interrupt:
结束线程在调用Object类的wait方法或该类的join方法、sleep方法过程中的阻塞状态,并在调用wait、join和sleep方法处产生InterruptedException异常。
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { TimeThread timeThread = new TimeThread(); timeThread.start(); try { //5秒后继续执行代码 Thread.sleep(5000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } //interrupt提前结束了timeThread线程的阻塞状态 timeThread.interrupt(); } }
class TimeThread extends Thread{ @Override public void run() { System.out.println(new Date()); try { sleep(10000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("---------------"); } }
执行结果:

join:
执行该方法的线程进入阻塞状态,直到调用该方法的线程结束后再由阻塞转为就绪状态。
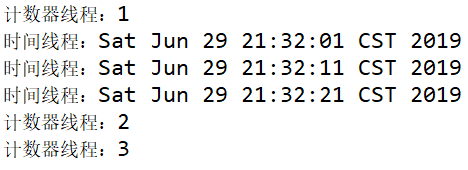
import java.util.Date; class TimeThread extends Thread{ @Override public void run() { for(int i=0;i<=2; i++){ System.out.println("时间线程:"+new Date()); try { Thread.sleep(10000);//休眠时间为10秒,所以每隔10秒打印一次时间 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } class CounterThread extends Thread { private TimeThread timeThread; public CounterThread(TimeThread timeThread){ this.timeThread = timeThread; } @Override public void run() { for(int i=1;i<=3; i++){ if(i==2){ try { timeThread.join();//需要走完TimeThread线程中run()方法,即执行三次打印时间 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } System.out.println("计数器线程:"+i); } } }
public class Program { public static void main(String[] args) { TimeThread timeThread = new TimeThread(); timeThread.start(); new CounterThread(timeThread).start(); } }
执行结果:
currentThread:
返回当前正在执行的线程对象,即执行该方法的线程对象
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { TimeThread timeThread = new TimeThread("线程一"); timeThread.start(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); System.out.println("主线程:" + timeThread.getName()); } }
class TimeThread extends Thread{ public TimeThread(String name) { super(name); } @Override public void run() { System.out.println("timeThread线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); } }
执行结果会有两种:这种现象的原因是两个线程对竞争CPU资源当主线程先获取CPU执行权的执行权的时候就会出现第二种结果,当线程一先获取的CPU的执行权的时候则会出现第一种结果。


isAlive:
判定该线程是否处于就绪、运行或阻塞状态,如果是则返回true,否则返回false。
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Thread mainThread = Thread.currentThread(); TimeThread timeThread = new TimeThread(mainThread); //输出false当前的线程对象虽然已经创建,但是还未开启 System.out.println(timeThread.isAlive()); timeThread.start(); //输出true因为timeThread线程有sleep将该线程变为阻塞 //主线程拿到CPU的执行权 System.out.println(timeThread.isAlive()); } }
class TimeThread extends Thread{ Thread thread; public TimeThread(Thread thread) { this.thread = thread; } @Override public void run() { //输出为true或false //当timeThread线程运行到这里之前主线程拿到CPU的执行权 //主线程执行完毕变成死亡状态将返回false //但当timeThread线程运行到这里主线程未拿到CPU的执行权 //就会执行下面的代码主线程为就绪状态则会返回true System.out.println(thread.isAlive()); try { //阻塞状态10秒 sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } //输出为false,主线程后面的代码很短,当该线程变成阻塞状态 //主线程拿到执行权,将把剩下的代码执行完毕,变成死亡状态 //如果在主线程中开启该线程的代码后面把主线程也阻塞 //并超过10s这里将返回true,上面阻塞前也一定返回true System.out.println(thread.isAlive()); } }
执行结果:

setDaemon:守护线程必须在启动之前设置
用于将一个尚未调用线程start方法的线程设置为守护线程。守护线程主要用于为其他线程的运行提供服务(Java中的垃圾回收机制就是守护线程),这种线程属于创建它的线程
进程中所启动的其他非守护线程不会随着某一个非守护线程的结束而结束
进程随着最后一个非守护线程的结束而结束
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { TimeThread timeThread = new TimeThread(); //设置timeThread为守护线程 timeThread.setDaemon(true); timeThread.start(); } }
class TimeThread extends Thread{ @Override public void run() { //当开启线程之后如果该线程拿到CPU的执行权则会有输出 //但当开启线程之后主线程拿到执行权,主线程结束 //又因为该进程中没有其他的非守护线程,所以守护线程结束,该进程也结束 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); try { sleep(5000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
执行结果有三种:
由于主线程和守护线程竞争CPU资源,因此当主线程争到时直接结束无输出,当守护线程争到时Thread-2或Thread-0


或者无输出