动机:在软件构建过程中 ,如果某一特定领域的问题比较复杂,类似的模式不断重复出现,如果使用普通的编程方式来实现将面临非常频繁的变化。在这种情况下,将特定领域的问题表达为某种语法规则的句子,然后构建一个解释器来解释这样的句子,从而达到解决问题的目的。
意图:给定一个语言,定义它的文法的一种表示,并定义一种解释器,这个解释器使用该表示来解释语言中的句子。
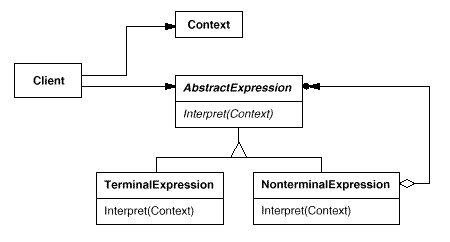
UML图解:
示例:接收中文形式的数字表示并能以罗马形式数字输出,应用解释器模式设计,如:四百七十一万六千四百五十二 =》4716452。代码如下
namespace Interpreter
{
/// <summary>
/// 定义一个数据上下文
/// </summary>
public class Context
{
string statement="";//待解释的数据
int data;//解释之后的数据
public Context (string statement)
{
this.statement = statement;
}
public int Data
{
get { return data; }
set { data = value; }
}
public string Statement
{
get { return statement; }
set { statement = value; }
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 抽象表达式解释器
/// </summary>
public abstract class Expression
{
protected Dictionary<string, int> table = new Dictionary<string, int>(9);
public Expression()
{
table.Add("一", 1);
table.Add("二", 2);
table.Add("三", 3);
table.Add("四", 4);
table.Add("五", 5);
table.Add("六", 6);
table.Add("七", 7);
table.Add("八", 8);
table.Add("九", 9);
}
/// <summary>
/// 解释给定的中文表示数字上下文对象
/// </summary>
/// <param name="context"></param>
public virtual void Interpreter(Context context)
{
if (context.Statement.Length == 0)
{
return;
}
foreach (string key in table.Keys)
{
int value=table[key];
if (context.Statement.EndsWith(key+GetPostfix()))
{
context.Data += value * this.Multiplier();
context.Statement = context.Statement.Substring(0, context.Statement.Length - GetLength());
}
if (context.Statement.EndsWith("零"))//应对如"四百七十一万零六千四百零五十二"中出现'零'的情况
{
context.Statement=context.Statement.Substring(0,context.Statement.Length-1);
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 获取如“六千四百五十二”中,获取千位的'千'字,百位的'百'字,十位的'十'字
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public abstract string GetPostfix();
/// <summary>
/// 陪增级数(个-1,十位-10,百位-100,千位-1000)
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public abstract int Multiplier();
/// <summary>
/// 获取符合文法的一组长度(如获取“四百”,“五十”的长度)
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public virtual int GetLength()
{
return this.GetPostfix().Length + 1;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 个位解释器 解析个位
/// </summary>
public class GeExpression : Expression
{
public override string GetPostfix()
{
return "";
}
public override int Multiplier()
{
return 1;
}
public override int GetLength()
{
return 1;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 十位解释器 解析个位+十位
/// </summary>
public class ShiExpression : Expression
{
public override string GetPostfix()
{
return "十";
}
public override int Multiplier()
{
return 10;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 百位解释器 解析个位+十位+百位
/// </summary>
public class BaiExpresssion : Expression
{
public override string GetPostfix()
{
return "百";
}
public override int Multiplier()
{
return 100;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 千位解释器 解析个位+十位+百位+千位
/// </summary>
public class QianExpression : Expression
{
public override string GetPostfix()
{
return "千";
}
public override int Multiplier()
{
return 1000;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 万位解释器 解析个位+十位+百位+千位+万位
/// </summary>
public class WanExpression : Expression
{
public override void Interpreter(Context context)
{
if (context.Statement.Length == 0)
{
return;
}
ArrayList tree = new ArrayList();
tree.Add(new GeExpression());
tree.Add(new ShiExpression());
tree.Add(new BaiExpresssion());
tree.Add(new QianExpression());
foreach (string key in table.Keys)
{
if (context.Statement.EndsWith(this.GetPostfix()))
{
int temp = context.Data;
context.Data = 0;
context.Statement=context.Statement.Substring(0, context.Statement.Length - 1);
foreach(Expression expression in tree)
{
expression.Interpreter(context);
}
context.Data = temp+this.Multiplier()*context.Data;
}
}
}
public override string GetPostfix()
{
return "万";
}
public override int Multiplier()
{
return 10000;
}
}
//通过Interpreter模式很容易扩展亿相对的YiExpression类
public class App
{
public static void Main()
{
string chinese="四百七十一万六千四百五十二";
Context context =new Context(chinese);
ArrayList tree = new ArrayList();//需按顺序添加个十百千万等解释表达式对象
tree.Add(new GeExpression());
tree.Add(new ShiExpression());
tree.Add(new BaiExpresssion());
tree.Add(new QianExpression());
tree.Add(new WanExpression());
foreach (Expression exp in tree)
{
exp.Interpreter(context);
}
Console.WriteLine("{0}={1}",chinese,context.Data);
}
}
}
Interpreter模式的几个要点:
1.Interpreter模式的应用场景时Interpreter模式应用中的难点,只有满足“业务规则频繁变化,且 类似的模式不断重复出现,并且容易抽象为语法规则的问题”才合适使用Interpreter模式。
2.使用Interpreter模式来表示文法规则,从而可以使用面向对象技巧来方便地“扩展”文法。
3.Interpreter模式比较适合简单的文法表示,对于复杂的文法表示,Interpreter模式会产生比较大的类 层次结构,需要求助于语法分析生成器这样的标准工具。