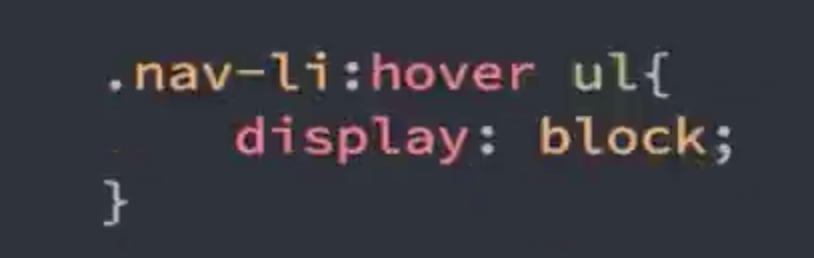
html的三种布局方式:
- 标准流(默认,顺序布局)
- 浮动
- 定位
两大元素
- 块级元素(div,table,h1~h6,ul,li,p...) 独占一行
- 内联元素(a,span,img,input) 和相邻内联元素在同一行,一行宽度不够会重起一行
position:relative:对宽高无影响
left:10px top:10px 向右移动10px,向下移动10px
right:10px bottom:10px 向左移动10px,向上移动10px
position:absolute(脱离正常的文档流):此时元素b高度为0,没有设置left,top,right,bottom(

若此时有一个非absolute的元素a,则按照标准流先排列a,再排列b
若此时给元素b设置了left,top等属性,也是先排列a,再排列b,b有可能覆盖a
.test{ position: absolute; 100px; height: 100px; background: red; } .parent{ 200px; height: 200px; background: blue; margin-top:200px; margin-left:200px; } <div class="parent"> <div class="test"> </div> </div>
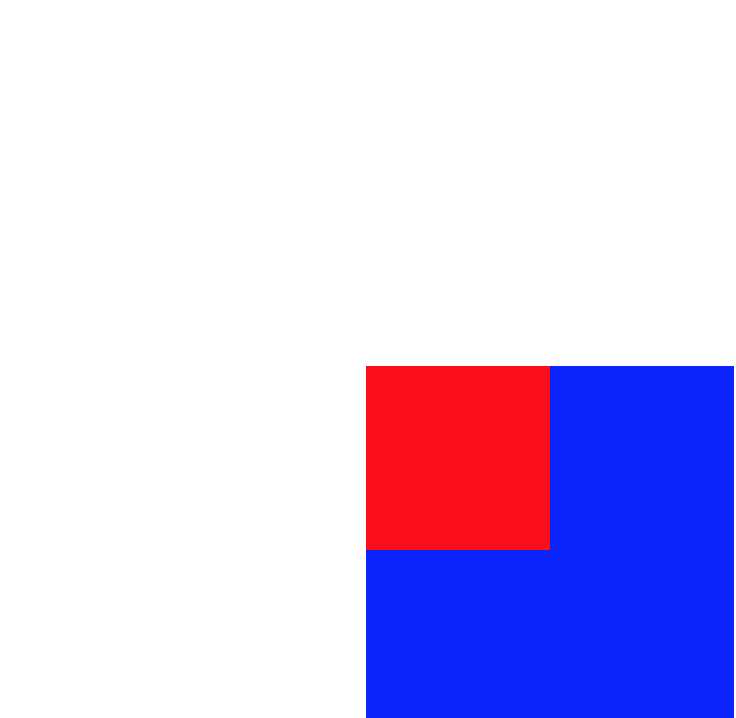
.test{ position: absolute; 100px; height: 100px; background: red; left:0;top:0; } .parent{ 200px; height: 200px; background: blue; margin-top:200px; margin-left:200px; }
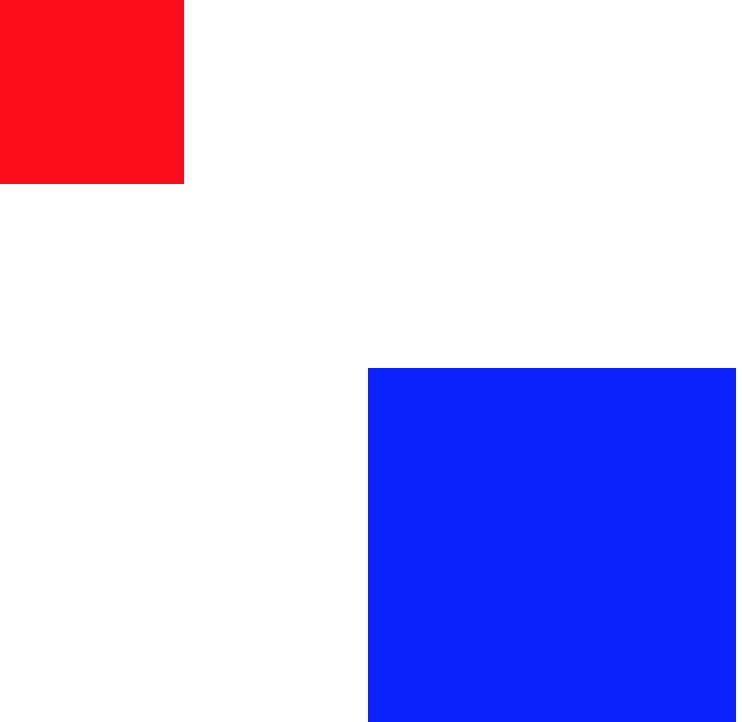
.test{ position: absolute; 100px; height: 100px; background: red; left:0; top:0; } .parent{ 200px; height: 200px; background: blue; margin-top:200px; margin-left:200px; position: relative; }
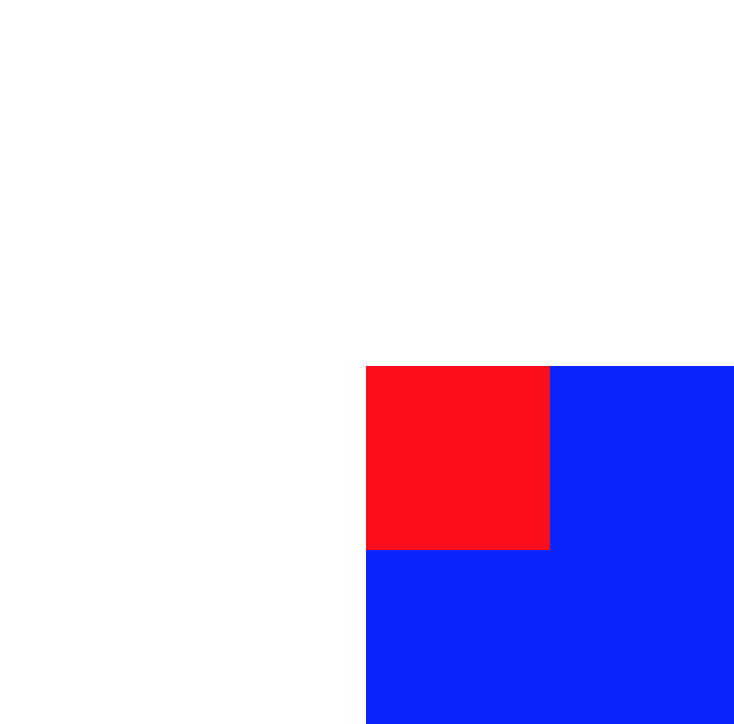
position:fixed
不受制于父元素,即使父元素有定位。固定在屏幕的某个地方,不会随任何元素而移动