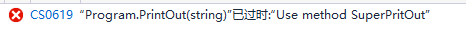有一些博客可以查阅
https://blog.csdn.net/FantasiaX/article/details/1627694
https://blog.csdn.net/fantasiax/article/details/1636913
特性的一种允许我们向程序的程序集增加元数据的语言结构,它是用于保存程序结构信息的某种特殊类型的类
- 将应用了特性的程序结构叫做 目标
- 设计用来获取和使用元数据的程序叫做特性的消费者
- .Net预定了很多特性,我们也可以声明自定义的特性

应用特性
在结构前放置特性片段来应用特性
特性片段被方括号包围,其中是特性名称和特性的参数列表

预定义保留的特性
obsolete特性

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Reflection; namespace ConsoleApp2 { class Program { [Obsolete("Use method SuperPritOut")] static void PrintOut(string str) { Console.WriteLine(str); } static void Main(string[] args) { PrintOut("start of Main"); } } }
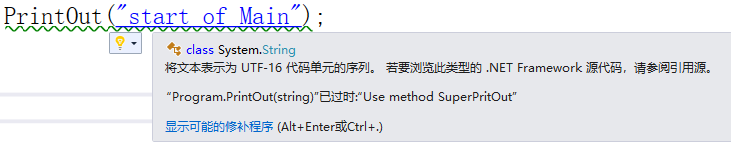
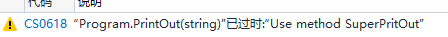
[Obsolete("Use method SuperPritOut",true)]
Conditional特性
参考顶端链接
调用者信息特性
调用者信息特性可以访问文件路径,代码行数,调用成员的名称等源代码信息

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Reflection; using System.Runtime.CompilerServices; namespace ConsoleApp2 { class Program { public static void MyRrace(string message, [CallerFilePath]string fileName="", [CallerLineNumber]int lineNumber=0, [CallerMemberName]string callingMember = "") { Console.WriteLine("File: {0}",fileName); Console.WriteLine("File: {0}",lineNumber); Console.WriteLine("File: {0}",callingMember); Console.WriteLine("File: {0}", message); } static void Main(string[] args) { MyRrace("Simple message"); } } }

DebuggerStepThrough特性
单步调试时,常常希望调试器不要进入某些方法,我们只想执行该方法,然后继续调试下一行,这个方法可以帮助你


其他预定义的特性

特性的更多内容
多个特性可以叠在一起,或者特性之间使用逗号分隔

可以放在其他的程序结构
显式地标注特性,从而将它应用到特殊的目标结构,在特性片段的开始处放置目标类型,后面跟冒号

全局特性

对于assembly:和module特性的限制是他们必须出现在using指令之后,并在任何命名空间或类声明之前,return:特性出现在方法声明之前
自定义特性
所有特性类都派生自System.Attribute
声明一个自定义的特性,需要
- 声明一个System.Attribute的类
- 给它起一个后缀Attribute结尾的名字
安全起见,声明一个sealed的特性类(当对一个类应用 sealed 修饰符时,此修饰符会阻止其他类从该类继承)

在应用特性时,构造函数的时参必须是在编译期能确定值的常量表达式
如果应用的特性构造函数没有参数,可以省略圆括号


限制特性的使用
AttributeUsage特性限制特性使用在某个目标类型上

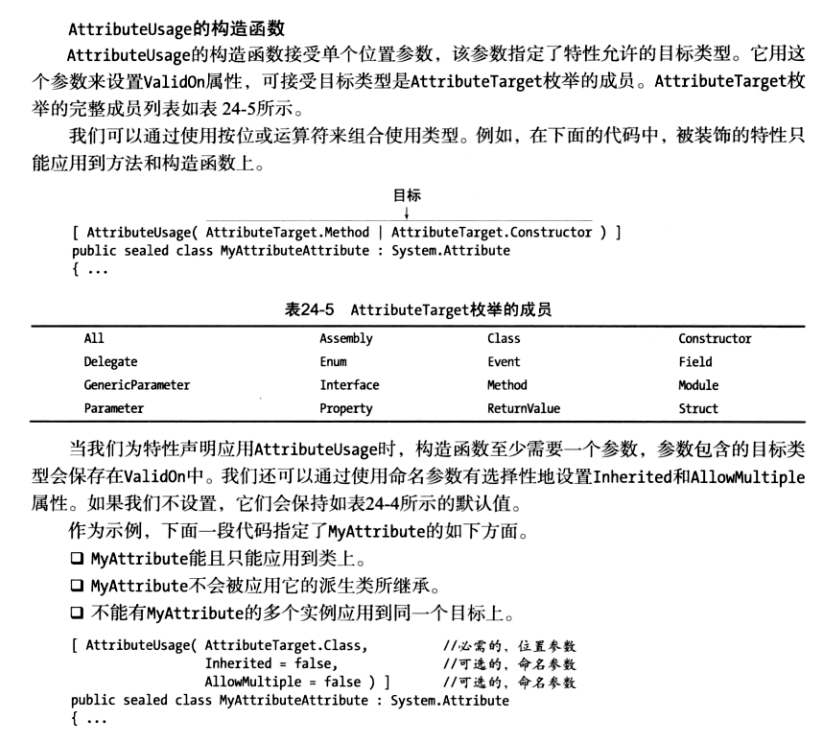
自定义特性的最佳实践

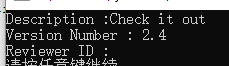
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Class)] public sealed class ReviewCommentAttribute : Attribute { public string Description { get; set; } public string VerionNumber { get; set; } public string ReviewerID { get; set; } public ReviewCommentAttribute(string desc,string ver) { Description = desc; VerionNumber = ver; } }
访问特性
可以使用Type对象的IsDEfined方法来检测某个特性是否应用到类上




GetCustomAttributes方法

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Reflection; using System.Runtime.CompilerServices; using System.Diagnostics; namespace ConsoleApp2 { [AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Class)] public sealed class ReviewCommentAttribute : Attribute { public string Description { get; set; } public string VerionNumber { get; set; } public string ReviewerID { get; set; } public ReviewCommentAttribute(string desc,string ver) { Description = desc; VerionNumber = ver; } } [ReviewComment("Check it out","2.4")] class MyClass { } class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Type t = typeof(MyClass); object[] AttArr = t.GetCustomAttributes(false); foreach (Attribute a in AttArr) { ReviewCommentAttribute attr = a as ReviewCommentAttribute; if (null != attr) { Console.WriteLine("Description :{0}",attr.Description); Console.WriteLine("Version Number : {0}",attr.VerionNumber); Console.WriteLine("Reviewer ID : {0}",attr.ReviewerID); } } } } }