strings 。那么其中“~ ”和“~* ”前缀表示正则location ,“~ ”区分大小写,“~* ”不区分大小写;其他前缀(包括:“=”,“^~ ”和“@ ”)和无任何前缀的都属于普通location 。
To determine which location directive matches a particular query, the literal strings are checked first.
译文:对于一个特定的 HTTP 请求( a particular query ), nginx 应该匹配哪个 location 块的指令呢(注意:我们在 nginx.conf 配置文件里面一般会定义多个 location 的)?匹配 规则是:先匹配普通location (再匹配正则表达式)。注意:官方文档这句话就明确说了,先普通location ,而不是有些同学的误区“先匹配正则location ”。
Literal strings match the beginning portion of the query – the most specific match will be used.
前面说了“普通location ”与“正则location ”之间的匹配规则是:先匹配普通location ,再匹配正则location 。那么,“普通location ”内部(普通location 与普通location )是如何匹配的呢?简单的说:最大前缀匹配。原文:1、match the beginning portion of the query (说的是匹配URI 的前缀部分beginning portion ); 2 、the most specific match will be used (因为location 不是“严格匹配”,而是“前缀匹配”,就会产生一个HTTP 请求,可以“前缀匹配”到多个普通location ,例如:location /prefix/mid/ {} 和location /prefix/ {} ,对于HTTP 请求/prefix/mid/t.html ,前缀匹配的话两个location 都满足,选哪个?原则是:the most specific match ,于是选的是location /prefix/mid/ {} )。
Afterwards, regular expressions are checked in the order defined in the configuration file. The first regular expression to match the query will stop the search.
这段话说了两层意思,第一层是:“Afterwards, regular expressions are checked ”, 意思是普通location 先匹配,而且选择了最大前缀匹配后,不能就停止后面的匹配,最大前缀匹配只是一个临时的结果,nginx 还需要继续检查正则location (但至于最终才能普通location 的最大前缀匹配,还是正则location 的匹配,截止当前的内容还没讲,但后面会讲)。第二层是“regular expressions are checked in the order defined in the configuration file. The first regular expression to match the query will stop the search. ”,意思是说“正则location ”与“正则location”内部的匹配规则是:按照正则location 在配置文件中的物理顺序(编辑顺序)匹配的(这句话就说明location 并不是一定跟顺序无关,只是普通location 与顺序无关,正则location 还是与顺序有关的),并且只要匹配到一条正则location ,就不再考虑后面的(这与“普通location ”与“正则location ”之间的规则不一样,“普通location ”与“正则location ”之间的规则是:选择出“普通location ”的最大前缀匹配结果后,还需要继续搜索正则location )。
If no regular expression matches are found, the result from the literal string search is used.
这句话回答了“普通location ”的最大前缀匹配结果与继续搜索的“正则location ”匹配结果的决策关系。如果继续搜索的“正则location ”也有匹配上的,那么“正则location ”覆盖 “普通location ”的最大前缀匹配(因为有这个覆盖关系,所以造成有些同学以为正则location 先于普通location 执行的错误理解);但是如果“正则location ”没有能匹配上,那么就用“普通location ”的最大前缀匹配结果。
For case insensitive operating systems, like Mac OS X or Windows with Cygwin, literal string matching is done in a case insensitive way (0.7.7). However, comparison is limited to single-byte locale’s only.
Regular expression may contain captures (0.7.40), which can then be used in other directives.
It is possible to disable regular expression checks after literal string matching by using “^~” prefix.If the most specific match literal location has this prefix: regular expressions aren’t checked.
通常的规则是,匹配完了“普通location ”指令,还需要继续匹配“正则location ”,但是你也可以告诉Nginx :匹配到了“普通location ”后,不再需要继续匹配“正则location ”了,要做到这一点只要在“普通location ”前面加上“^~ ”符号(^ 表示“非”,~ 表示“正则”,字符意思是:不要继续匹配正则)。
By using the “=” prefix we define the exact match between request URI and location. When matched search stops immediately. E.g., if the request “/” occurs frequently, using “location = /” will speed up processing of this request a bit as search will stop after first comparison.
除了上文的“^~ ”可以阻止继续搜索正则location 外,你还可以加“= ”。那么如果“^~ ”和“= ”都能阻止继续搜索正则location 的话,那它们之间有什么区别呢?区别很简单,共同点是它们都能阻止继续搜索正则location ,不同点是“^~ ”依然遵守“最大前缀”匹配规则,然而“= ”不是“最大前缀”,而是必须是严格匹配(exact match )。
这里顺便讲下“location / {} ”和“location = / {} ”的区别,“location / {} ”遵守普通location 的最大前缀匹配,由于任何URI 都必然以“/ ”根开头,所以对于一个URI ,如果有更specific 的匹配,那自然是选这个更specific 的,如果没有,“/ ”一定能为这个URI 垫背(至少能匹配到“/ ”),也就是说“location / {} ”有点默认配置的味道,其他更specific的配置能覆盖overwrite 这个默认配置(这也是为什么我们总能看到location / {} 这个配置的一个很重要的原因)。而“location = / {} ”遵守的是“严格精确匹配exact match ”,也就是只能匹配 http://host:port/ 请求,同时会禁止继续搜索正则location 。因此如果我们只想对“GET / ”请求配置作用指令,那么我们可以选“location = / {} ”这样能减少正则location 的搜索,因此效率比“location / {}” 高(注:前提是我们的目的仅仅只想对“GET / ”起作用)。
On exact match with literal location without “=” or “^~” prefixes search is also immediately terminated.
前面我们说了,普通location 匹配完后,还会继续匹配正则location ;但是nginx 允许你阻止这种行为,方法很简单,只需要在普通location 前加“^~ ”或“= ”。但其实还有一种“隐含”的方式来阻止正则location 的搜索,这种隐含的方式就是:当“最大前缀”匹配恰好就是一个“严格精确(exact match )”匹配,照样会停止后面的搜索。原文字面意思是:只要遇到“精确匹配exact match ”,即使普通location 没有带“= ”或“^~ ”前缀,也一样会终止后面的匹配。
先举例解释下,后面例题会用实践告诉大家。假设当前配置是:location /exact/match/test.html { 配置指令块1},location /prefix/ { 配置指令块2} 和 location ~ .html$ { 配置指令块3} ,如果我们请求 GET /prefix/index.html ,则会被匹配到指令块3 ,因为普通location /prefix/ 依据最大匹配原则能匹配当前请求,但是会被后面的正则location 覆盖;当请求GET /exact/match/test.html ,会匹配到指令块1 ,因为这个是普通location 的exact match ,会禁止继续搜索正则location 。
To summarize, the order in which directives are checked is as follows:
- Directives with the “=” prefix that match the query exactly. If found, searching stops.
- All remaining directives with conventional strings. If this match used the “^~” prefix, searching stops.
- Regular expressions, in the order they are defined in the configuration file.
- If #3 yielded a match, that result is used. Otherwise, the match from #2 is used.
这个顺序没必要再过多解释了。但我想用自己的话概括下上面的意思“正则 location 匹配让步普通location 的严格精确匹配结果;但覆盖普通 location 的最大前缀匹配结果”。
It is important to know that nginx does the comparison against decoded URIs. For example, if you wish to match “/images/ /test”, then you must use “/images/ /test” to determine the location.
在浏览器上显示的URL 一般都会进行URLEncode ,例如“空格”会被编码为 ,但是Nginx 的URL 的匹配都是针对URLDecode 之后的。也就是说,如果你要匹配“/images/ /test ”,你写location 的时候匹配目标应该是:“/images/ /test ”。
Example:
location = / {
# matches the query / only.
[ configuration A ]
}
location / {
# matches any query, since all queries begin with /, but regular
# expressions and any longer conventional blocks will be
# matched first.
[ configuration B ]
}
location ^~ /images/ {
# matches any query beginning with /images/ and halts searching,
# so regular expressions will not be checked.
[ configuration C ]
}
location ~* .(gif|jpg|jpeg)$ {
# matches any request ending in gif, jpg, or jpeg. However, all
# requests to the /images/ directory will be handled by
# Configuration C.
[ configuration D ]
}
上述这4 个location 的配置,没什么好解释的,唯一需要说明的是location / {[configuration B]} ,原文的注释严格来说是错误的,但我相信原文作者是了解规则的,只是文字描述上简化了下,但这个简化容易给读者造成“误解:先检查正则location ,再检查普通location ”。原文:“matches any query, since all queries begin with /, butregular expressions and any longer conventional blocks will be matched first. ”大意是说:“location / {} 能够匹配所有HTTP 请求,因为任何HTTP 请求都必然是以‘/ ’开始的(这半句没有错误)。但是,正则location 和其他任何比‘/ ’更长的普通location (location / {} 是普通location 里面最短的,因此其他任何普通location 都会比它更长,当然location = / {} 和 location ^~ / {} 是一样长的)会优先匹配(matched first )。” 原文作者说“ but regular expressions will be matched first. ”应该只是想说正则 location 会覆盖这里的 location / {} ,但依然是普通location / {} 先于正则 location 匹配,接着再正则 location 匹配;但其他更长的普通 location ( any longer conventional blocks )的确会先于 location / {} 匹配。
Example requests:
- / -> configuration A
- /documents/document.html -> configuration B
- /images/1.gif -> configuration C
- /documents/1.jpg -> configuration D
Note that you could define these 4 configurations in any order and the results would remain the same.
需要提醒下:这里说“in any order ”和“… remain the same ”是因为上面只有一个正则location 。文章前面已经说了正则location 的匹配是跟编辑顺序有关系的。
While nested locations are allowed by the configuration file parser, their use is discouraged and may produce unexpected results.
实际上 nginx 的配置文件解析程序是允许 location 嵌套定义的( location / { location /uri/ {} } )。但是我们平时却很少看见这样的配置,那是因为 nginx 官方并不建议大家这么做,因为这样会导致很多意想不到的后果。
The prefix “@” specifies a named location. Such locations are not used during normal processing of requests, they are intended only to process internally redirected requests (see error_page ,try_files ).
文章开始说了location 的语法中,可以有“= ”,“^~ ”,“~ ”和“~* ”前缀,或者干脆没有任何前缀,还有“@ ”前缀,但是后面的分析我们始终没有谈到“@ ”前缀。文章最后点内容,介绍了“@”的用途:“@ ”是用来定义“Named Location ”的(你可以理解为独立于“普通location (location using literal strings )”和“正则location (location using regular expressions )”之外的第三种类型),这种“Named Location ”不是用来处理普通的HTTP 请求的,它是专门用来处理“内部重定向(internally redirected )”请求的。注意:这里说的“内部重定向(internally redirected )”或许说成“forward ”会好点,以为内internally redirected 是不需要跟浏览器交互的,纯粹是服务端的一个转发行为。
安装Nginx
wget http://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.4.6.tar.gz
tar zxvf nginx-1.1.0.tar.gz
./configure
make
make install
需要注意的是在 configure 这步遇到点小麻烦:
./configure: error: the HTTP rewrite module requires the PCRE library.
安装 nginx 的时候, rewrite 模块默认是需要被安装的。但是 rewrite 模块所依赖的 PCRE 库需要额外安装。
You can either disable the module by using –without-http_rewrite_module
option, or install the PCRE library into the system, or build the PCRE library
statically from the source with nginx by using –with-pcre=<path> option.
解决办法: http://apps.hi.baidu.com/share/detail/34331473
先执行: yum -y install pcre-devel openssl openssl-devel 把依赖的东西安装上。
备注: PCRE (Perl Compatible Regular Expressions )是perl语言正则表达式。 Nginx的rewrite的正则表达式采用的是Perl语法集(常识:正则表达式有不同的语法集,我们常见的grep指令如果需要采用Perl语法集,需要grep -P 来指定)。
location 实例练习
Nginx 的语法形式是: location [=|~|~*|^~|@] /uri/ { … } ,意思是可以以“ = ”或“ ~* ”或“ ~ ”或“ ^~ ”或“ @ ”符号为前缀,当然也可以没有前缀(因为 [A] 是表示可选的 A ; A|B 表示 A 和 B 选一个),紧接着是 /uri/ ,再接着是{…} 指令块,整个意思是对于满足这样条件的 /uri/ 适用指令块 {…} 的指令。
上述各种 location 可分两大类,分别是:“普通 location ”,官方英文说法是 location using literal strings 和“正则 location ”,英文说法是 location using regular expressions 。其中“普通 location ”是以“ = ”或“ ^~ ”为前缀或者没有任何前缀的 /uri/ ;“正则 location ”是以“ ~ ”或“ ~* ”为前缀的 /uri/ 。
那么,当我们在一个 server 上下文编写了多个 location 的时候, Nginx 对于一个 HTTP 请求,是如何匹配到一个 location 做处理呢?用一句话简单概括 Nginx 的 location 匹配规则是:“正则 location ”让步 “普通 location”的严格精确匹配结果;但覆盖 “普通 location ”的最大前缀匹配结果。理解这句话,我想通过下面的实例来说明。
#1 先普通 location ,再正则 location
周边不少童鞋告诉我, nginx 是“先匹配正则 location 再匹配普通 location ”,其实这是一个误区, nginx 其实是“先匹配普通 location ,再匹配正则 location ”,但是普通 location 的匹配结果又分两种:一种是“严格精确匹配”,官方英文说法是“ exact match ”;另一种是“最大前缀匹配”,官方英文说法是“ Literal strings match the beginning portion of the query – the most specific match will be used. ”。我们做个实验:
例题 1 :假设 nginx 的配置如下
server {
listen 9090;
server_name localhost;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
deny all;
}
location ~ .html$ {
allow all;
}
}
附录 nginx 的目录结构是: nginx->html->index.html
上述配置的意思是: location / {… deny all;} 普通 location 以“ / ”开始的 URI 请求(注意任何 HTTP 请求都必然以“/ ”开始,所以“ / ”的意思是所有的请求都能被匹配上),都拒绝访问; location ~.html$ {allow all;} 正则 location以 .html 结尾的 URI 请求,都允许访问。
测试结果:
[root@web108 ~]# curl http://localhost:9090/
<html>
<head><title>403 Forbidden</title></head>
<body bgcolor=”white”>
<center><h1>403 Forbidden</h1></center>
<hr><center>nginx/1.1.0</center>
</body>
</html>
[root@web108 ~]# curl http://localhost:9090/index.html
<html>
<head>
<title>Welcome to nginx!</title>
</head>
<body bgcolor=”white” text=”black”>
<center><h1>Welcome to nginx!</h1></center>
</body>
</html>
[root@web108 ~]# curl http://localhost:9090/index_notfound.html
<html>
<head><title>404 Not Found</title></head>
<body bgcolor=”white”>
<center><h1>404 Not Found</h1></center>
<hr><center>nginx/1.1.0</center>
</body>
</html>
[root@web108 ~]#
测试结果如下:
| URI 请求 | HTTP 响应 |
| curl http://localhost:9090/ | 403 Forbidden |
| curl http://localhost:9090/index.html | Welcome to nginx! |
| curl http://localhost:9090/index_notfound.html | 404 Not Found |
curl http://localhost:9090/ 的结果是“ 403 Forbidden ”,说明被匹配到“ location / {..deny all;} ”了,原因很简单HTTP 请求 GET / 被“严格精确”匹配到了普通 location / {} ,则会停止搜索正则 location ;
curl http://localhost:9090/index.html 结果是“ Welcome to nginx! ”,说明没有被“ location / {…deny all;} ”匹配,否则会 403 Forbidden ,但 /index.html 的确也是以“ / ”开头的,只不过此时的普通 location / 的匹配结果是“最大前缀”匹配,所以 Nginx 会继续搜索正则 location , location ~ .html$ 表达了以 .html 结尾的都 allow all; 于是接着就访问到了实际存在的 index.html 页面。
curl http://localhost:9090/index_notfound.html 同样的道理先匹配 location / {} ,但属于“普通 location 的最大前缀匹配”,于是后面被“正则 location ” location ~ .html$ {} 覆盖了,最终 allow all ; 但的确目录下不存在index_notfound.html 页面,于是 404 Not Found 。
如果此时我们访问 http://localhost:9090/index.txt 会是什么结果呢?显然是 deny all ;因为先匹配上了 location / {..deny all;} 尽管属于“普通 location ”的最大前缀匹配结果,继续搜索正则 location ,但是 /index.txt 不是以 .html结尾的,正则 location 失败,最终采纳普通 location 的最大前缀匹配结果,于是 deny all 了。
[root@web108 ~]# curl http://localhost:9090/index.txt
<html>
<head><title>403 Forbidden</title></head>
<body bgcolor=”white”>
<center><h1>403 Forbidden</h1></center>
<hr><center>nginx/1.1.0</center>
</body>
</html>
[root@web108 ~]#
#2 普通 location 的“隐式”严格匹配
例题 2 :我们在例题 1 的基础上增加精确配置
server {
listen 9090;
server_name localhost;
location /exact/match.html {
allow all;
}
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
deny all;
}
location ~ .html$ {
allow all;
}
}
测试请求:
[root@web108 ~]# curl http://localhost:9090/exact/match.html
<html>
<head><title>404 Not Found</title></head>
<body bgcolor=”white”>
<center><h1>404 Not Found</h1></center>
<hr><center>nginx/1.1.0</center>
</body>
</html>
[root@web108 ~]#
结果进一步验证了“普通 location ”的“严格精确”匹配会终止对正则 location 的搜索。这里我们小结下“普通 location”与“正则 location ”的匹配规则:先匹配普通 location ,再匹配正则 location ,但是如果普通 location 的匹配结果恰好是“严格精确( exact match )”的,则 nginx 不再尝试后面的正则 location ;如果普通 location 的匹配结果是“最大前缀”,则正则 location 的匹配覆盖普通 location 的匹配。也就是前面说的“正则 location 让步普通location 的严格精确匹配结果,但覆盖普通 location 的最大前缀匹配结果”。
#3 普通 location 的“显式”严格匹配和“ ^~ ” 前缀
上面我们演示的普通 location 都是不加任何前缀的,其实普通 location 也可以加前缀:“ ^~ ”和“ = ”。其中“ ^~”的意思是“非正则,不需要继续正则匹配”,也就是通常我们的普通 location ,还会继续搜索正则 location (恰好严格精确匹配除外),但是 nginx 很人性化允许配置人员告诉 nginx 某条普通 location ,无论最大前缀匹配,还是严格精确匹配都终止继续搜索正则 location ;而“ = ”则表达的是普通 location 不允许“最大前缀”匹配结果,必须严格等于,严格精确匹配。
例题 3 :“ ^~ ”前缀的使用
server {
listen 9090;
server_name localhost;
location /exact/match.html {
allow all;
}
location ^~ / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
deny all;
}
location ~ .html$ {
allow all;
}
}
把例题 2 中的 location / {} 修改成 location ^~ / {} ,再看看测试结果:
| URI 请求 | 修改前 | 修改后 |
| curl http://localhost:9090/ | 403 Forbidden | 403 Forbidden |
| curl http://localhost:9090/index.html | Welcome to nginx! | 403 Forbidden |
| curl http://localhost:9090/index_notfound.html | 404 Not Found | 403 Forbidden |
| curl http://localhost:9090/exact/match.html | 404 Not Found | 404 Not Found |
除了 GET /exact/match.html 是 404 Not Found ,其余都是 403 Forbidden ,原因很简单所有请求都是以“ / ”开头,所以所有请求都能匹配上“ / ”普通 location ,但普通 location 的匹配原则是“最大前缀”,所以只有/exact/match.html 匹配到 location /exact/match.html {allow all;} ,其余都 location ^~ / {deny all;} 并终止正则搜索。
例题 4 :“ = ”前缀的使用
server {
listen 9090;
server_name localhost;
location /exact/match.html {
allow all;
}
location = / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
deny all;
}
location ~ .html$ {
allow all;
}
}
例题 4 相对例题 2 把 location / {} 修改成了 location = / {} ,再次测试结果:
| URI 请求 | 修改前 | 修改后 |
| curl http://localhost:9090/ | 403 Forbidden | 403 Forbidden |
| curl http://localhost:9090/index.html | Welcome to nginx! | Welcome to nginx! |
| curl http://localhost:9090/index_notfound.html | 404 Not Found | 404 Not Found |
| curl http://localhost:9090/exact/match.html | 404 Not Found | 404 Not Found |
| curl http://localhost:9090/test.jsp | 403 Forbidden | 404 Not Found |
最能说明问题的测试是 GET /test.jsp ,实际上 /test.jsp 没有匹配正则 location ( location ~.html$ ),也没有匹配 location = / {} ,如果按照 location / {} 的话,会“最大前缀”匹配到普通 location / {} ,结果是 deny all 。
#4 正则 location 与编辑顺序
location 的指令与编辑顺序无关,这句话不全对。对于普通 location 指令,匹配规则是:最大前缀匹配(与顺序无关),如果恰好是严格精确匹配结果或者加有前缀“ ^~ ”或“ = ”(符号“ = ”只能严格匹配,不能前缀匹配),则停止搜索正则 location ;但对于正则 location 的匹配规则是:按编辑顺序逐个匹配(与顺序有关),只要匹配上,就立即停止后面的搜索。
配置 3.1
server {
listen 9090;
server_name localhost;
location ~ .html$ {
allow all;
}
location ~ ^/prefix/.*.html$ {
deny all;
}
}
配置 3.2
server {
listen 9090;
server_name localhost;
location ~ ^/prefix/.*.html$ {
deny all;
}
location ~ .html$ {
allow all;
}
}
测试结果:
| URI 请求 | 配置 3.1 | 配置 3.2 |
| curl http://localhost:9090/regextest.html | 404 Not Found | 404 Not Found |
| curl http://localhost:9090/prefix/regextest.html | 404 Not Found | 403 Forbidden |
解释:
Location ~ ^/prefix/.*.html$ {deny all;} 表示正则 location 对于以 /prefix/ 开头, .html 结尾的所有 URI 请求,都拒绝访问; location ~.html${allow all;} 表示正则 location 对于以 .html 结尾的 URI 请求,都允许访问。 实际上,prefix 的是 ~.html$ 的子集。
在“配置 3.1 ”下,两个请求都匹配上 location ~.html$ {allow all;} ,并且停止后面的搜索,于是都允许访问, 404 Not Found ;在“配置 3.2 ”下, /regextest.html 无法匹配 prefix ,于是继续搜索 ~.html$ ,允许访问,于是 404 Not Found ;然而 /prefix/regextest.html 匹配到 prefix ,于是 deny all , 403 Forbidden 。
配置 3.3
server {
listen 9090;
server_name localhost;
location /prefix/ {
deny all;
}
location /prefix/mid/ {
allow all;
}
}
配置 3.4
server {
listen 9090;
server_name localhost;
location /prefix/mid/ {
allow all;
}
location /prefix/ {
deny all;
}
}
测试结果:
| URI 请求 | 配置 3.1 | 配置 3.2 |
| curl http://localhost:9090/prefix/t.html | 403 Forbidden | 403 Forbidden |
| curl http://localhost:9090/prefix/mid/t.html | 404 Not Found | 404 Not Found |
测试结果表明:普通 location 的匹配规则是“最大前缀”匹配,而且与编辑顺序无关。
#5 “@” 前缀 Named Location 使用
REFER: http://wiki.nginx.org/HttpCoreModule#error_page
假设配置如下:
server {
listen 9090;
server_name localhost;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
allow all;
}
#error_page 404 http://www.baidu.com # 直接这样是不允许的
error_page 404 = @fallback;
location @fallback {
proxy_pass http://www.baidu.com;
}
}
上述配置文件的意思是:如果请求的 URI 存在,则本 nginx 返回对应的页面;如果不存在,则把请求代理到baidu.com 上去做个弥补(注: nginx 当发现 URI 对应的页面不存在, HTTP_StatusCode 会是 404 ,此时error_page 404 指令能捕获它)。
测试一:
[root@web108 ~]# curl http://localhost:9090/nofound.html -i
HTTP/1.1 302 Found
Server: nginx/1.1.0
Date: Sat, 06 Aug 2011 08:17:21 GMT
Content-Type: text/html; charset=iso-8859-1
Location: http://localhost:9090/search/error.html
Connection: keep-alive
Cache-Control: max-age=86400
Expires: Sun, 07 Aug 2011 08:17:21 GMT
Content-Length: 222
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC “-//IETF//DTD HTML 2.0//EN”>
<html><head>
<title>302 Found</title>
</head><body>
<h1>Found</h1>
<p>The document has moved <a href=”http://www.baidu.com/search/error.html”>here</a>.</p>
</body></html>
[root@web108 ~]#
当我们 GET /nofound.html 发送给本 nginx , nginx 找不到对应的页面,于是 error_page 404 = @fallback ,请求被代理到 http://www.baidu.com ,于是 nginx 给 http://www.baidu.com 发送了 GET /nofound.html ,但/nofound.html 页面在百度也不存在,百度 302 跳转到错误页。
直接访问 http://www.baidu.com/nofound.html 结果:
[root@web108 ~]# curl http://www.baidu.com/nofound.html -i
HTTP/1.1 302 Found
Date: Sat, 06 Aug 2011 08:20:05 GMT
Server: Apache
Location: http://www.baidu.com/search/error.html
Cache-Control: max-age=86400
Expires: Sun, 07 Aug 2011 08:20:05 GMT
Content-Length: 222
Connection: Keep-Alive
Content-Type: text/html; charset=iso-8859-1
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC “-//IETF//DTD HTML 2.0//EN”>
<html><head>
<title>302 Found</title>
</head><body>
<h1>Found</h1>
<p>The document has moved <a href=”http://www.baidu.com/search/error.html”>here</a>.</p>
</body></html>
[root@web108 ~]#
测试二:访问一个 nginx 不存在,但 baidu 存在的页面
[root@web108 ~]# curl http://www.baidu.com/duty/ -i
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Date: Sat, 06 Aug 2011 08:21:56 GMT
Server: Apache
P3P: CP=” OTI DSP COR IVA OUR IND COM ”
P3P: CP=” OTI DSP COR IVA OUR IND COM ”
Set-Cookie: BAIDUID=5C5D2B2FD083737A0C88CA7075A6601A:FG=1; expires=Sun, 05-Aug-12 08:21:56 GMT; max-age=31536000; path=/; domain=.baidu.com; version=1
Set-Cookie: BAIDUID=5C5D2B2FD083737A2337F78F909CCB90:FG=1; expires=Sun, 05-Aug-12 08:21:56 GMT; max-age=31536000; path=/; domain=.baidu.com; version=1
Last-Modified: Wed, 05 Jan 2011 06:44:53 GMT
ETag: “d66-49913b8efe340″
Accept-Ranges: bytes
Content-Length: 3430
Cache-Control: max-age=86400
Expires: Sun, 07 Aug 2011 08:21:56 GMT
Vary: Accept-Encoding,User-Agent
Connection: Keep-Alive
Content-Type: text/html
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC “-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN”
“http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd”>
。。。。
</body>
</html>
显示,的确百度这个页面是存在的。
[root@web108 ~]# curl http://localhost:9090/duty/ -i
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: nginx/1.1.0
Date: Sat, 06 Aug 2011 08:23:23 GMT
Content-Type: text/html
Connection: keep-alive
P3P: CP=” OTI DSP COR IVA OUR IND COM ”
P3P: CP=” OTI DSP COR IVA OUR IND COM ”
Set-Cookie: BAIDUID=8FEF0A3A2C31D277DCB4CC5F80B7F457:FG=1; expires=Sun, 05-Aug-12 08:23:23 GMT; max-age=31536000; path=/; domain=.baidu.com; version=1
Set-Cookie: BAIDUID=8FEF0A3A2C31D277B1F87691AFFD7440:FG=1; expires=Sun, 05-Aug-12 08:23:23 GMT; max-age=31536000; path=/; domain=.baidu.com; version=1
Last-Modified: Wed, 05 Jan 2011 06:44:53 GMT
ETag: “d66-49913b8efe340″
Accept-Ranges: bytes
Content-Length: 3430
Cache-Control: max-age=86400
Expires: Sun, 07 Aug 2011 08:23:23 GMT
Vary: Accept-Encoding,User-Agent
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC “-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN”
“http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd”>
<html>
。。。
</body>
</html>
当 curl http://localhost:9090/duty/ -i 时, nginx 没找到对应的页面,于是 error_page = @fallback ,把请求代理到 baidu.com 。注意这里的 error_page = @fallback 不是靠重定向实现的,而是所说的“ internally redirected (forward )”。
ubuntu下面的管理脚本:

#!/bin/bash # nginx Startup script for the Nginx HTTP Server # it is v.0.0.2 version. # chkconfig: - 85 15 # description: Nginx is a high-performance web and proxy server. # It has a lot of features, but it's not for everyone. # processname: nginx # pidfile: /var/run/nginx.pid # config: /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf #注意:这里的三个变量需要根据具体的环境而做修改。 nginxd=/opt/nginx/sbin/nginx nginx_config=/opt/nginx/conf/nginx.conf nginx_pid=/opt/nginx/logs/nginx.pid RETVAL=0 prog="nginx" # Check that networking is up. [ -x $nginxd ] || exit 0 # Start nginx daemons functions. start() { if [ -e $nginx_pid ];then echo "nginx already running...." exit 1 fi echo -n $"Starting $prog: " $nginxd -c ${nginx_config} RETVAL=$? echo [ $RETVAL = 0 ] return $RETVAL } # Stop nginx daemons functions. stop() { echo -n $"Stopping $prog: " $nginxd -s stop RETVAL=$? echo [ $RETVAL = 0 ] && rm -f /var/lock/subsys/nginx $nginx_pid } # reload nginx service functions. reload() { echo -n $"Reloading $prog: " kill -HUP `cat ${nginx_pid}` RETVAL=$? echo } # See how we were called. case "$1" in start) start ;; stop) stop ;; reload) reload ;; restart) stop start ;; status) status $prog RETVAL=$? ;; *) echo $"Usage: $prog {start|stop|restart|reload|status|help}" exit 1 esac exit $RETVAL
Nginx设置alias实现虚拟目录 alias与root的用法区别
Nginx 貌似没有虚拟目录的说法,因为它本来就是完完全全根据目录来设计并工作的。如果非要给nginx安上一个虚拟目录的说法,那就只有alias标签比较"像",干脆来说说alias标签和root标签的区别吧。最基本的区别:alias指定的目录是准确的,root是指定目录的上级目录,并且该上级目录要含有location指定名称的同名目录。另外,根据前文所述,使用alias标签的目录块中不能使用rewrite的break。
说不明白,看下配置:
location /abc/ {
alias /home/html/abc/; alias路径后面一定要带上/
}
在这段配置下,http://test/abc/a.html就指定的是/home/html/abc/a.html。这段配置亦可改成
location /abc/ {
root /home/html/;
}
这样,nginx就会去找/home/html/目录下的abc目录了,得到的结果是相同的。但是,如果我把alias的配置改成:
location /abc/ {
alias /home/html/def/;
}
那么nginx将会从/home/html/def/取数据,这段配置还不能直接使用root配置,如果非要配置,只有在/home/html/下建立一个 def->abc的软link(快捷方式)了。一般情况下,在location /中配置root,在location /other中配置alias是一个好习惯。至于alias和root的区别,我估计还没有说完全,如果在配置时发现奇异问题,不妨把这两者换换试试。
nginx alias的设置
alias路径后面一定要带上/
nginx也有像apache的别名功能,格式为:
location ~ /alias {
root /home/www/default;
index index.php;
}
但nginx在处理php脚本时,需要传递给fastcgi才能处理,所以比apache的别名设置多一个,下面我们以phpmyadmin别名设置为例:
location ~ ^/phpmyadmin.+.php$ {
root /home/www/default;
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
location ~ /phpmyadmin {
root /home/www/default;
index index.php;
}
我的一次错误配置:
}
location ^~ /my {
root html/my;
}
http://a.com/my/b.txt
显示404错误,我看日志:
[error] 6736#0: *767 open() "/opt/xad/html/my/my/b.txt" failed (2: No such file or directory), c
root里面会自动带上路径的,。
root&alias文件路径配置
nginx指定文件路径有两种方式root和alias,这两者的用法区别,使用方法总结了下,方便大家在应用过程中,快速响应。root与alias主要区别在于nginx如何解释location后面的uri,这会使两者分别以不同的方式将请求映射到服务器文件上。
[root]
语法:root path
默认值:root html
配置段:http、server、location、if
[alias]
语法:alias path
配置段:location
实例:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
location ~ ^/weblogs/ { root /data/weblogs/www.jb51.net; autoindex on; auth_basic "Restricted"; auth_basic_user_file passwd/weblogs;} |
如果一个请求的URI是/weblogs/httplogs/www.jb51.net-access.log时,web服务器将会返回服务器上的/data/weblogs/www.jb51.net/weblogs/httplogs/www.jb51.net-access.log的文件。
root会根据完整的URI请求来映射,也就是/path/uri。[
因此,前面的请求映射为path/weblogs/httplogs/www.jb51.net-access.log。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
location ^~ /binapp/ { limit_conn limit 4; limit_rate 200k; internal; alias /data/statics/bin/apps/;} |
alias会把location后面配置的路径丢弃掉,把当前匹配到的目录指向到指定的目录。如果一个请求的URI是/binapp/a.jb51.net/favicon时,web服务器将会返回服务器上的/data/statics/bin/apps/a.jb51.net/favicon.jgp的文件。
1. 使用alias时,目录名后面一定要加"/"。
2. alias可以指定任何名称。
3. alias在使用正则匹配时,必须捕捉要匹配的内容并在指定的内容处使用。
4. alias只能位于location块中。
location有先后顺序:
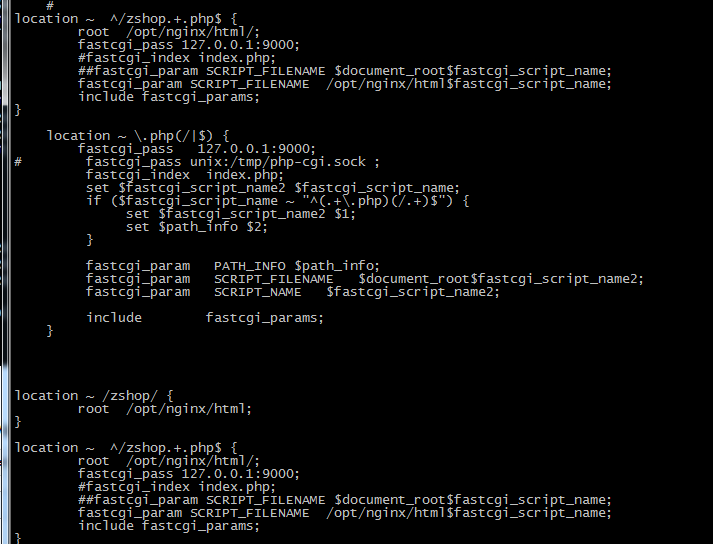
我想匹配zhop/a.php,但最终说找不到文件,原来是先匹配了第一个 location ~ .php(/|$) { ,他这个匹配到了就不会去匹配location ~ ^/zshop.+.php$ { .
所以需要把zshop放在前面。这个浪费了几个小时。切记。
location ^~ /images/ 和 location /images/ 区别
Nginx正则表达式之匹配操作符详解
nginx可以在配置文件中对某些内置变量进行判断,从而实现某些功能。例如:防止rewrite、盗链、对静态资源设置缓存以及浏览器限制等等。由于nginx配置中有if指令,但是没有对应else指令,所以判断要分为匹配和不匹配。
字符串表达式支持正则表达式,能设定大小写是否敏感。因此共有四个操作符,
如下:
~ 区分大小写(大小写敏感)匹配成功
~* 不区分大小写匹配成功
!~ 区分大小写匹配失败
!~* 不区分大小写匹配失败
1: 限制某些类型的客户端的访问
if指令
所有的Nginx内置变量都可以通过if指令和正则表达式来进行匹配,并且根据匹配结果进行一些操
| 代码如下 | 复制代码 |
|
location / { |
|
#限制IE访问
如果把MSIE改成 Mozilla 就基本上把IE和firefox这样pc浏览器限制了
2和3主要是针对盗链做处理
2:针对不同的文件类型
可能这个指令是我们平时使用正则匹配用的最多的指令:
| 代码如下 | 复制代码 |
|
|
|
3:针对不同的目录
| 代码如下 | 复制代码 |
|
location /img/ { |
|
1.^~ 标识符后面跟一个字符串。
Nginx将在这个字符串匹配后停止进行正则表达式的匹配(location指令中正则表达式的匹配的结果优先使用),如:location ^~ /images/,你希望对/images/这个目录进行一些特别的操作,如增加expires头,防盗链等,但是你又想把除了这个目录的图片外的所有图片只进行增加expires头的操作,这个操作可能会用到另外一个location,例如:location ~* .(gif|jpg|jpeg)$,这样,如果有请求/images/1.jpg,nginx如何决定去进行哪个location中的操作呢?结果取决于标识符^~,如果你这样写:location /images/,这样nginx会将1.jpg匹配到location ~* .(gif|jpg|jpeg)$这个location中,这并不是你需要的结果,而增加了^~这个标识符后,它在匹配了/images/这个字符串后就停止搜索其它带正则的location。
2.= 表示精确的查找地址,
如location = /它只会匹配uri为/的请求,如果请求为/index.html,将查找另外的location,而不会匹配这个,当然可以写两个location,location = /和location /,这样/index.html将匹配到后者,如果你的站点对/的请求量较大,可以使用这个方法来加快请求的响应速度。
3.@ 表示为一个location进行命名,即自定义一个location,这个location不能被外界所访问,只能用于Nginx产生的子请求,主要为error_page和try_files。
注意,这3个标识符后面不能跟正则表达式,虽然配置文件检查会通过,而且没有任何警告,但是他们并不会进行匹配。
综上所述,location指令对于后面值的匹配顺序为:
1.标识符“=”的location会最先进行匹配,如果请求uri匹配这个location,将对请求使用这个location的配置。
2.进行字符串匹配,如果匹配到的location有^~这个标识符,匹配停止返回这个location的配置。
3.按照配置文件中定义的顺序进行正则表达式匹配。最早匹配的location将返回里面的配置。
4.如果正则表达式能够匹配到请求的uri,将使用这个正则对应的location,如果没有,则使用第二条匹配的结果。
https://www.cnblogs.com/lidabo/p/4169396.html
关于一些对location认识的误区
1、 location 的匹配顺序是“先匹配正则,再匹配普通”。
矫正: location 的匹配顺序其实是“先匹配普通,再匹配正则”。我这么说,大家一定会反驳我,因为按“先匹配普通,再匹配正则”解释不了大家平时习惯的按“先匹配正则,再匹配普通”的实践经验。这里我只能暂时解释下,造成这种误解的原因是:正则匹配会覆盖普通匹配(实际的规则,比这复杂,后面会详细解释)。
2、 location 的执行逻辑跟 location 的编辑顺序无关。
矫正:这句话不全对,“普通 location ”的匹配规则是“最大前缀”,因此“普通 location ”的确与 location 编辑顺序无关;但是“正则 location ”的匹配规则是“顺序匹配,且只要匹配到第一个就停止后面的匹配”;“普通location ”与“正则 location ”之间的匹配顺序是?先匹配普通 location ,再“考虑”匹配正则 location 。注意这里的“考虑”是“可能”的意思,也就是说匹配完“普通 location ”后,有的时候需要继续匹配“正则 location ”,有的时候则不需要继续匹配“正则 location ”。两种情况下,不需要继续匹配正则 location :( 1 )当普通 location 前面指定了“ ^~ ”,特别告诉 Nginx 本条普通 location 一旦匹配上,则不需要继续正则匹配;( 2 )当普通location 恰好严格匹配上,不是最大前缀匹配,则不再继续匹配正则。
总结一句话: “正则 location 匹配让步普通 location 的严格精确匹配结果;但覆盖普通 location 的最大前缀匹配结果”
那些实用的Nginx规则
https://www.cnblogs.com/yhaing/p/8616194.html
Nginx 301 重定向实现不带www跳转到www
1.先说本人测试通过的方法,也是来自官方文档的方法。官方文档:http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/converting_rewrite_rules.html
本人网站测试地址:uuid.online(因CSDN原因,链接地址只能填www.uuid.online,测试时先跳转到这个地址,再删除www测试)
直接上本人的配置文件。
server {
listen 80;
server_name uuid.online;
return 301 http://www.uuid.online$request_uri;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.uuid.online;
...
}
2.目前网络上搜索出来的方法如下
a.
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.uuid.online uuid.online;
if ($http_host =uuid.online) {
rewrite (.*) http://www.uuid.online$1;
}
...
}
不推荐用这种方法,不是我不推荐,是nginx官方不推荐啊!!!原话如下:This is a wrong, cumbersome, and ineffective way.翻译过来就是:这是一种错误的,难处理的,无效的方法。
官方原文链接地址:http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/converting_rewrite_rules.html
b.该方法未测试,不评价。
如下:在ngxin域名的配置文件vhost/www.abc.com.conf(具体视你域名配置文件) 编辑如下:
.....
......
server
{
........
server_name www.abc.com ;//只留一个
......
}
文件的底部添加如下代码块(独立于上面的代码外): (这个可以,测试过)
server {
server_name abc.com;
rewrite ^(.*)$ http://www.abc.com$1 permanent;
}
另外补充说明一点:
